Abstract
Soil acidity potentially limits wheat production over about 750,000 ha in north-eastern Victoria. Soils in this region are progressively acidifying and, with concentration on an annual crop-pasture system, the sub-soil is often highly acidic. A deep tillage implement was used to inject slurries of lime into the subsoil on 2 soils with similar acidity, to evaluate the efficacy of this method and the effect on wheat yield. Replicated field experiments were conducted at 2 sites (Lilliput and Stewarton), with 6 soil management treatments. The treatments were a control; unlimed + deep tillage; surface incorporated lime (2.5 t/ha) + deep tillage; and 3 slurry injections (SI) of lime (1.0, 2.5, 5.01/ha) in the deep tillage operation. Wheat (cv. Oxley) was sown for 2 consecutive seasons, and grain yield, kernel weight and nitrogen as well as soil pH and Al and physical measurements were taken.
On the Lilliput soil, SI lime increased soil pH by 0.9 units (0–30 cm depth) with the highest rate, and increased the pH by 1.7 units along the tillage line. The pH was increased by 0.7 units mid-distance between the tines. Surface liming increased pH (0.8 units) only at 0–10 cm.
With the Stewarton soil, pH was increased by only 0.3 units at the highest SI rate, with the only significant pH increase occurring at the 0–30 cm depth along the tillage line. However surface liming increased pH (0–10 cm) by 0.9 units. The Stewarton soil was very dense and compacted.
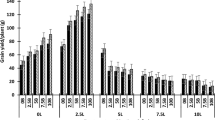
Grain yield was increased with each lime treatment at Lilliput, with the 5.0 t/ha SI giving highest yields in both seasons. Deep tillage increased grain yield at Stewarton in both seasons, but there was no significant yield increase with any lime treatment. The data demonstrate that wheat yields can be increased by amelioration of subsoil acidity, but that soil physical characteristics have to be considered before practical application of this lime sub-soiling method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson D L and Hendrick J G 1983 Subsoil lime injector. Soil Sci. Am. J. 47, 337–339.
Blarney F P C, Edwards D G and Asher C J 1983 Effects of aluminium, OH:Al and P:Al molar ratios, and ionic strength on soybean root elongation in solution culture. Soil Sci. 136, 197–207.
Brooke H D, Ellington A and Melville P W 1986 Slurry injector for the amelioration of subsoils. Proc. Conf. Agric. Engineering. pp 15–16. Adelaide.
Brooke H D, Coventry D R, Reeves T G and Jarvis D K 1989 Liming and deep ripping responses for a range of field crops. Plant and Soil 115, 1–6.
Coventry D R and Slattery W J 1991 Acidification of soil associated with lupins grown in a crop rotation in northeastern Victoria. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 42.
Coventry D R, Reeves T G, Brooke H D, Ellingron A and Slattery W J 1987 Increasing wheat yields in north-eastern Victoria by liming and deep ripping. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 27, 679–685.
Coventry D R, Walker B R, Morrison G R, Hyland M T, Avery J C, Maden J J L and Bartram D C 1989 Yield responses to lime of wheat and barley on acid soils in north-eastern Victoria. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 29, 209–214.
Ellington A 1986 Effects of deep ripping, direct drilling, gypsum and lime on soils, wheat growth and yield. Soil Tillage Res. 8, 29–49.
Farina M P W and Channon P 1988a Acid-subsoil amelioration. I. A comparison of several mechanical procedures. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52, 169–175.
Farina M P W and Channon P 1988b Acid-subsoil amelioration. II. Gypsum effects on growth and subsoil chemical properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52, 175–180.
Higginson F R and Rayment G 1990 Australian Soil and Survey Laboratory Handbook. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
Kemper W D 1965 Aggregate stability. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Ed. C A Black. pp 511–519. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI.
McDonald R C and Isbell R F 1984 Soil profile. In Australian Soil and Land Survey: Field Handbook. Eds. R C McDonald, R F Isbell, J G Speight, J Walker and M S Hopkins. pp 83–126. Inkata Press, Melbourne.
Noble A D, Suraner M E and Alva A K 1988 The pH dependency of aluminium phytotoxicity alleviation by calcium sulphate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52, 1398–1402.
Northcote K H 1971 A Factual Key for the Recognition of Australia Soils, 3rd Edn. Rellim Technical Publication South Aust.
Pavan M A, Bingham F T and Pratt P F 1984 Redistribution of exchangeable calcium, magnesium, and aluminium following lime or gypsum applications to a Brazilian oxisol. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 48, 33–38.
Reeve N G and Sumner M E 1972 Amelioration of subsoil acidity in Natal oxisols by leaching of surface-applied amendments. Agrochemophysica 4, 1–6.
Reeves T G and Ellington A 1985 Soil acidification in NE Victoria. Proc. 3rd Aust. Agron. Conf. 223 p. Aust. Soc. Agron., Hobart.
Ridley A M, Slattery W J, Helyar K R and Cowling A M 1990 The importance of the carbon cycle to acidification of a grazed annual pasture. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 30, 529–537.
Ritchey K D, Souza D M G, Lobato E and Correa O 1980 Calcium leaching to increase rooting depth in a Brazilian savannah oxisol. Agron. J. 72, 40–44.
Ritchie G S P 1989 The chemical behaviour of aluminium, hydrogen and manganese in acid soils. In Soil Acidity and Plant Growth. Ed. A D Robson. pp 1–60. Academic Press, Sydney.
Scott B J and Rodman L A 1987 A lime spreader for use in field research. J. Aust. Inst. Agric. Sci. 53, 197–199.
Sumner M E, Shahandeh H, Bouton J and Hammel J 1986 Amelioration of an acid soil profile through deep liming and surface application of gypsum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 1254–1258.
Wilson A D and Sargeant G A 1963 The colorimetric determination of aluminium in minerals by pyrocatechol violet. The Analyst 88, 109–112.
Venprakas M J 1988 Bulk density values diagnostic of restricted root growth in coarse-textured soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 52, 1117–1121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Coventry, D.R. (1991). The injection of slurries of lime, associated with deep tillage, to increase wheat production on soils with subsoil acidity. In: Wright, R.J., Baligar, V.C., Murrmann, R.P. (eds) Plant-Soil Interactions at Low pH. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, vol 45. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3438-5_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-3438-5_49
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5520-8
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-3438-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive