Abstract
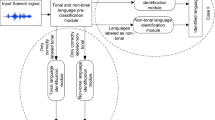
This paper proposes an automatic tonal and non-tonal language classification system for North East (NE) Indian languages using formants and prosodic features. The state-of-the-art system for tonal/non-tonal classification uses mostly prosodic features and considers the utterance-level analysis unit during feature extraction. To this end, the present work explores formants and studies if it has complimentary information with respect to prosody. It also analyzes different analysis units for feature extraction, namely syllable, di-syllable, word, and utterance. Classification techniques based on Gaussian mixture model—universal background model (GMM-UBM), neural network and i-vector have been explored in this work. The paper presents NIT Silchar language database (NITS-LD) prepared in-house to carry out experimental validation. It covers seven NE Indian languages and uses data from All India radiobroadcast news archives. Experimental analysis suggests that artificial neural network (ANN) based on syllable level features provides the lowest EERs of 31.8, 36 and 37.8% for test data of durations, 30, 10, and 3 s, respectively, when the combination of prosodic features and formants are used. The addition of formants helps to improve the system performance by up to 6.8, 7.8 and 9.2% for test data of the three different durations with respect to that of prosodic features.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Wang, E.E. Ambikairajah, H.C. Choi, Automatic tonal and non-tonal language classification and language identification using prosodic information, in International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing, (ISCSLP) (2006), pp. 485–496
D. Dan, D. Robert Ladd, Linguistic tone is related to the population frequency of the adaptive haplogroups of two brain size genes, ASPM and microcephalin, in PANS (2007). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610848104
C. Qu, H. Goad, The interaction of stress and tone in standard Chinese: Experimental findings and theoretical consequences, in Tone: Theory and Practice, Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (2012)
B. Gold, L. Rabiner, Analysis of digital and analog formant synthesizers. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 16, 81–94 (1968)
H.-N. Lin, C.-J.C. Lin, Perceiving vowels and tones in Mandarin: The effect of literary Phonetic systems on phonological awareness, in Proceedings of the 22nd North American Conference on Chinese Linguistics (NACCL-22) and The 18th International Conference on Chinese Linguistics (ICCL-18), Harvard University, Cambridge, 2010, pp. 429–437
D. Martinez, E. Lleida, A. Ortega, A. Miguel, Prosodic features and formant modelling for an I-vector based language recognition system, in ICASSP (2013), pp. 6847–6851
M. Atterer, D.R. Ladd, On the phonetics and phonology of “segmental anchoring” of F0. J. Phon. 32, 177–197 (2004)
A.K. Singh, A computational phonetic model for Indian language scripts, in Constraints on Spelling Changes: Fifth International Workshop on Writing Systems, Nijmegen, The Netherlands (2006)
L. Mary, B. Yegnanarayana, Extraction and representation of prosodic features for language and speaker recognition. Speech Commun. 50(10), 782–796 (2008)
S.R.M. Prasanna, B.V.S. Reddy, P. Krishnamurthy, Vowel onset point detection using source, spectral peaks, and modulation spectrum energies. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 17, 556–565 (2009)
Y. Muthusamy, R. Cole, B. Oshika, The OGI multi-language telephone speech corpuses, in Proceedings of International Conference Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP) (1992), pp. 895–898
D. Talkin, A robust algorithm for pitch tracking (RAPT), in Speech Coding and Synthesis, ed. by W.B. Klein, K.K. Paliwal (Elsevier, New York, 1995)
D. Reynolds, Gaussian Mixture Models. Encyclopedia of Biometric Recognition (Springer, New York, 2008)
B. Yegnanarayana, Artificial Neural Networks (Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi, 2005)
N. Dehak, P. Torres-Carrasquillo, D. Reynolds, R. Dehak, Language recognition via I-vectors and dimensionality reduction, in Interspeech Conference, Florence, Italy (2011), pp. 857–860
A.O. Hatch, S. Kajarekar, A. Stolcke, Within-class covariance normalization for SVM-based speaker recognition, in Proceedings ICSLP (2006), pp. 1471–1474
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge TEQIP III (NIT Silchar) for funding participation in the conference.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bhanja, C.C., Laskar, M.A., Laskar, R.H. (2020). Formants and Prosody-Based Automatic Tonal and Non-tonal Language Classification of North East Indian Languages. In: Elçi, A., Sa, P., Modi, C., Olague, G., Sahoo, M., Bakshi, S. (eds) Smart Computing Paradigms: New Progresses and Challenges. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 767. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9680-9_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9680-9_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-9679-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-9680-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)