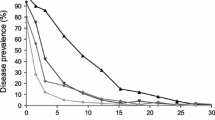
Abstract
Understanding the nature and scope of the dispersal of plant pathogen propagules is fundamental to the understanding of disease epidemic development. This has been appreciated for many years, and the measurement and modelling of both plant pathogen propagule dispersal and plant disease spread has been a cornerstone of plant disease epidemiology. Work on the diffusion of spore clouds was done as early as 1918 (Schmidt, 1918). Since the classic work of Gregory (1945) there has been much progress in work on dispersal of plant pathogen spores and spread of the diseases they cause. However, there is still much to learn before we can understand and predict the spread of plant diseases in space and time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aylor, D.E. (1975) Force required to detach conidia of Helminthosporium maydis. Plant Physiology, 55, 99–101.
Aylor, D.E. (1978) Dispersal in time and space: aerial pathogens, in Plant Disease; an Advanced
Treatise (eds J.G. Horsfall and E.B. Cowling), Academic Press, New York, pp. 159–168. Aylor, D.E. (1982) Modelling spore dispersal in a barley crop. Agricultural Meteorology,26, 215–219.
Aylor, D.E. (1987) Deposition gradients of Puccinia recondita near a source. Phytopathology, 77, 1442–1448.
Aylor, D.E. (1989) Aerial spore dispersal close to a focus of disease. Agriculture and Forest Meteorology, 47, 109–122.
Aylor, D.E. (1990) The role of intermittent wind in the dispersal of plant pathogens. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 28, 73–92.
Aylor, D.E. and Ferrandino, F.J. (1989) Dispersion of spores released from an elevated line source within a wheat canopy. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 46, 251–273.
Aylor, D.E and Ferrandino, F.J. (1990) Initial spread of bean rust close to an inoculated bean leaf. Phytopathology, 80, 1469–1476.
Aylor, D.E. and Parlange, J.-Y. (1975) Ventilation required to entrain small particles from leaves. Plant Physiology, 56, 97–99.
Aylor, D.E., McCartney, H.A. and Bainbridge, A. (1981) Deposition of particles liberated in gusts of wind. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 10, 1212–1221.
Bainbridge, A. and Legg, B.J. (1976) Release of barley-mildew conidia from shaken leaves. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 66, 495–498.
Berger, R.D. and Luke, H.H. (1979) Spatial and temporal spread of oat crown rust. Phytopathology, 69, 199–201.
Brennan, R.M., Fitt, B.D.L., Taylor, G.S. and Colhoun, J. (1985) Dispersal of Septoria nodorum pycnidiospores by simulated rain and wind. Phytopathologische Zeitschrift, 112, 291–297.
Butterworth, J. and McCartney, H.A. (1992) Effect of drop size on the removal of Bacillus subtilis from foliar surfaces by water splash. Microbial Releases, 1, 177–185.
Cammack, R.H. (1958) Factors affecting infection gradients from a point source of Puccinia polysora in plots of Zea mays. Annals of Applied Biology, 46, 186–197.
Campbell, C.L. and Madden, L.V. (1990) Introduction to Plant Disease Epidemiology, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 532 pp.
Chamberlain, A.C. (1953) Aspects of travel and deposition of aerosol and vapour clouds. Report AERE-R, UK, Atomic Energy Research Establishment, Harwell.
Chamberlain, A.C. (1975) The movement of particles in plant communities, in Vegetation and the Atmosphere, Vol. 1, (ed. J.L. Monteith ), Academic Press, London, pp. 155–203.
Cionco, R.M., Ohmstede, W.D. and Appleby, J.F. (1963) Meteorological Research Notes Number 5, USAERDAA, Fort Huachuca, Arizona.
Fatemi, F. and Fitt B.D.L. (1983) Dispersal of Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides and Pyrenopeziza brassicae spores in splash droplets. Plant Pathology, 32, 401–404.
Fitt, B.D.L. and Lysandrou, M. (1984) Studies on mechanisms of splash dispersal of spores, using Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides spores. Phytopathologische Zeitschrift, 111, 323–331.
Fitt, B.D.L. and McCartney, H.A. (1986) Spore dispersal in relation to epidemic models, in Plant Disease Epidemiology, Vol.1: Population Dynamics and Management, (eds K.J. Leonard and W.E. Fry ), Macmillan, New York, pp. 311–345.
Fitt, B.D.L., Walklate, P.J., McCartney, H.A. et al. (1986) A rain tower and wind tunnel for studying the dispersal of plant pathogens by rain and wind. Annals of Applied Biology, 109, 661–671.
Fitt, B.D.L., Gregory, P.H., Todd, A.D. et al. (1987) Spore dispersal and plant disease gradients: a comparison between two empirical models. Journal of Phytopathology, 118, 227–242.
Fitt, B.D.L., McCartney, H.A. and Walklate, P.J. (1989) Role of rain in the dispersal of pathogen inoculum. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 27, 241–270.
Fitt, B.D.L, Inman, A.J., Lacey, M.E. and McCartney, H.A. (1992) Splash dispersal of spores of Pseudocercosporella capsellae (white leaf spot) from oilseed rape leaves of different inclination, flexibility and age. Zeitschrift far Pflanzenkrankheiten and Pflanzenschutz, 99, 234–244.
Ferrandino, F.J (1993) Dispersive epidemic waves; I: focus expansion in a linear planting. Phytopathology, 83, 795–802.
Ferrandino, F.J. (1996) Length scale of disease spread: fact or artifact of experimental geometry. Phytopathology, 86, 807–811.
Gladders, P. and Musa, T. (1980) Observations on the epidemiology of Leptosphaeria maculans stem canker in winter oilseed rape. Plant Pathology, 29, 28–37.
Grace, J. (1977) Plant Response to Wind, Academic Press, London, 204 pp.
Gregory, P.H. (1945) The dispersion of air-borne spores. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 28, 26–72.
Gregory, P.H. (1968) Interpreting plant disease dispersal gradients. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 6, 189–212.
Gregory, P.H. (1973) The Microbiology of the Atmosphere, 2nd edn, Leonard Hill, London, 377 pp.
Gregory, P.H., Griffin, M.J., Maddison, A.C. and Ward, M.R. (1984) Cocoa black pod: a reinterpretation. Cocoa Growers Bulletin, 35, 1–18.
Hammett, K.R.W. and Manners, J.G. (1974) Conidium liberation in Erysiphe graminis. III: wind tunnel studies. Transactions of the British Mycological Society, 62, 267–282.
Hirst, J.M., Stedman, O.J. and Hurst, G.W. (1967) Long distance spore transport: vertical sections of spore clouds over the sea. Journal of General Microbiology, 48, 357–377.
Horst, T.W. (1977) A surface depletion model for deposition from a Gaussian plume. Atmospheric Environment, 11, 41–46.
Huber, L., Fitt, B.D.L. and McCartney, H.A. (1996) The incorporation of pathogen spores into rain-splash droplets: a modelling approach. Plant Pathology, 45, 506–518.
Huber, L., McCartney, H.A. and Fitt, B.D.L. (1997) Influence of target characteristics on the amount of water splashed by impacting drops. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 87, 201–211.
Ingold, C.T. (1971) Fungal Spores; their Liberation and Dispersal, Clarendon Press, Oxford. 302 pp.
Inman, A.J. (1993) The biology and epidemiology of white leaf spot (Pseudocercosporella capsellae) on oilseed rape. PhD thesis, University of London.
Jeger, M.J. (1983) Analysing epidemics in time and space. Plant Pathology, 32, 5–11.
Jeger, M.J. (1990) Mathematical analysis and modeling of spatial aspects of plant disease epidemics, in Epidemics of Plant Diseases, (ed. J. Kranz ), Springer Verlag, New York, pp. 53–95.
Jeger, M.J., Jones, D.G. and Griffiths, E. (1983) Disease spread of non-specialised fungal pathogens from inoculated point sources in intraspecific mixed stands of cereal cultivars. Annals Applied Biology, 102, 237–244.
Johnson, K.B. and Powelson, M.L. (1983) Analysis of spore dispersal gradients of Botrytis cinerea and grey mould disease gradients in snap beans. Phytopathology, 73, 741–746.
Kampmeijer, P. and Zadoks, J.C. (1974) A Simulator of Foci and Epidemics in Mixtures, Multilines and Mosaics of Resistant and Susceptible Plants. Simulation Monograph, Pudoc, Wageningen, 50 pp.
Lacey, J. (1986) Water availability and fungal reproduction: patterns of spore production, liberation and dispersal, in Water Fungi and Plants, (eds P.G. Ayres and L. Boddy ), Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 87–104.
Lacey, J., Lacey, M.E. and Fitt, B.D.L. (1997) Philip Herries Gregory 1907–1986: pioneer aero-biologist, versatile mycologist. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 35, 1–14.
Legg, B.J. (1983) Movement of plant pathogens in the crop canopy. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, London, B302, 559–574.
Legg, B.J. and Powell, F.A. (1979) Spore dispersal in a barley crop: a mathematical model. Agricultural Meteorology, 20, 47–67.
Macdonald, O.C. (1988) Splash on leaves and the dispersal of spore carrying droplets. PhD thesis, University of London.
Macdonald, O.C. and McCartney, H.A. (1987) Calculation of splash droplet trajectories. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 39, 95–110.
Macdonald, O.C. and McCartney, H.A. (1988) A photographic technique for investigating splashing of water drops on leaves. Annals of Applied Biology, 113, 627–638.
Madden, L.V., (1992) Rainfall and dispersal of fungal spores. Advances in Plant Pathology, 8, 39–79.
Madden, L.V., Yang, X. and Wilson, L.L. (1996) Effects of rain on splash dispersal of Colletotrichum acutatum. Phytopathology, 86, 864–874.
Maddison, A.C., Holt, J. and Jeger, M.J. (1996) Spatial dynamics of a monocyclic disease in a perennial crop. Ecological Modelling, 88, 45–52.
McCartney, H.A. (1990a) The dispersal of plant pathogen spores and pollen from oilseed rape crops. Aerobiologia, 6, 147–152.
McCartney, H.A. (1990b) Dispersal mechanisms through the air, in Dispersal in Agricultural Habitats, (eds R.G.H. Bunce and D.C. Howard ), Belhaven Press, London, pp. 133–158.
McCartney, H.A. (1997a) Modelling the dispersal of fungal spores and pollens by wind, in Aerobiology, (ed. S.N. Agashe ), Oxford and IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi, pp. 327–332.
McCartney, H.A. (1997b) The influence of environment on the development and control of disease, in Environmentally Safe Approaches to Crop Disease Control, (ed J. Rechcigl ), CRC Press, Bocan Ratan, Florida, pp. 3–31.
McCartney, H.A. and Bainbridge, A. (1987) Deposition of Erysiphe graminis conidia on a barley crop. I: sedimentation and impaction. Journal of Phytopathology, 118, 243–257.
McCartney, H.A. and Fitt, B.D.L. (1985) Construction of dispersal models, in Advances in Plant Pathology, Vol.3: Mathematical Modelling of Crop Disease, (ed. C.A. Gilligan ), Academic Press, London, pp. 107–143.
McCartney, H.A. and Lacey, M.E. (1990) The production and release of ascospores of Pyrenopeziza brassicae Sutton et Rawlinson on oilseed rape. Plant Pathology, 39, 17–32.
McCartney, H.A., Fitt, B.D.L. and Schmechel, D. (1997) Sampling bioaerosols in plant pathol-ogy. Journal of Aerosol Science, 28, 349–364.
Minogue, K.P. (1986) Disease gradients and the spread of disease, in Plant Disease Epidemiology, Vol. 1: Population Dynamics and Management, (eds K.J. Leonard and W.E. Fry ), Macmillan, New York, pp. 285–310.
Minogue, K.P. and Fry, W.E. (1983a) Models for the spread of disease: model description. Phytopathology, 73, 1168–1172.
Minogue, K.P. and Fry, W.E. (1983b) Models for the spread of disease: some experimental results. Phytopathology, 73, 1173–1176.
Monteith, J.L. (1973) Principles of Environmental Physics, Edward Arnold, London. 241 pp. Monteith, J.L. and Unsworth, M.H. (1990) Principles of Environmental Physics, 2nd edn, Edward Arnold, London, 291 pp.
Mundt, C.C. (1995) Models from plant pathology on the movement and fate of new genotypes of microorganisms in the environment. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 33, 467–488.
Mundt, C.C. and Leonard, K.J. (1985) Modification of Gregory’s model for describing plant disease gradients. Phytopathology, 75, 930–935.
Oke, T.R. (1978) Boundary Layer Climates, Methuen and Co., London, 372 pp.
Pasquill, F. and Smith, F.B. (1983) Atmospheric Diffusion, 3rd edn, Ellis Horwood, Chichester.
Paysour, R.E. and Fry, W.E. (1983) Interplot interference: a model for planning field experi-ments with aerially disseminated pathogens. Phytopathology, 73, 1014–1020.
Reynolds, K.M., Madden, L.V., Reichard, D.L. and Ellis, M.A. (1987) Method for study of rain-drop impaction on plant surfaces with application for predicting inoculum dispersal by rain. Phytopathology, 77, 226–232.
Rowe, R.C. and Powelson, R. L. (1973) Epidemiology of Cercosporella foot rot of wheat disease spread. Phytopathology, 63, 984–988.
Scherm, W. (1996) On the velocity of epidemic waves in model plant disease epidemics. Ecological Modelling, 87, 217–222.
Schmidt, W. (1918) Die Verbreitung von Samen and Blütenstaud durch die Luftbewegung. Osterreichische Botanische Zeitshrift, 67, 313–328.
Shaw, M.W. (1987) Assessment of upward movement of rain splash using a fluorescent tracer method and its application to the epidemiology of cereal pathogens. Plant Pathology, 36, 201–213.
Shaw, M.W. (1994) Modeling stochastic processes in plant pathology. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 32, 523–544.
Shaw, M.W. and Royle, D.J. (1993) Factors determining the severity of epidemics of Mycosphaerella graminicola (Septoria tritici) on winter wheat in the UK. Plant Pathology, 42, 882–899.
Shaw, R.H. and McCartney, H.A. (1985) Gust penetration into plant canopies. Atmospheric Environment, 19, 827–830.
Shaw, R.H., Ward, D.P and Aylor, D.E. (1979) Frequency of occurrence of fast gusts of wind inside a corn canopy. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 18, 167–171.
Soleimani, M.J., Deadman, M.L. and McCartney, H.A. (1996) Splash dispersal of Pseudocercosporella herpotrichoides spores in wheat monocrop and wheat—clover bicrop canopies from simulated rain. Plant Pathology, 45, 1052–1063.
Thom, A.S. (1975) Momentum, mass and heat exchange of plant communities. In: Vegetation and the Atmosphere, Vol. 1, (ed. J.L. Monteith ), Academic Press, London, pp. 155–203.
Ulbricht, C.W. (1983) Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribu-tion. Journal of Climate and Applied Meteorology, 22, 1764–1775.
Van den Bosch, F., Zadoks, J.C. and Metz, J.A.J. (1988a) Focus expansion in plant disease. I: The constant rate focus expansion. Phytopathology, 78, 55–58.
Van den Bosch, E, Zadoks, J.C. and Metz, J.A.J. (1988b) Focus expansion in plant disease. II: Realistic parameter-sparse models. Phytopathology, 78, 59–64.
Van der Plank, J.E. (1963) Plant Disease: Epidemics and Control, Academic Press, New York, 349 pp.
Vloutoglou, I., Fitt, B.D.L. and Lucas, J.A. (1995) Periodicity and gradients in dispersal of Alternaria linicola in linseed crops. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 101, 639–653.
Wadia, K.D.R., McCartney, H.A. and Butler, D.R. (1997) Dispersal of Phaeoisariopsis personata conidia from groundnut by wind and rain. Mycological Research, 102, 355–360.
Walklate, P.J. (1986) A Markov-chain particle dispersion model based on airflow data: exten-sion to large water droplets. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 37, 313–318.
Walklate, P.J. (1987) A random-walk model for dispersion of heavy particles in turbulent air flow. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 39, 175–190.
Walklate, P.J. (1989) Vertical dispersal of plant pathogens by splashing. Part I: the theoretical relationship between rainfall and upward rain-splash. Plant Pathology, 38, 56–63.
Walklate, P.J., McCartney, H.A. and Fitt, B.D.L. (1989) Vertical dispersal of plant pathogens by splashing. II: Experimental study of the relationship between rain drop size and maximum splash height. Plant Pathology, 38, 64–70.
Welham, S.J., McCartney, H.A. and Fitt, B.D.L. (1995) A case study in measurement and analysis of disease gradients. Aspects of Applied Biology, 43, 77–85.
Yang, X. and Madden, L.V. (1993) Effects of ground cover, rain intensity, and strawberry plants on splash of simulated raindrops. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 65, 1–20.
Yang, X., Madden, L.V, Reichard, D.L. et al. (1991) Motion analysis of drop impaction on a strawberry surface. Agriculture and Forest Meteorology, 56, 67–92.
Yang, X., Madden, L.V, Reichard, D.L et al. (1992) Splash dispersal of Colletotrichum acutatum and Phytophthora cactorum from strawberry fruit by single drop impactions. Phytopathology, 82, 332–340.
Zadoks, J.C. and Schein, R.D. (1979) Epidemiology and Plant Disease Management, Oxford University Press, New York, 427 pp.
Zadoks, J.C. and Van den Bosch, E (1994) On the spread of plant disease: a theory on foci. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 32, 503–521.
Zawolek, M.W. and Zadoks, J.C. (1992) Studies in focus development: an optimum for dual dispersal of plant pathogens. Phytopathology, 82, 1288–1297.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
McCartney, H.A., Fitt, B.D.L. (1998). Dispersal of foliar fungal plant pathogens: mechanisms, gradients and spatial patterns. In: Jones, D.G. (eds) The Epidemiology of Plant Diseases. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-3302-1_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-3302-1_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-017-3304-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-3302-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive