Abstract
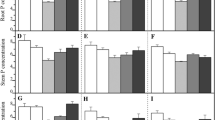
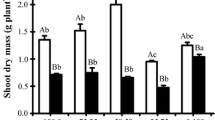
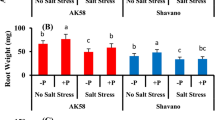
Plant tolerance to Al toxicity has been associated with differential nitrate and ammonium uptake and solution pH changes. Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] genotypes with tolerance (SC283) and sensitivity (ICA-Nataima) to Al toxicity were grown with different nitrate/ammonium ratios (39:1, 9:1, and 3:1) at 0 and 300 μM Al to determine genotypic differences in nitrate and ammonium uptake, changes in nutrient solution pH, and relationships of these traits to Al toxicity tolerance in the genotypes. ICA-Nataima had greater reductions in nitrate and ammonium uptake than SC283 when plants were grown with Al, but SC283 had higher nitrate and ICA-Nataima had higher ammonium uptake when plants were grown without Al. Differences in nitrate and ammonium uptake were associated with changes in solution pH; pH decreased as long as ammonium was in solution and increased when ammonium was depleted from solution. Greater changes in solution pH occurred when plants were grown with 39:1 compared to 9:1 and 3:1 nitrate/ammonium ratios. Solution pH values were lower when plants were grown with than without Al. The genotypes maintained their relative differences in Al toxicity tolerance when plants were grown separately or together in the same container with Al and with different nitrate/ammonium ratios.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardo L M, Clark R B and Maranville J W 1984a Nitrate/ammonium ratio effects on nutrient solution pH, dry matter yield, and nitrogen uptake of sorghum. J. Plant Nutr. 7, 1389–1400.
Bernardo L M, Clark R B and Maranville J W 1984b Nitrate/ammonium ratio effects on mineral element uptake by sorghum. J. Plant Nutr. 7, 1401–1414.
Blarney F P, Edwards D G and Asher C J 1983 Effects of aluminum, OH:Al and P:Al molar ratios, and ionic strength on soybean root elongation in solution culture. Soil Sci. 136, 197–207.
Cambraia J, Pimenta J, Estevao M M and Sant’anna R 1989 Aluminum effects on nitrate uptake and reduction in sorghum. J. Plant Nutr. 12, 1435–1445.
Clark R B 1982 Nutrient solution growth of sorghum and corn in mineral nutrition studies. J. Plant Nutr. 5, 1039–1057.
Dodge C S and Hiatt A J 1972 Relationship of pH to ion uptake imbalance by varieties of wheat (Triticum vulgare). Agron. J. 64, 476–481.
Fageria N K, Baligar V C and Wright R J 1988 Aluminum toxicity in crop plants. J. Plant Nutr. 11, 303–319.
Fleming A L 1983 Ammonium uptake by wheat varieties differing in Al tolerance. Agron. J. 75, 726–730.
Foy C D, Burns G R, Brown J C and Fleming A L 1965 Differential aluminum tolerance to two wheat varieties associated with plant-induced pH changes around their roots. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29, 64–67.
Foy C D, Fleming A L, Burns G R and Armiger W H 1967 Characterization of differential aluminum tolerance among varieties of wheat and barley. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 31, 513–521.
Jarvis S C and Robson A D 1983 The effects of nitrogen nutrition of plants on the development of acidity in Western Australian soils. II. Effects of differences in cation/ anion balance between plant species grown under non-leaching conditions. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 34, 355–365.
Keltjens W G 1987 Nitrogen source and aluminum toxicity of two sorghum genotypes differing in aluminum susceptibility. J. Plant Nutr. 10, 841–856.
Keltjens W G 1988 Short-term effects of Al on nutrient uptake, H+ efflux, root respiration and nitrate reductase activity of two sorghum genotypes differing in Al-susceptibility. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 19, 1155–1163.
Keltjens W G and van Ulden P S R 1987 Effects of Al on nitrogen (NH +4 and NO −3 ) uptake, nitrate reductase activity and proton release in two sorghum cultivars differing in Al tolerance. Plant and Soil 104, 227–234.
Klimashevskii E L and Berezovski K K 1973 Genetic resistance of plants to ionic toxicity in the root zone. Soviet Plant Physiol. 20, 51–54.
Klotz F and Horst W J 1988 Effect of ammonium-and nitrate-nitrogen nutrition on aluminium tolerance of soybean (Glycine max L.). Plant and Soil 111, 59–65.
McCain S and Davies M S 1983 The influence of background solution on root responses to aluminium in Holcus lanatus L. Plant and Soil 73, 425–430.
McLean E O 1976 Chemistry of soil aluminum. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 7, 619–636.
Miyasaka S C, Kochian L V, Shaff J E and Foy C D 1989 Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in wheat: An investigation of genotypic differences in rhizosphere pH, K+, and H+ transport, and root-cell membrane potentials. Plant Physiol. 91, 1188–1196.
Mugwira L M, Edgawhary S M and Patel S U 1978 Aluminium tolerance in triticale, wheat and rye as measured by root growth characteristics and aluminium concentration. Plant and Soil 50, 681–690.
Newman E J 1966 A method of estimating the total length of root in a sample. J. Appl. Ecol. 3, 133–145.
Nye P H 1981 Changes of pH across the rhizosphere induced by roots. Plant and Soil 61, 7–26.
Riley D and Barber S A 1971 Effect of ammonium and nitrate fertilization on phosphorus uptake as related to root-induced pH changes at the root-soil interface. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 35, 301–306.
Rorison I H 1985 Nitrogen source and the tolerance of Deschampsia flexuosa, Holcus lanatus and Bromus erectus to aluminum during seedling growth. J. Ecol. 73, 83–90.
SAS User’s Guide 1985 Statistics. Version 5 ed. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC.
Sposito G (Ed.) 1989 Aluminum. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Taylor G J 1988a The physiology of aluminum tolerance. In Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 24. Aluminum and its Role in Biology. Ed. H Sigel. pp 165–198. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Taylor G J 1988b Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). V. Nitrogen nutrition, plant-induced pH, and tolerance to aluminum; correlation without causality? Can. J. Bot. 66, 694–699.
Taylor G J and Foy C D 1985a Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). I. Differential pH induced by winter cultivars in nutrient solutions. Am. J. Bot. 72, 695–701.
Taylor G J and Foy C D 1985b Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). II. Differential pH induced by spring cultivars in nutrient solutions. Am. J. Bot. 72, 702–706.
Taylor G J and Foy C D 1985c Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). III. Long-term pH changes induced in nutrient solutions by winter cultivars differing in tolerance to aluminum. J. Plant Nutr. 8, 613–628.
Taylor G J and Foy C D 1985d Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance in Triticum aestivum L. (wheat). IV. The role of ammonium and nitrate nutrition. Can. J. Bot. 63, 2181— 2186.
Tennant D 1975 A test of a modified line intersect method of estimating root length. J. Ecol. 63, 995–1001.
Wagatsuma T and Ezoe Y 1985 Effect of pH on ionic species of aluminum in medium and on aluminum toxicity under solution culture. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 31, 547–561.
Wagatsuma T and Yamasaku K 1985 Relationship between differential aluminum tolerance and plant-induced pH change of medium among barley cultivars. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 31, 521–535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Galvez, L., Clark, R.B. (1991). Nitrate and ammonium uptake and solution pH changes for Al-tolerant and Al-sensitive sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) genotypes grown with and without aluminium. In: Wright, R.J., Baligar, V.C., Murrmann, R.P. (eds) Plant-Soil Interactions at Low pH. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, vol 45. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3438-5_91
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3438-5_91
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5520-8
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-3438-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive