Abstract
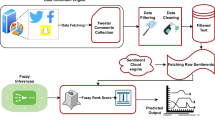
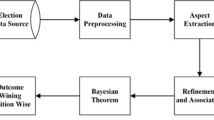
Fortunately or unfortunately the new era of web-dependent life has made our decision-making to start from the web ranking; one can express sentiments with opportunity. The decision is additionally examined via web-based networking media, for example, Twitter. In this article, endeavors are made to examine the practicality of utilizing aggregate learning acquired micro post presented on Twitter to anticipate the victor of a Cricket coordinate. For forecasts, we utilize three unique strategies that rely upon the all-out tweet behind the amusement for group, fan assessments toward group, and fans score expectations on twitter. By joining these strategies, we arrange winning group expectation in a Cricket diversion before the beginning of amusement. Our outcomes are sufficiently promising to be utilized for winning group figure. Besides, the adequacy of Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Interference System (ANFIS) is to recover tweets from Twitter, examine deliberately, and draw a precise outcome dependent on its inspiration and cynicism. In this, we have displayed an execution of unsupervised technique for nostalgic investigation for IPL 2019 match. Here we can anticipate the result of cricket coordinate before its initiation, in light of the tweets shared by their fans utilizing Twitter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khare, R., & Cutting, D. (2004). Nutch: A flexible and scalable open-source web search engine. Commerce Net Labs Technical Report, 1.
Gonz´alez-Ib´anez, R., Muresan, S., & Wacholder, N. (2011). Identifying sarcasm in Twitter: A closer look. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Vol. 2).
Paul, M. J., Dredze, M., & Broniatowski, D. (2014). Twitter improves influenza forecasting PLOS Currents Outbreaks. https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.outbreaks.90b9ed0f59bae4ccaa683a39865d9117 .
Neethu, M. S., Rajasree, R. (2013). sentiment analysis in twitter using machine learning techniques. In 4th ICCCNT (Vol. 6, No. 6), Tiruchengode, India.
Sahayak, V., Shete, V., & Pathan, A. (2015). Sentiment analysis on twitter data. International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced Engineering (IJIRAE), 2(1), 178–183.
Singh, V. K., Piryani, R., Uddin, A., & Waila, P. (2013). Sentiment analysis of movie reviews and blog posts. In 3rd IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC) (pp. 893–898).
Boiy, E., Hens, P., Deschacht, K., & Moens, K. (2007). Automatic sentiment analysis in on-line text. In Proceedings ELPUB2007 Conference on Electronic Publishing (pp. 349–360) Vienna, Austria.
Turney, P. D. (2002). Thumbs up or thumbs down? Semantic orientation applied to unsupervised classification of reviews. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL) (pp. 417–424).
Azam, N., Abulaish, M., & Haldar, N. A. H. (2015). Twitter data mining for events classification and analysis. In Second International Conference on Soft Computing and Machine Intelligence (pp. 79–83).
Niculae, V., Kumar, S., Boyd-Graber, J., & Danescu-Niculescu-Mizi, C. (2015), lLinguistic harbingers of betrayal: A case study on an online strategy game. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics And the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Vol. 1, pp. 1650–1659).
Shi, L., Agarwal, N., Agarwal, A., Garg, R., & Spoelstra, J.: Predicting US primary elections with Twitter. In Social Network and Social Media Analysis: Methods, Models and Applications, NIPS (2012).
O’Connor, B., Balasubramanyan, R., & Routledge, B. R., & Smith, N. A. (2010). From tweets to polls: Linking text sentiment to public opinion time series. In Proceedings of the Fourth International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (Vol. 42).
Schumaker, R. P., Solieman, O. K., & Chen, H. (2010). Sports knowledge management and data mining. Annual Review of Information Science and Technology, 44, 115–157.
Choi, Hyunyoung, & Varian, Hal. (2012). Predicting the present with Google Trends. Economic Record, 88(1), 2–9.
Karpoff, J. M. (1987). The relation between price changes and trading volume: A survey. The Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 22(1), 09–126.
Kirka, D., & Katz, G. (2011). Burberry seizes the moment at London fashion week.
Patil, M., & Sharma, N. (2019). Sports data analytics : A case study of off-field behavior of players using statistical approach. In 3rd International Conference on Data Management, Analytics and Innovation (Vol. 1016, pp. 267–279). Lincoln University College, Malaysia, Conference Proc. Published in Springer (AISC Series).
Rahnama, A. H. A. (2014). Distributed real-time sentiment analysis for big data social streams (pp. 789–794). “978-1-4799-6773-5/14/$31.00 © IEEE.
Hovy, D., Berg-Kirkpatrick, T., Vaswani, A., & Hovy, E. (2013). Learning whom to trust with MACE. In Proceedings of NAACL-HLT.
Mustafa, R. U., Nawaz, M. S., Lali, M. I. U., Zia, T., & Mehmood, W. (2017). Predicting the cricket match outcome using crowd opinions on social networks: A study of machine learning methods. Malaysian Journal of Computer Science, 30(1), 63–76.
Fung, K. (2014). Google flu trends failure shows good data > big data. In Harvard business review/HBR blog network (2014).
Asur, S., & Huberman, B. A. (2010). Predicting the future with social media. In IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (pp. 492–499), Toronto, ON.
Chung, J., & Mustafaraj, E. (2011). Can collective sentiment expressed on twitter predict political elections? Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, 1770–1771.
Coppersmith, G., Harman, C., & Dredze, M. (2014). Measuring post traumatic stress disorder in Twitter. In International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media (pp. 159–170).
Kim, K. (2003). Financial time series forecasting using support vector machines. Neurocomputing, 55(1–2), 307–319.
Khan, A., & Zuberi, V. (1999). Stock Investing for everyone: Tools for investing like the pros. Wiley investment series: Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-35731-5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Anbazhagu, U.V., Anandan, R. (2021). Predicting the Cricket Match Outcome Using ANFIS Classifier for Viewers Opinions on Twitter Data. In: Sharma, N., Chakrabarti, A., Balas, V., Martinovic, J. (eds) Data Management, Analytics and Innovation. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1174. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5616-6_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5616-6_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5615-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5616-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)