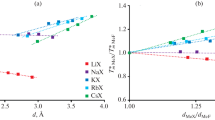
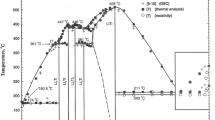
Abstract
General background on molten metal halides: chemical coordinates, melting parameters, transport coefficients. Overview on liquid structure. Primitive model for structure and thermodynamics. Background on interionic forces: cohesion and lattice vibrations in alkali halide crystals, ionic binding in alkali halide molecules. Structure of alkali halide melts and chemical short-range order. Liquid-solid and liquid-gas coexistence. Cluster formation in trichloride melts and their mixtures with alkali chlorides. Clusters in aluminium-alkali fluoride mixtures and solutions of sodium metal in molten cryolite. Ionic transport, viscosity and dynamics of density fluctuations.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rovere, M. and Tosi, M. P. (1986) Structure and dynamics of molten salts, Rep. Progr. Phys. 49, 1001–1081.
Tosi, M. P., Price, D. L., and Saboungi, M.-L. (1993) Ordering in metal halide melts, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 44, 173–211.
Pettifor, D. G. (1986) The structure of binary compounds: I. Phenomenological structure maps, J. Phys. C 19, 285–313.
Talion, J. L. (1982) The entropy change on melting of simple substances, Phys. Lett. A 87, 139–143.
Akdeniz, A. and Tosi, M. P. (1992) Correlations between entropy and volume of melting in halide salts, Proc. R. Soc. London A 437, 85–96.
Wasse, J. C., Salmon, P. S., and Delaplane, R. G. (2000) Structure of molten trivalent metal bromides studied by using neutron diffraction: the systems DyBr3, YBr3, HoBr3 and ErBr3, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 9539–9550.
Bhatia, A. B. and Thornton, D. E. (1970) Structural aspects of the electrical resistivity of binary alloys, Phys. Rev. B 2, 3004–3013.
McGreevy, R. L. and Mitchell, E. W. J. (1982) The determination of the partial pair distribution functions for molten strontium chloride, J. Phys. C15, 5537–5550.
Tatlipinar, H., Akdeniz, Z., Pastore, G., and Tosi, M. P. (1992) Atomic size effects on local coordination and medium-range order in molten trivalent metal halides, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 4, 8933–8944.
Biggin, S. and Enderby, J. E. (1981) The structure of molten zinc chloride, J. Phys. C 14, 3129–3136.
Price, D. L., Moss, S. C., Reijers, R., Saboungi, M.-L., and Susman, S. (1989) Intermediate-range order in glasses and liquids, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1, 1005–1008.
Waisman, A. and Lebowitz, J. L. (1972) Mean spherical model integral equation for charged hard spheres, J. Chem. Phys. 56, 3086–3099.
Painter, K. R., Ballone, P., Tosi, M. P., Grout, P. J., and March, N. H. (1983) Capacitance of metal-molten salt interfaces, Surf. Sci. 133, 89–100.
Löwdin, P. O. (1956) Quantum theory of cohesive properties of solids, Phil. Mag. Suppl. 5, 1–172.
Gygi, F., Maschke, K., and Andreoni, W. (1984) Electron charge density of alkali halides beyond the rigid-ion approximation, Solid State Commun. 49, 437–439.
Böbel, G., Cortona, P., Sommers, C., and Fumi, F. G. (1983) Electron density in NaF and KCl crystals in the self-consistent local-density-functional approximation, Acta Crystallogr. A 39, 400–407.
Born, M. and Huang, K. (1954) Dynamical Theory of Crystal Lattices, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Tosi, M. P. (1964) Cohesion of ionic solids in the Born model, Solid State Phys. 16, 1–120.
Fumi, F. G. and Tosi, M. P. (1964) Ionic sizes and Born repulsive parameters in the NaCl-type alkali halides: the Huggins-Mayer and Pauling forms, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 25, 31–44.
Fumi, F. G. and Tosi, M. P. (1957) Lattice calculations on point imperfections in the alkali halides, Disc. Faraday. Soc. 23, 91–98.
Cochran, W. (1971) Lattice dynamics of ionic and covalent crystals, Crit. Rev. Solid State Sci.2, 1–44.
Tosi, M. P. and Doyama, M. (1967) Ionic-model theory of polar molecules, Phys. Rev.160, 716–718.
Kahn, L. R., Hay, P. J., and Shavitt, I. (1974) Theoretical study of curve crossing: ab initio calculations on the four lowest 1∑+ states of LiF, J. Chem. Phys.61, 3530–3546.
Galli, G., Andreoni, W., and Tosi, M. P. (1986) Stability and ionization-induced structural transitions of sodium chloride microclusters from Hartree-Fock calculations: Na2Cl2 + and Na2Cl2 +, Phys. Rev. A 34, 3580–3586.
Jordan, K. D. (1979) Structure of alkali halides: theoretical methods, in Alkali Halide Vapors: Structure, Spectra and Reaction Dynamics, Academic, New York, 479–534.
Brumer, P. and Karplus, M. (1973) Perturbation theory and ionic models for alkali halide systems: diatomics, J. Chem. Phys. 58, 3903–3918.
Sangster, M. J. L. and Dixon, M. (1976) Interionic potentials in alkali halides and their use in simulations of the molten salts, Adv. Phys. 25, 247–342.
Rosenfeld, Y. and Ashcroft, N. W. (1979) Theory of simple classical fluids: universality in the short-range structure, Phys. Rev. A 20, 1208–1235.
Ballone, P., Pastore, G., and Tosi, M. P. (1984) Structure and thermodynamic properties of molten alkali chlorides, J. Chem. Phys. 81, 3174–3180.
Ross, M. and Rogers, F. J. (1985) Structure of dense shock-melted alkali halides: evidence for a continuous pressure-induced structural transition in the melt, Phys. Rev. B 31, 1463–1468.
D’Aguanno, B., Rovere, M., Tosi, M. P., and March, N. H. (1983) Freezing of ionic melts into normal and superionic phases, Phys. Chem. Liquids 13, 113–122.
Fisher, M. E. (1999) Understanding criticality: simple fluids and ionic fluids, in New Approaches to Problems in Liquid State Theory, Kluwer, Dordrecht, 3–8.
Mott, N. F. (1974) Metal-Insulator Transitions, Taylor and Francis, London.
Fisher, M. E. and Zuckerman, D. M. (1998) Exact thermodynamic formulation of chemical association, J. Chem. Phys. 109, 7961–7981.
Akdeniz, Z. and Tosi, M. P. (1999) A refined ionic model for clusters relevant to molten chloroaluminates, Z. Naturforsch. 54 a, 180–186.
Akdeniz, Z., Çaliskan, M., ÇiÇek, Z., and Tosi, M. P. (2000) Polymeric structures in aluminium and gallium halides, Z. Naturforsch. 55 a, 575–580.
Gilbert, B., Mamantov, G., and Begun, G. N. (1975) Raman spectra of aluminum fluoride containing melts and the ionic equilibrium in molten cryolite type mixtures, J. Chem. Phys. 62, 950–955
Gilbert, B. and Materne, T. (1990) Reinvestigation of molten fluoroaluminates Raman spectra: the question of the existence of AlF5 2- ions, Appl. Spectrosc. 44, 299–305.
Robert, E., Olsen, J. E., Danek, V., Tixhon, E., Φstvold, T., and Gilbert, B. (1997) Structure and thermodynamics of alkali fluorides-aluminum fluoride-alumina melts. Vapour pressue, solubility, and Raman spectroscopic studies, J. Phys. Chem. B101, 9447–9457.
Akdeniz, Z., ÇiÇek, Z., and Tosi, M. P. (1999) Theoretical evidence for the stability of the (AlF5)2- complex anion, Chem. Phys. Lett. 308, 479–485.
Brooker, M. H., and Papatheodorou, G. N. (1983) Vibrational spectroscopy of molten salts and related glasses and vapors, Adv. Molten Salt Chem. 5, 26–184.
Grjotheim, K., Krohn, C., Malinovsky, M., Matiasovsky, K., and Thonstad, J. (1982) Aluminium Electrolysis — Fundamentals of the Hall-Héroult Process, Aluminium-Verlag, Dusseldorf.
Akdeniz, Z. and Tosi, M. P. (1991) Structure breaking and electron localization in liquid cryolite-sodium solutions, Phil. Mag. B64, 167–179.
Akdeniz, Z. and Tosi, M. P. (1989) Stability diagrams for fourfold coordination of polyvalent metal ions in molten mixtures of halide salts, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 1, 2381–2394.
Akdeniz, Z., Li, W., and Tosi, M. P. (1988) Classification of stability for tetrahedral halocomplexes in molten-salt mixtures, Europhys. Lett. 5, 613–617.
Trullas, J., Girò, A., and Silbert, M. (1990) Potentials and correlation functions for the copper-halide and silver-halide melts. II: Time correlation functions and ionic transport properties, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2, 6643–6650.
Tankeshwar, K. and Tosi, M. P. (1991) Ionic diffusion in superionic-conductor melts, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 3, 7511–7518.
Tankeshwar, K. and Tosi, M. P. (1992) Theory of the Chemla effect in molten (Li,K)Cl, Solid State Commun. 84, 245–247.
Ciccotti, G., Jacucci, G., and McDonald, I. R. (1976) Transport properties of molten alkali halides, Phys. Rev. A 13, 426–436.
Sjöblom, C.-A. and Behn, A. (1968) Self-diffusion in molten zinc chloride, Z.Naturforsch. 23 a, 495–49
Tatlipinar, H., Amoruso, M., and Tosi, M. P. (2000) Ionic charge transport in strongly structured molten salts, Physica B 275, 281–284.
Hirschfelder, J. O., Curtiss, C. E., and Bird, R. B. (1964) Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids, Wiley, New York.
Abe, Y. and Nagashima, A. (1981) The principle of corresponding states for alkali halides viscosity, J. Chem. Phys. 75, 3977–3985.
Voronel, A., Veliyulin, E., Grande, T., and Φye, H. A. (1997) Universal viscosity behaviour of regular and glassforming ionic melts, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, L247–L249.
Voronel, A., Veliyulin, E., Machvariani, V. Sh., Kisliuk, A., and Quitmann, D. (1998) Fractional Stokes-Einstein law for ionic transport in liquids, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2630–2633.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tosi, M.P. (2002). Molten Salts: Fundamentals. In: Gaune-Escard, M. (eds) Molten Salts: From Fundamentals to Applications. NATO Science Series, vol 52. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0458-9_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0458-9_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-0459-9
Online ISBN: 978-94-010-0458-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive