Abstract
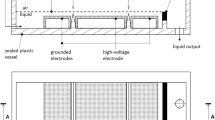
This paper presents an experimental study on new water treatment by streamer propagation alternated with electrospray generation. We demonstrate the importance of timing control of both an electrospray generation and streamer initiation. Recently, much attention has been given to the water treatment using discharge plasma in a gas-liquid region. In this study, for a further increase in the contact area between water and discharge plasma, both fine water droplets and discharge plasma are formed in the same region. We have already succeeded in alternate expansion of both fine droplets and streamer corona from the same syringe needle electrode. The purpose of this paper is to expose electrosprayed droplets to streamer discharges by timing control of both an electrospray generation and streamer initiation. To this end, both repetitive pulses and an AC voltage are superimposed on a DC voltage applied to a syringe needle electrode. Peak voltage value, frequency, and phase of these superimposed voltages are optimized. It is observed that streamers propagate through a spray region (gas-liquid region), by using a gated image intensifier. In this case, it is shown that persistent substances in water are decomposed. These results suggest that electrosprayed droplets are exposed to streamer discharges and as a result, active species are generated.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yasuoka K (2009) Progress in direct plasma water treatment. IEEJ Trans Fundam Mater 129(1):15–22
Sato M (2000) Pulsed discharge processing of organic contaminants in water. Jpn Soc Appl Phys 69(3):301–304
Akiyama H (2000) Streamer discharge in liquids and their applications. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul 7(5):646–653
Levlin E (2010) Conductivity measurements for controlling municipal waste-water treatment. In: Proceedings of a Polish-Swedish-Ukrainian seminar, pp 51–62
Sugai T, Suzuki T, Minamitani Y, Nose T (2012) Investigation of optimum applied voltage for water treatment by pulsed streamer discharge in air-sprayed water droplets. Electr Eng Jpn 180(2):1–8
Wang Z, Xu D, Chen Y, Hao C, Zhang X (2008) Plasma decoloration of dye using dielectric barrier discharges with earthed spraying water electrodes. J Electrostat 66(9–10):476–481
Iijima T (2005) New oxidation technology by using oh radical with long lifetime in plasma. In: Proceedings of the 17th world congress & exhibition of international ozone association, Strasbourg, France, pp 1–11
Njatawidjaja E, Sugiarto AT, Ohshima T, Sato M (2005) Decoloration of electrostatically atomized organic dye by the pulsed streamer corona discharge. J Electrostat 63(5):353–359
Ohneda H, Harano A, Sadakata M, Takarada T (2002) Improvement of NOx removal efficiency using atomization of finedroplets into corona discharge. J Electrostat 55(3–4):321–332
Malik MA (2010) Water purification by plasmas: which reactors are most energy efficient? Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(1):21–31
Kerker M (1975) Laboratory generation of aerosols. Adv Coll Interface Sci 5(2):105–172
Kondo T, Ozaki R, Kadowaki K (2017) Effect of superposed repetitive pulses onto DC voltage on discharge extension into fog water produced by electrospray. In: Proceedings of 2017 international symposium on electrical insulating materials (ISEIM). IEEE, Toyohashi, Japan, pp 390–393
Tamaru K, Yudate S, Ozaki R, Kadowaki K (2019) Alternate expansion of streamer corona and fine water droplets from a syringe needle subjected to rippled voltage. IEEJ Trans Fundam Mater 139(4):205–211
Yudate S, Miyoshi S, Tamada R, Ozaki R, Kadowaki K (2020) Photographic investigation of repetitive pulsed discharge light from needle electrode spraying water. In: Proceedings of 2020 international symposium on electrical insulating materials (ISEIM) (on-line conference). IEEE, pp 194–197
Morad MR, Rajabi A, Razavi M, Sereshkeh SRP (2016) A very stable high throughput Taylor cone-jet in electrohydrodynamics. Sci Rep 6:38509
Minamitani Y, KObayashi T, Ohba Y, Higashiyama Y (2010) The characteristic of decomposition of LAS in a water droplets Spray by pulsed power discharge in air. IEEJ Trans Fundam Mater 130(6):561–566
Deng H, He Z, Ma J, Xu Y, Liu J, Guo R (2010) Initiation and propagation of discharge in liquid droplets: effect of droplet sizes. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 38(12–1):3282–3288
Minamitani Y, Yamada T (2016) Investigation of the influence of droplets to streamer discharge in water treatment by pulsed discharge in air spraying water droplets. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 44(10):2173–2180
Li XD, Liu Y, Zhou GY, Liu SW, Li ZY, Lin FC (2017) Subsonic streamers in water: initiation, propagation and morphology. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:255301
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yudate, S., Tamada, R., Takahashi, T., Ozaki, R., Kadowaki, K. (2022). Timing Control of Streamer Initiation and Electrospray Generation for Waste Water Treatment. In: Md. Zain, Z., Sulaiman, M.H., Mohamed, A.I., Bakar, M.S., Ramli, M.S. (eds) Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electrical, Control and Computer Engineering. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 842. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8690-0_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8690-0_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-8689-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-8690-0
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)