Abstract
Posterior staphylomas involve a wider area than the area covered in 50 degree fundus photos. Wide-field fundus images can accommodate an entire extent of wide staphylomas. Although wide-field fundus images do not provide 3D information, the pigmentary alterations along the staphyloma edges may be a good indicator of staphylomas.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
It is difficult to show the entire extent of posterior staphylomas as well as staphyloma edges in the conventional 50 degree fundus photos, because the most common type of staphylomas involve a wider area. In this chapter, wide-field fundus images obtained with Optos® and Mirante® are shown to capture the entire extent of posterior staphylomas (findings along the staphyloma edges). Although wide-field fundus images do not provide three-dimensional information, pigmentary alterations along staphyloma edges may be a good indicator of staphyloma edges. In Optos images, a combination of pseudo-color images, red-free fundus images, and fundus autofluorescence images is reported to be useful to delineate the pigmentary alterations along staphyloma edges [1,2,3]. Different from Optos, Mirante® provides real color images (Figs. 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, and 6.4).
Wide macular staphyloma in the left fundus of a 78-year-old woman with an axial length of 28.2 mm. (Top left) Pseudo-color fundus image shows depigmentation along the upper margin of wide macular staphyloma. (Top right) Fundus autofluorescence image shows hypo-fluorescence especially along the upper temporal border of staphyloma. (Bottom left) Red-free fundus image shows the hyper-reflectance along the upper margin of staphyloma. (Bottom right) Three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (3D MRI) of the left eye viewed from the side shows posterior outpouching of the posterior segment due to a wide macular staphyloma
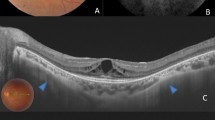
Narrow macular staphyloma in the left fundus of a 64-year-old woman with an axial length of 30.2 mm. (Top left) Pseudo-color fundus image shows slight depigmentation along the upper and nasal border of the staphyloma. (Top middle) Fundus autofluorescence image shows slight hypo-autofluorescence along the upper edge of the staphyloma. (Top right) Red-free fundus image shows a slight hyper-reflectance along the upper margin of staphyloma. (Bottom left) Fluorescein angiographic image shows granular hyper-fluorescence along the upper staphyloma border. (Bottom right) Three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (3D MRI) of the left eye viewed from the side shows the posterior pole of the eye is pointed and the eye shows a cylinder shape
Peripapillary staphyloma in the right fundus of a 67-year-old woman with an axial length of 26.9 mm. (Top left) Pseudo-color fundus photo shows yellowish depigmentation along the margin of peripapillary staphyloma. (Top right) Fundus autofluorescence image shows slight hyper-fluorescence along the temporal margin of the staphyloma and hypo-fluorescence along the nasal margin of the staphyloma. (Bottom left) Red-free fundus image shows a slight hyper-reflectance along the staphyloma border. (Bottom right) Three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (3D MRI) of the right eye viewed from the inferior shows the nasally distorted shape of the eye
Real color wide-field fundus image of posterior staphylomas obtained with Mirante (Nidek, Japan). (Left). Right fundus of a 67-year-old woman with an axial length of 27.3 mm shows wide macular staphyloma with depigmented staphyloma border. (Right) Left fundus of a 79-year-old woman with an axial length of 26.2 mm shows wide macular staphyloma with depigmented staphyloma border. Scleral ridge is seen temporal to the optic disc
References
Ohno-Matsui K. Proposed classification of posterior staphylomas based on analyses of eye shape by three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(9):1798–809.
Ohno-Matsui K, Alkabes M, Salinas C, et al. Features of posterior staphylomas analyzed in wide-field fundus images in patients with unilateral and bilateral pathologic myopia. Retina. 2017;37(3):477–86.
Ohno-Matsui K, Jonas JB. Posterior staphyloma in pathologic myopia. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2019;70:99–109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ishida, T. (2020). Wide-Field Fundus Imaging of Posterior Staphyloma. In: Ohno-Matsui, K. (eds) Atlas of Pathologic Myopia. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4261-9_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4261-9_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4260-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4261-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)