Abstract
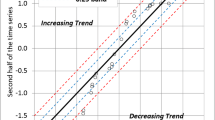
Confirmation of global climatic change requires analysis of quasi-periodic processes which is usually performed by one-dimensional time-series analysis. In our paper, a two-dimensional spatial analysis in the form of kriging over a moving block of data as described in Journel and Rossi (Math Geology, Vol 21, N.7: 715–39) is applied to time series data. The analysis allows separation of seasonal quasi-periodicity from over-the-years time behaviour and is thus a powerful method for use in climatology or for application to other quasi-periodic time series. This has been achieved by introducing a new morphological transformation “montage”, which is an inverse operation to “stripe sampling” by Serra (1982).
The technique has been applied to a 100 year time series of rainfall data for Perth, Western Australia. It was found that the geostatistical method was capable not only of identifying a previously unreported 22 year (a double solar cycle) periodicity in rainfall, but also was able to predict, a year ahead, the heavy rainfall experienced in winter (May–August) 1991 in Perth.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, M.S. (1975) The Statistical Analysis of Spatial Pattern. Chapman and Hall, London.
Carr, J.R. (1990) Application of spatial filter theory to kriging: Math Geol. 22, 1063–1079.
Carr, J.R. and Myers, D.E. (1984) Application of the theory of regionalized variables to the spatial analysis of Landsat data: 9th William T. Pecora Memorial Remote Sensing Symposium, Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Computer Society Press, Silver Spring, Maryland, p. 55–61.
Journel, A.G and Rossi, M.E. (1989) When do we need a trend model in kriging? Math. Geol. 21(7) 715–739.
Lean, J. (1991) Variations in the sun’s radiative output. Review of Geophysics 29,4, 505–535.
Marsily, G. de. (1986) Quantitative Hydrogeology. Academic Press, London.
Matheron, G. (1975). The theory of regionalised variables and its applications. Cahiers du Centre de Morphologie Mathematique de Fountainebleau No. 5.
Matheron, G. (1989) Estimating and Choosing. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Newell, N.E., Newell, R.E., Hsuing, J. and Zhongziang, W. (1989) Global marine temperature variation and the solar magnetic cycle. Geophys. Res. Let. 16(4) 311–314.
Pittock, A.B. (1978) A critical look at long-term sun-weather relationships. Review of Geophysics and Space Physics Vol. 16 No. 3 pp. 400–420.
Pittock, A.B. (1983) Solar variability, weather and climate: an update. Quart. J.R. Met. Soc. 198, 23–55.
Priestley, M.B. (1981) Spectral Analysis and Time Series, Vol. I and II. Academic Press, London.
Pittock, A.B., Walsh, K. and Frederiksen, J.S. (1989) General circulation model simulation of mild nuclear winter. Climate Dynamics, 3, 191–206.
Serra, J. (1982) Image Analysis and Mathematical Morphology. Vol. 1. Academic Press, London.
Webb, D.F., Davis, J.M. and Mcintosh, P.S. (1984) Observations of the reappearance of polar coronal holes and the reversal of the polar magnetic field. Solar Physics, 92, 109–132.
Yakowitz, S.J. and Szidarovszky F. (1985) A comparison of kriging with non-parametric regression methods. J. Multivariate Anal. 16, 21–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1993 Kluwer Academic Publishers
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Allison, H., Davis, G.B. (1993). Analysis of Quasi-Periodic Time Series by a Geostatistical Method with Application to Climatology. In: Soares, A. (eds) Geostatistics Tróia ’92. Quantitative Geology and Geostatistics, vol 5. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1739-5_44
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-1739-5_44
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-0-7923-2157-6
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-1739-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive