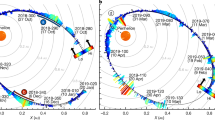
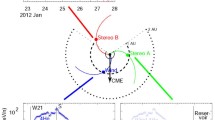
Abstract
Through space exploration an amazing variety of populations of energetic particles have been discovered in our Sun’s surroundings. Wherever we look in the heliosphere, we find processes that can accelerate ions and electrons of the local plasma to energies of ~0.01 to ~1000MeV, or even more.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J.H., Garcia-Munoz, M., Grigorov, N.L., Klecker, B., Kondratyeva, M.A., Mason, G.M., McGuire, R.E., Mewaldt, R.A., Panasyuk, M.I., Tretyakova, Ch.A., Tylka, A.J. and Zhuravlev, D.A. (1991). The charge state of the anomalous component of cosmic rays. Astrophysical Journal, 375, L45–L48.
Armstrong, T.P., Krimigis, S.M. and Behannon, K.W. (1970). Proton fluxes at 300 keV associated with propagating interplanetary shock waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75, 5980–5988.
Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J. and Strong I.B. (1968). Outward flow of protons from the Earth’s bow shock. Journal of Geophysical Research, 73, 5777–5782.
Axford, W.I. (1965). Anisotropic diffusion of solar cosmic rays. Planetary and Space Science, 13, 1301–1309.
Axford, W.I., Leer, E. and Skadron, G. (1977). The acceleration of cosmic rays by shock waves. In Proceedings of the 15th Interational Cosmic Ray Conference, Plovdiv, Vol. 11, pp. 132–137.
Barnes, C.W. and Simpson, J.A. (1976). Evidence for interplanetary acceleration of nucleons in corotating interaction regions. Astrophysical Journal, 210, L91–L96.
Bell, A.R. (1978). The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 182, 147–156.
Bertaux, J.L. and Blamont, J.E. (1971). Evidence for a source of an extraterrestrial hydrogen Lyman-alpha emission: The interstellar wind. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 11, 200–217.
Biswas, S., Durgaprasad, N., Nevatia, J., Sarkar, S. and Venkatavaradan, V.S. (1977). Energy spectra and abundances of carbon to nickel ions in the low energy 8–100MeV/amu cosmic rays observed in the Skylab experiment. In Proceedings of the 15th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Plovdiv, Vol. 2, pp. 327–332.
Biswas, S., Durgaprasad, N. and Trivedi, S.S. (1981). On the origin of the low energy rays from stellar sources. Earth Planet Science (Indian Academy of Sciences), 90, 337–344.
Blandford, R.D. and Ostriker, J.P. (1978). Particle acceleration by astrophysical shocks. Astrophysical Journal, 221, L29–L32.
Blum, P.W. and Fahr, H.-J. (1970). Interaction between interstellar hydrogen and the solar wind. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 4, 280–290.
Breneman, H.H. and Stone, E.C. (1985). Solar coronal and photospheric abundances from solar energetic particle measurements. Astrophysical Journal, 299,L57–L61.
Bryant, D.A., Cline, T.L., Desai, U.D. and McDonald, F.B. (1962). Explorer 12 observations of solar cosmic rays and energetic storm particle events after the solar flare of September 28, 1961. Journal of Geophysical Research, 67, 4983–5000.
Bryant D.A., Cline, T.L., Desai, U.D. and McDonald, F.B. (1965). Continual acceleration of solar protons in the MeV range. Physical Review Letters, 14, 481–484.
Burlaga, L.F., McDonald, F.B., Goldstein, M.L. and Lazarus, A.J. (1985). Cosmic ray modulation and turbulent interaction regions near 11AU. Journal of Geophysical Research, 90, 12027–12039.
Burlaga, L.F., Ness, N.F., Belcher, J.W., Lazarus, A.J. and Richardson, J.D. (1996). Voyager observations of the magnetic field, interstellar pickup ions and solar wind in the distant heliosphere. Space Science Reviews, 78, 33–42.
Cane, H.V., McGuire, R.E. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1986). Two classes of solar energetic particle events associated with impulsive and long-duration soft x-ray flares. Astrophysical Journal, 301, 448–459.
Cane, H.V. and Reames, D.V. (1990). The relationship between energetic particles and flare properties for impulsive solar flares. Astrophysical Journal, 73, 253–258.
Cane, H.V., Reames, D.V. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1988). The role of interplanetary shocks in the longitude distribution of solar energetic particles. Journal of Geophysical Research, 93, 9555–9567.
Cane, H.V., Reames, D.V. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1991). Solar particle abundances at energies of greater than 1 MeV per nucleon and the role of interplanetary shocks. Astrophysical Journal, 373, 675–682.
Cane, H.V., Sheeley, Jr., N.R. and Howard, R.A. (1987). Energetic interplanetary shocks, radio emission and coronal mass ejections. Journal of Geophysical Research, 92, 9869–9874.
Cane, H.V., von Rosenvinge, T.T. and McGuire, R.E. (1990). Energetic particle observations at the Helios 1 spacecraft of shocks associated with coronal mass ejections. Journal of Geophysical Research, 95, 6575–6579.
Carrington, R.C. (1860). Description of a singular appearance seen on the sun on September 1, 1859. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 20, 13–15.
Chapman, S. and Bartels, J. (1940). Geomagnetism. Oxford University Press, London.
Christian, E.R., Cummings, A.C. and Stone, E.C. (1988). Evidence for anomalous cosmic-ray hydrogen. Astrophysical Journal, 334, L77–L80.
Chupp, E.L., Forrest, D.J., Higbie, P.R., Suri, A.N., Tsai, C. and Dunphy, P.P. (1973). Solar gamma ray lines observed during the solar activity of August 2 to August 11, 1972. Nature, 241, 333–335.
Cliver, E.W. (1996). Solar flare gamma-ray emission and energetic particles in space. In R. Ramaty, N. Mandzhavidze and X.M. Hua, (eds), High Energy Solar Physics, AIP Conference Proceedings, 374, pp. 45–60.
Cliver, E.W. (2000). Solar flares photons and energetic particles in space. In R.A. Mewaldt, J.R. Jokipii, M.A. Lee, E. Möbius and T.H. Zurbuchen (eds), Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles observed in the Heliosphere, ACE-2000 Symposium, AIP Conference Proceedings, 528, pp. 21–31.
Cliver, E.W., Forrest, D.J., Cane, H.V., Reames, D.V., McGuire, R.E., von Rosenvinge, T.T., Kane, S.R. and MacDowall, R.J. (1989). Solar flare nuclear gamma-rays and interplanetary proton events. Astrophysical Journal, 343, 953–970.
Cliver, E.W., Kahler, S.W. and Mclntosh, P.S. (1983). Solar proton flares with weak impulsive phases. Astrophysical Journal, 264, 699–707.
Cliver, Kahler, S.W., Shea, M.A. and Smart, D.F. (1982). Injection of ~2GeV protons, ~ 1 MeV electrons, and ~ 100keV electrons in solar cosmic ray flares. Astrophysical Journal, 260, 362–370.
Cohen, C.M.S., Mewaldt, R.A., Leske, R.A., Cummings, A.C. and Stone, E.C. (1999). New observations of heavy ion-rich solar particle events from ACE. Geophysical Research Letters, 26, 2697–2700.
Cook, W.R., Stone, E.C. and Vogt, R.E. (1980). Elemental composition of solar energetic nuclei. Astrophysical Journal, 238, L97–L101.
Cummings, A.C., Mewaldt, R.A., Blake, J.B., Cummings J.R., Fränz, M., Hovestadt, D., Klecker, B., Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., Stone, E.C., von Rosenvinge, T.T. and Webber, W.R. (1995). Anomalous cosmic ray oxygen gradients throughout the heliosphere. Geophysical Research Letters, 22, 341–344.
Cummings, A.C. and Stone E.C. (1987). Elemental composition of the anomalous cosmic ray component. In Proceedings of the 20th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Moscow, Vol. 3, pp. 413–416.
Cummings, A.C., Stone, E.C. and Steenberg, CD. (1999). Composition of anomalous cosmic rays and other ions from Voyager observations. In Proceedings of the 26th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Utah, Vol. 7, pp. 531–534.
Cummings, A.C., Stone, E.C. and Webber, W.R. (1984). Evidence that the anomalous cosmic-ray component is singly ionized. Astrophysical Journal, 287, L99–L103.
Decker, R.B. (1981). The modulation of low-energy proton distributions by propagating interplanetary shock waves. A numerical simulation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 4537–4554.
Decker, R.B., Pesses, M.E. and Krimigis, S.M. (1981). Shock-associated low-energy ion enhancements observed by Voyagers 1 and 2. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 8819–8831.
Desai, M.I., Mason G.M., Dwyer, J.R., Mazur, J.E., Von Rosenvinge, T.T. and Lepping, R.P. (2000). Characteristics of energetic (≥30keVnuc_1) ions observed by the Wind/STEP instrument upstream of the Earth’s bow shock. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 61–78.
Dessler, A. (1967). Solar wind and interplanetary field. Review of Geophysics, 5, 1–41.
Domingo, V.R., Hynds, R.J. and Stevens G. (1979). A solar proton event of possible non-flare origin. In Proceedings of the 16th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Kyoto, Vol. 5, pp. 192–197.
Dwyer, J.R., Mason, G.M., Desai, M.I., Mazur, J.E. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (2000). The spatial size of ion events measured far upstream of the earth’s bow shock by ACE/ULEIS and WIND/STEP. Geophysical Research Letters, 27, 65–68.
Eichler, D. (1981). A cosmic-ray-mediated shock in the solar system. Astrophysical Journal, 247, 1089–1092.
Ellison, D.C., Möbius, E. and Paschmann, G. (1990). Particle injection and acceleration at Earth’s bow shock: comparison of upstream and downstream events. Astrophysical Journal, 352, 376–394.
Fan, C.Y., Gloeckler, G. and Simpson, J.A. (1965). Protons and helium nuclei within interplanetary magnetic regions which corotate with the Sun. In Proceedings of the 9th International Cosmic Ray Conference, London, Vol. l,pp. 109–111.
Fichtel, C.E. and Guss, D.E. (1961). Heavy nuclei in solar cosmic rays. Physical Review Letters, 6, 495–497.
Fisk, L.A. (1971). Increases in the low-energy cosmic ray intensity at the front of propagating interplanetary shock waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 76, 1662–1672.
Fisk, L.A. (1976a). The acceleration of energetic particles in the interplanetary medium by transit time damping, Journal of Geophysical Research, 81, 4633–4645.
Fisk, L.A. (1976b). Solar modulation and a galactic origin for the anomalous component observed in low-energy cosmic rays. Astrophysical Journal, 206, 333–341.
Fisk, L.A. (1978). 3He-rich flares: A possible explanation. Astrophysical Journal 224, 1048–1055.
Fisk, L.A. (1986). The anomalous component, its variation with latitude and related aspects of modulation. In R.G. Marsden (ed.), The Sun and the Heliosphere in Three Dimensions, Reidel, Dordrecht, pp. 401–411.
Fisk, L.A. (1996). Motions of footpoints of heliospheric magnetic field lines at the Sun: Implications for recurrent energetic particle events at high heliographic latitudes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101, 15,547–15,554.
Fisk, L.A., Kozlovsky, B. and Ramaty, R. (1974). An interpretation of the observed oxygen and nitrogen enhancements in low-energy cosmic rays. Astrophysical Journal, 190, L35–L37.
Fisk, L.A. and Lee, M.A. (1980). Shock acceleration of energetic particles in corotating interaction regions in the solar wind. Astrophysical Journal, 237, 620–626.
Forbush, S.E. (1946). Three unusual cosmic-ray increases possibly due to charged particles form the Sun. Physical Review, 70, 771.
Fowler, P.H., Redfern, R.M. and Swordy, S.P. (1979). Do comets provide material for the anomalous component of the cosmic rays? Nature, 279, 622–624.
Garcia-Munoz, M., Mason, G.M. and Simpson, J.A. (1973). A new test for solar modulation theory: the 1972 May-July low-energy galactic cosmic-ray proton and helium spectra. Astrophysical Journal, 182, L81–L84.
Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Fisk, L.A. and Von Steiger, R. (1995). C+ pickup ions in the heliosphere and their origin. Journal of Geophysical, 100, 23,373–23,377.
Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Mall, G., Von Steiger, R., Galvin, A.B. and Ogilvie, K.W. (1994). Interstellar oxygen, nitrogen and neon in the heliosphere. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 282, 924–933.
Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G. and von Steiger, R. (1996). Origin of C+ ions in the heliosphere. Space Science Reviews, 78, 43–52.
Gloeckler, G. (1970). The measurements of non-relativistic charged particles of extra-terrestrial origin. In H. Ögelman and J.R. Wayland (eds), Introduction to Experimental Techniques of High-Energy Astrophysics, NASA Publ.SP-243, pp. 1–61.
Gloeckler, G. (1975). Low energy particle composition. In Proceedings of the 14th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Munich, Vol. 11, pp. 3784–3804.
Gloeckler, G. (1979). Composition of energetic particle populations in interplanetary space. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 17, 569–582.
Gloeckler, G. (1999). Observation of injection and pre-acceleration processes in the slow solar wind. Space Science Reviews, 89, 91–104.
Gloeckler, G., Balsiger, H., Bürgi, A., Bochsler, P., Fisk, L.A., Galvin, A.B., Geiss, J., Gliem, F., Hamilton, D.C., Holzer, T.E., Hovestadt, D., Ipavich, F.M., Kirsch, E., Lundgren, R.A., Ogilvie, K.W., Sheldon, R.B. and Wilken, B. (1995). The solar wind and supra-thermal ion composition investigation on the Wind spacecraft. Space Science Reviews, 71, 79–124.
Gloeckler, G., Cain, J., Ipavich, F.M., Tums, E.O., Bedini, P., Fisk, L.A., Zurbuchen T.H., Bochsler, P., Fischer, J., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F., Geiss, J. and Kallenbach, R. (1998). Investigation of the composition of solar and interstellar matter using solar wind and pick up ion measurements with SWICS and SWIMS on the ACE spacecraft. Space Science Reviews, 86, 497–538.
Gloeckler, G., Fisk, L.A. and Geiss, J. (1997). Anomalously small magnetic field in the local interstellar cloud. Nature, 386, 374–377.
Gloeckler, G., Fisk, L.A., Geiss, J., Schwadron, N.A. and Zurbuchen, T.H. (2000a). Elemental composition of the inner source pickup ions. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 7459–7463.
Gloeckler, G., Fisk, L.A., Zurbuchen, T.H. and Schwadron, N.A. (2000b). Sources, injection and acceleration of heliospheric ion populations. In R.A. Mewaldt, J.R. Jokipii, M.A. Lee, E. Möbius and T.H. Zurbuchen (eds.), Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles Observed in the Heliosphere, ACE-2000 Symposium, AIP Conference Proceedings, 528, 221–228.
Gloeckler, G. and Geiss, J. (1996). Abundance of 3He in the local interstellar cloud. Nature, 381, 210–212.
Gloeckler, G. and Geiss, J. (1998). Interstellar and inner source pickup ions observed with SWICS on Ulysses. Space Science Reviews, 86, 127–159.
Gloeckler, G. and Geiss J. (2001). Heliospheric phenomena deduced from pickup ion observations. In R.G. Marsden (ed.), The 3-D Heliosphere at Solar Maximum. Proceedings of the 34th ESLAB Symposium. Space Science Review, 97, 169–181.
Gloeckler, G., Geiss, J., Balsiger, H., Bedini, P., Cain, J.C., Fischer, J., Fisk, L.A., Galvin, A.B., Geiss, J., Gliem, F., Hamilton, D.C., Hollweg, J.V., Ipavich, F.M., Joos, R., Livi, S., Lundgren, R., Mall, U., McKenzie, J.F., Ogilvie, K.W., Ottens, F., Rieck, W., Tums, E.O., von Steiger, R., Weiss, W. and Wilken, B. (1992). The solar wind ion composition spectrometer.Astronomy and Astrophysics Suppl.,92, 267–289.
Gloeckler, G., Geiss, J., Balsiger, H., Fisk, L.A., Galvin, A.B., Ipavich, F.M., Ogilvie, K.W., von Steiger, R. and Wilken, B. (1993). Detection of interstellar pick-up hydrogen in the solar system. Science, 261, 70–73.
Gloeckler, G., Geiss, J. and Fisk, L.A. (2001). Heliospheric and interstellar phenomena revealed from observations of pickup ions. In A. Balogh, E.J. Smith, and R.G. Marsden (eds), The Heliosphere near Solar Minimum: The Ulysses Perspective. Springer-Praxis, Berlin, 287–326.
Gloeckler, G., Geiss, J., Roelof, E.C., Fisk, L.A., Ipavich, F.M., Ogilvie, K.W., Lanzerotti, L.J., von Steiger, R. and Wilken, B. (1994). Acceleration of interstellar pickup ions in the disturbed solar wind observed on Ulysses. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99, 17,637–17,643.
Gloeckler, G., Hovestadt, D. and Fisk, L.A. (1979). Observed distribution functions of H, He, C, O, and Fe in corotating energetic particles streams: Implications for interplanetary acceleration and propagation. Astrophysical Journal, 230, L191–L195.
Gloeckler, G. and Hsieh, K.C. (1979). Time-of-flight technique identification at energies from 2 to 400 keV/nucleon. Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 165, 537–544.
Gloecker, G., Sciambi, R.K., Fan, C.Y. and Hovestadt, D. (1976). A direct measurement of the charge states of energetic iron emitted by the sun. Astrophysical Journal Letters, 209, L93–L96.
Gosling, J.T. (1993). The solar flare myth. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98, 18937–18949.
Gosling, J.T., Hildner, E., MacQueen, R.M., Munro, R.H., Poland, A.I. and Ross, C.L. (1974). Mass ejections from the Sun: a view from Skylab. Journal of Geophysical Research, 79, 4581–4587.
Greenstadt, E.W., Green, I.M., Inouye, G.T., Hundhausen, A.J., Bame, S.J. and Strong, I.B. (1968). Corrrelated magnetic field and plasma observations of the Earth’s bow shock. Journal of Geophysical Research, 73, 51–60.
Hoppe, M.M. and Russell, C.T. (1982). Particle acceleration at planetary bow shocks waves. Nature, 295, 41–42.
Hoppe, M.M., Russell, C.T., Frank, L.A., Eastman, T.E. and Greenstadt, E.W. (1981). Upstream hydromagnetic waves and their association with backstreaming ion populations: ISEE 1 and 2 observations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 4471–4492.
Hovestadt, D. and Vollmer, O. (1971). A satellite experiment for detecting low energy heavy cosmic rays. In Proceedings of the 12th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Hobart, Vol. 4, 1608–1613.
Hovestadt, D., Vollmer, O., Gloeckler, G. and Fan C.Y. (1973). Differential energy spectra of low energy (<8.5MeV per nucleon) heavy cosmic rays during solar quiet times. Physical Review Letters, 31, 650–653.
Hoyle, F. and Clayton, D.D. (1974). Nucleosynthesis in white-dwarf atmospheres. Astrophysical Journal, 191, 705–710.
Hsieh, K.C. and Simpson, J.A. (1970). The relative abundances an energy spectra of 3He and 4He from solar flares. Astrophysical Journal, 162,L191–L196.
Hudson, H., Haisch, B. and Strong, K.T. (1995). Comment on ‘The solar flare myth’ by J.T. Gosling. Journal of Geophysical Research, 100,3473–3477.
Intriligator, D.S., Siscoe, G.L. and Miller, W.D. (1996). Interstellar pickup H+ ions at 8.3 AU: Pioneer 10 plasma and magnetic field analyses.Geophysical Research Letters, 23, 2181–2184.
Jokipii, J.R. (1971). Deceleration and acceleration of cosmic rays in the solar wind. Physical Review Letters, 26, 666–669.
Jokipii, J.R. (1982). Particle drift, diffusion, and acceleration at shocks.Astrophysical Journal, 255, 716–720.
Jokipii, J.R. (1986). Particle acceleration at the termination shock 1:Applications to the solar wind and the anomalous component. Journal of Geophysical Research, 91, 2929–2932.
Jokipii, J.R. (1992). Constraints on the acceleration of anomalous cosmic rays. Astrophysical Journal, 393, L41–L43.
Jokipii, J.R., Kota, J., Giacalone, J., Horbury, T.S. and Smith, E.J. (1995).Interpretation and consequences of large-scale magnetic variances at high heliographic latitude. Geophysical Research Letters, 22, 3385–3388.
Kahler, S.W. (1994). Injection profiles of solar energetic particles as functions of coronal mass ejection heights. Astrophysical Journal, 428,837–842.
Kahler, S.W., Hildner, E. and Van Hollebeke, M.A.I. (1978). Prompt solar proton events and coronal mass ejections. Solar Physics, 57, 429–443.
Kennel, C.F., Coroniti, F.V., Scarf, F., Livesey, W.A., Russell, C.T., Smith,E.J., Wenzel, K.P. and Scholer, M. (1986). A test of Lee’s quasi-linear theory of ion acceleration by interplanetary travelling shocks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 91, 11,917–11,928.
Keppler, E. (1998). The acceleration of charged particles in corotating interaction regions (CIR): A review with particular emphasis on the Ulysses mission. Surveys in Geophysics, 19, 211–278.
Keppler, E., Fränz, M., Korth, A., Krupp, N., Reuss, M.K., Wilken, B.,Balogh, A., Forsyth, R.J., Quenby, J.J. and Blake, B. (1995). Energetic particle observations at high heliographic latitudes. Space Science Reviews, 72, 285–290.
Klecker, B. (1977). The anomalous component of low energy cosmic rays:A comparison of observed spectra with model calculations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 82, 5287–5291.
Klecker, B. (1995). The anomalous component of cosmic rays in the 3-D heliosphere. Space Science Reviews, 72, 419–430.
Klecker, B., Hovestadt, D., Gloeckler, G. and Fan, C.Y. (1980). On the charge state of the anomalous oxygen component. Geophysical Research Letters, 7, 1033–1036.
Klecker, B., Hovestadt, D., Gloeckler, G., Ipavich, F.M., Scholer, M., Fan,C.Y. and Fisk, L.A. (1984). Direct determination of the ionic charge distribution of helium and iron in 3He-Rich solar energetic particle events. Astrophysical Journal, 281, 458–462.
Klecker, B., McNab, M.C., Blake, J.B., Hamilton, D.C., Hovestadt, D.,Kästle, H., Looper, M.D., Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E. and Scholer, M.(1995). Charge states of anomalous cosmic-ray nitrogen, oxygen, and neon: Sampex observations. Astrophysical Journal, 442, L69–L72.
Klecker, B., Mewaldt, R.A., Bieber, J.W., Cummings, A.C., Drury, L.,Giacalone, J., Jokipii, J.R., Jones, F.C., Krainev, M.B., Lee, M.A., Le Roux, J.A., Marsden, R.G., McDonald, F.B., McKibben, R.B., Baring,M.G., Ellison, D.C., Lanzerotti, L.J., Leske, R.A., Mazur, J.E., Moraal,H., Oetliker, M., Ptuskin, V.S., Selesnick, R.S. and Trattner, K.J. (1998).Anomalous cosmic rays. Space Science Reviews, 83, 259–308.
Klecker, B., Oetliker, M., Blake, J.B., Hovestadt, D., Mason, G.M., Mazur,J.E. and McNab, M.C. (1997). Multiply charged anomalous cosmic ray N, O, and Ne: observations with HILT/SAMPEX. In Proceedings of the 25th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Durban, Vol. 2, 273–276.
Krimigis, S.M. (1992). Voyager energetic particle observations at interplanetary shocks and upstream of planetary bow shocks: 1977–1990. Space Science Reviews, 59, 167–201.
Krimigis, S.M., Armstrong, T.P., Axford, W.I., Bostrom C.O., Fan, C.Y., Gloeckler, G. and Lanzerotti, L.J. (1977). The low energy charged particle (LECP) experiment on the Voyager spacecraft. Space Science Reviews, 21, 329–354.
Krimigis, S.M., Decker, R.B., Hamilton, D.C. and Gloeckler, G. (2000). Observations of pick-up ions in the outer heliosphere by Voyagers 1 and 2. In R.A. Mewaldt, J.R. Jokipii, M.A. Lee, E. Möbius, and T.H. Zurbuchen (eds), Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles observed in the Heliosphere, ACE-2000 Symposium, AIP Conference Proceedings, 528, 333–340.
Kunow, H., Lee, M.A., Fisk, L.A., Forsyth, R.J., Heber, B., Horbury, T.S., Keppler, E., Kóta, J., Lou, Y.Q., McKibben, R.B., Paizis, C., Potgieter, M.S., Roelof, E.C., Sanderson, T.R., Simnett, G.M., von Steiger, R., Tsurutani, B.T., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F. and Jokipii, J.R. (1999). Corotating interaction regions at high latitudes. Space Science Reviews, 89, 221–268.
Lee, M.A. (1982). Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration upstream of the Earth’s bow shock. Journal of Geophysical Research, 87, 5063–5080.
Lee, M.A. (1983). Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at interplanetary traveling shocks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88, 6109–6119.
Lee, M.A. (1997). Particle acceleration and transport at CME-driven shocks. In N. Crooker, J.A. Jocelyn and J. Feynman (eds), Coronal Mass Ejections. AGU Press, pp. 227–234.
Lee, M.A., Shapiro, V.D. and Sagdeev, R.Z. (1996). Pickup ion energization by shock surfing. Journal of Geophysical Research, 101, 4777–4789.
Leske, R.A., Mewaldt, R.A., Christian, E.R., Cohen, C.M.S., Cummings, A.C., Stone, E.C., von Rosenvinge, T.T. and Wiedenbeck, M.E. (1999b). Measurement of the isotopic composition of anomalous cosmic ray N, O, and Ne from ACE. In Proceedings of the 26th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Utah, Vol. 7, pp. 539–542.
Leske, R.A., Mewaldt, R.A., Cohen, C.M.S., Cummings, A.C., Stone, E.C., Wiedenbeck, M.E., Christian, E.R. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1999a). Event-to-event variations in the isotopic composition of neon in solar energetic particle events. Geophysical Research Letters, 26, 2693–2696.
Lin, R.P. (1970). The emission and propagation of ~40keV solar flare electrons. Solar Physics, 12, 266–303.
Lopate, C. and McKibben, R.B. (1991). The ratio 2H/1H as a test for the presence of anomalous protons at Pioneer-10 near solar minimum in 1987. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Cosmic Ray Conference, Dublin, Vol. 3, pp. 390–393.
Luhn, A., Klecker, B., Hovestadt, D., Gloeckler, G., Ipavich, F.M., Scholer, M., Fan, C.Y. and Fisk, L.A. (1984). Ionic charge states of N, Ne, Mg, Si and in solar energetic particle events. Advances in Space Research, 4(2-3), 161–164.
Luhn, A., Klecker, B., Hovestadt, D., and Möbius, E. (1987). The mean ionic charge of silicon in 3He-rich solar flares. Astrophysical Journal, 317, 951–955.
Mason, G., Gold, R.E., Krimigis, S.M., Mazur, J.E., Andrews, G.B., Daley, K.A., Dwyer, J.R., Heuerman, K.F., James, T.L., Kennedy, M.J., Lefevere, T., Malcom, H., Tossman, B. and Walpole, P.H. (1998). The ultra-low-energy isotope spectrometer (ULEIS) for the ACE spacecraft. Space Science Reviews, 86, 409–448.
Mason, G.M., Gloeckler, G. and Hovestadt, D. (1984). Temporal variations of nucleonic abundances in solar flare energetic particle events: II.Evidence for large-scale shock acceleration. Astrophysical Journal, 280, 902–916.
Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E. and Dwyer, J.R. (1999). 3He enhancements in large solar energetic particle events. Astrophysical Journal, 525, L133–L136.
Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., Dwyer, J.R., Reames, D.V. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1997). New spectral and abundance features of interplanetary heavy ions in corotating interaction regions. Astrophysical Journal, 486, L149–L152.
Mazur, J.E., Mason, G.M., Klecker, B. and McGuire, R.E. (1992). The energy spectra of solar flare hydrogen, helium, oxygen, and iron: evidence for stochastic acceleration. Astrophysical Journal, 401, 398–410.
Mazur, J.E., Mason, G.M., Lopper, M.D., Leske, R.A. and Mewaldt, R.A. (1999). Charge state of solar energetic particles using the geomagnetic cutoff technique: SAMPEX measurements in the 6 November 1997 solar particle event. Geophysical Research Letters, 26, 173–176.
McDonald, F.B., Lukasiak, A. and Webber, W.R. (1995). Pioneer 10 and Voyager 1 observations of anomalous cosmic-ray hydrogen in the outer heliosphere. Astrophysical Journal, 446, L101–L104.
McDonald, F.B., Teegarden, B.J., Trainor, J.H., von Rosenvinge, T.T. and Webber, W.R. (1976). The interplanetary acceleration of energetic nucleons. Astrophysical Journal, 203, L149–L154.
McDonald, F.B., Teegarden, B.J., Trainor, J.H. and Webber, W.R. (1974). The anomalous abundance of cosmic-ray nitrogen and oxygen nuclei at low energies. Astrophysical Journal, 187, L105–L108.
McKibben, R.B. (1977). An experimental test for the charge state of the anomalous helium component. Astrophysical Journal, 217, L113–L116.
Meyer, P., Parker, E.N. and Simpson, J.A. (1956). Solar cosmic rays of February, 1956 and their propagation through interplanetary space. Physical Review, 104, 768–783.
Mewaldt, R.A. (1999). Solar and interplanetary particles re-accelerated at the solar wind termination shock. Advances in Space Research, 23(3), 541–545.
Mewaldt, R.A. (2000). New views of solar energetic particles from the Advanced Composition Explorer. In B.L. Dingus, D.B. Kieda and M.H. Salamon (eds), 26th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Invited, Rapporteur and Highlight Papers, AIP Conference Proceedings, 516, 265–273.
Mewaldt, R.A., Cummings, J.R., Leske, R.A., Selesnick, R.S., Stone, E.C. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1996). A study of the composition and energy spectra of anomalous cosmic rays using the geomagnetic field. Geophysical Research Letters, 23, 617–620.
Miller, J.A. (1995). Much ado nothing. EOS, 76, 401–407.
Miller, J.A., Cargill, P.J., Emslie, A.G., Holman, G.D., Dennis, B.R., LaRosa, T.H., Winglee, R.M., Benka, S.G. and Tsuneta, S. (1997). Critical issues for understanding particle acceleration in impulsive solar flares. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 14,631-14,659.
Möbius, E., Hovestadt, D., Klecker, B., Scholer, M., Gloeckler, G. and Ipavich, F.M. (1985). Direct Observation of He+ pick-up ions of interstellar origin in the solar wind. Nature, 318, 426–429.
Möbius, E., Popecki, M., Klecker, B., Kistler, L.M., Bogdanov, A., Galvin, A.B., Heirtzler, D., Hovestadt, D., Lund, E.J., Morris, D. and Schmidt, W.K.H. (1999). Energy dependence of the ionic charge state distribution during the November 1997 solar energetic particle event. Geophysical Research Letters, 26, 145–148.
Mogro-Campero, A. and Simpson, J.A. (1972). The abundances of solar accelerated nuclei from carbon to iron. Astrophysical Journal, 177, L37–L41.
Murphy, R.J., Ramaty, R., Kozlovsky, B. and Reames, D.V. (1991). Solar abundances from gamma-ray spectroscopy: Comparisons with energetic particle, photospheric, and coronal abundances. Astrophysical Journal, 371, 793–803.
Ng, C.K., Reames D.V. and Tylka A.J. (1999). Effect of proton-amplified waves on the evolution of solar energetic particle composition in gradual events. Geophysical Research Letters, 26, 2145–2148.
Oschlies, K., Beaujean, R. and Enge, W. (1989). On the charge state of anomalous oxygen. Astrophysical Journal, 345, 776–781.
Pallavicini, R., Serio, S. and Vaiana, G.S. (1977). A survey of soft x-ray limb flare images: The relation between their structure in the corona and other physical parameters. Astrophysical Journal, 216, 108–122.
Palmer, I.D. and Gosling, J.T. (1978). Shock associated energetic proton events at large heliocentric distances. Journal of Geophysical Research, 83, 2037–2046.
Paschmann, G., Sckopke, N., Papamastorakis, I., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J. and Gosling, J.T. (1981). Characteristics of reflected and diffuse ions upstream from the Earth’s bow shock. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 4355–4364.
Pesses, M.E., Decker, R.B. and Armstrong, T.P. (1982). The acceleration of charged particles in interplanetary space. Space Science Reviews, 32, 185–204.
Pesses, M.E., Jokipii, J.R. and Eichler, D. (1981). Cosmic ray drift, shock wave acceleration, and the anomalous component of cosmic rays. Astrophysical Journal, 246, L85–L88.
Popecki, M.A., Möbius, E., Klecker, B., Kistler, L.M., Galvin, A.B., Heirtzler, D., Morris, D., Siren, C., Bogdanov, A. and Hovestadt, D. (1999). Time profiles of ionic charge states for rapidly rising solar active periods. In Proceedings of the 26th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Utah, Vol. 6, 187–190.
Price, P.B., Fleischer, R.L., Peterson, D.D., O’Ceallaigh, C., O’Sullivan, D. and Thompson, A. (1967). Identification of isotopes of energetic particles with dielectric track detectors. Physical Review, 164, 1618–1620.
Pyle, K.R., Simpson, J.A., Barnes, A. and Mihalov, J.D. (1984). Shock acceleration of nuclei and electrons in the heliosphere beyond 24 AU. Astrophysical Journal, 282, L107–L111.
Rao, U.R., McCracken, K.G. and Bukata, R.P. (1967). Cosmic ray propagation processes: 2. The energetic particle event. Journal of Geophysical Research, 72, 4325–4341.
Reames, D.V. (1988). Bimodal abundances in the energetic particles of solar and interplanetary origin. Astrophysical Journal, 330, L71–L75.
Reames, D.V. (1995). Solar energetic particles: a paradigm shift. Review of Geophysics Suppl., 33, 585–589.
Reames, D.V. (1999). Particle acceleration at the sun and in the heliosphere. Space Science Reviews, 90, 413–491.
Reames, D.V., Barbier, L.M. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1997b). Wind, EPACT observations of anomalous cosmic rays. Advances in Space Research, 19(5), 809–812.
Reames, D.V., Kahler, S.W. and Ng, C.K. (1997a). Spatial and temporal invariance in the spectra of energetic particles in gradual solar events. Astrophysical Journal, 491, 414–420.
Reames, D.V., Meyer, J.P. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1994). Energetic-particles abundances in impulsive solar flare events. Astrophysical Journal Suppl., 90, 649–667.
Reames, D.V., von Rosenvinge, T.T. and Lin, R.P. (1985). Solar 3He-rich event and nonrelativistic electron events: A new association. Astrophysical Journal, 292, 716–724.
Reid, G.C. (1964). A diffusive model for the initial phase of a solar proton event. Journal of Geophysical Research, 69, 2659–2667.
Reinecke, J.P.L. and Moraal, H. (1992). On the form of the 1987 hydrogen spectrum in the outer heliosphere. Astrophysical Journal, 392, 272–276.
Roelof, E.C. and Krimigis, S.M. (1973). Analysis and synthesis of coronal and interplanetary energetic particle, plasma, and magnetic field observations over three solar rotations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 78, 5375–5410.
Russell, C.T., Mewaldt, R.A. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (eds) (1998). The Advanced Composition Explorer mission. Space Science Reviews, 86, 1–4.
Sanderson, T.R., Reinhard, R. Van Nes, P. and Wenzel, K.P. (1985a). Observations of three-dimensional anisotropies of 35-to 1000-keV protons associated with interplanetary shocks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 90, 19–27.
Sanderson, T.R., Reinhard, R. Van Nes, P. and Wenzel, K.P. (1985b). Observations of 35-to 1600-keV protons and low-frequency waves upstream of interplanetary shocks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 90, 3973–3980.
Sanderson, T.R., Reinhard, R. and Wenzel, K.P. (1981). The propagation of upstream protons between the earth’s bow shock and ISEE 3. Journal of Geophysical Research, 86, 4425–4434.
Sarris, E.T., Krimigis, S.M. and Armstrong, T.P. (1976). Observations of high energy protons and electrons at ~35RE with IMP 7. Journal of Geophysical Research, 81, 2341–2355.
Scholer, M. and Burgess, D. (1992). The role of upstream waves in supercritical quasi-parallel shock re-formation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97, 8319–8326.
Scholer, M. Ipavich, F.M. Gloeckler, G. and Hovestadt, D (1983). Acceleration of low-energy protons and alpha particles at interplanetary shock waves. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88, 1977–1988.
Scholer, M. and Morfill, G. (1975). Simulation of solar flare particle interaction with interplanetary shock waves. Solar Physics, 45, 227–240.
Schwadron, N.A., Fisk, L.A. and Gloeckler, G. (1996). Statistical acceleration of interstellar pick-up ions in co-rotating interaction regions. Geophysical Research Letters, 23, 2871–2874.
Schwadron, N.A., Geiss, J., Fisk, L.A., Gloeckler, G., Zurbuchen, T.H. and von Steiger, R. (2000). Inner source distributions: Theoretical interpretation, implications, and evidence for inner source protons. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 7465–7472.
Selesnick, R.S., Mewaldt, R.A. and Cummings, J.R. (1997). Multiply charged anomalous cosmic rays above 15MeV/nucleon. In Proceedings of the 25th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Durban, Vol. 2, pp. 269–272.
Sheeley Jr, N.R., Howard, R.A., Koomen, M.J., Michels, D.J., Schwenn, R., Mühlhäuser, K.H. and Rosenbauer, H. (1985). Coronal mass ejections and interplanetary shocks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 90, 163–175.
Simnett, G.M. (1995). Protons in flares. Space Science Reviews, 73, 387–432.
Smith, E.J. (1993). Magnetic fields throughout the heliosphere. Advances in Space Research, 13(6), 5–14.
Smith, E.J. and Wolfe, J.H. (1976). Observations of interaction regions and corotating shocks between one and five AU: Pioneer 10 and 11. Geophysical Research Letters, 3, 137–140.
Sonett, C.P., Colburn, D.S., Davis, L., Smith, E.J. and Coleman, Jr, P.J. (1964). Evidence for a collisionfree magnetohydrodynamic shock wave in interplanetary space. Physical Review Letters, 13, 153–156.
Steenberg, C.D., Cummings, A.C. and Stone, E.C. (1999). Drift calculations on the calculations of anomalous cosmic rays during the 1998 solar minimum period. In Proceedings of the 26th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Utah, Vol. 7, pp. 593–596.
Stone, E.C., Cohen, C.M.S., Cook, W.R., Cummings, A.C., Gauld, B., Kecman, B., Leske, R.A., Mewaldt, R.A., Thayer, M.R., Dougherty, B.L., Grumm, R.L., Milliken, B.D., Radocinski, R.G., Wiedenbeck, M.E., Christian, E.R., Shuman, S. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1998). The solar isotope spectrometer for the Advanced Composition Explorer. Space Science Reviews, 86, 357–408.
Stone, E.C. and Cummings, A.C. (1997). Evidence for anomalous cosmic ray S, Si, and Fe in the outer heliosphere and for a non-ACR source of S at 1AU. In Proceedings of the 25th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Durban, Vol. 2, pp. 289–292.
Svestka, Z. and Fritzová-Svestková, L. (1974). Type II bursts and particle acceleration. Solar Physics, 36, 417–431.
Takashima, T., Doke, T., Hayashi, T., Kikuchi, J., Kobayashi, M., Shirai, H., Takehana, N., Ehara, M., Yamada, Y., Yanagita, S., Hasebe, N., Kashiwagi, T., Kato, C., Munakata, K., Kohno, T., Kondoh, K., Murakami, H., Nakamoto, A., Yanagimachi, T., Reames, D.V. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1997). The first observation of sulfur in anomalous cosmic rays by the Geotail and the Wind spacecraft. Astrophysical Journal, 477, L111–L113.
Teegarden, B.J., von Rosenvinge, T.T. and McDonald, F.B. (1973). Satellite measurements of the charge composition of solar cosmic rays in the 6≤Z≤26 interval. Astrophysical Journal, 180, 571–581.
Temerin, M. and Roth, I. (1992). The production of 3He and heavy ion enrichments in 3He-rich flares by electromagnetic hydrogen cyclotron waves. Astrophysical Journal, 391, L105–L108.
Toptyghin, I.N. (1980). Acceleration of particles by shocks in a cosmic plasma. Space Science Reviews, 26, 157–213.
Tums, E., Gloeckler, G., Fan, C.Y., Cain, J. and Sciambi, R. (1974). Instrument to measure energy and charge of low energy interplanetary particles. IEEE Transactions in Nuclear Science., NS-21(1), 210–217.
Van Hollebeke, M.A.I., McDonald, F.B., Trainor, J.H. and von Rosenvinge, T.T. (1978). The radial variation of corotating energetic streams in the inner and outer solar system. Journal of Geophysical Research, 83, 4723–4730.
Van Nes, P., Reinhard, R., Sanderson, T.R., Wenzel, K.P. and Zwickl, J. (1984). The energy spectrum of 35-to 1600-keV protons associated with interplanetary shocks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89, 2122–2132.
Vasyliunas, V.M. and Siscoe, G.L. (1976). On the flux and the energy spectrum of interstellar ions in the solar system. Journal of Geophysical Research, 81, 1247–1252.
Vernov, S.N., Chudakov, A.E., Vakulov, P.V., Gorchakov, E.V., Kontor, N.N., Logatchev, Y.I., Lyubimov, G.P., Pereslegina N.V. and Timofeev, G.A. (1970). Propagation of solar and galactic cosmic rays of low energies in interplanetary medium. In V. Manno and D.E. Page (eds), Intercorrelated Satellite Observations Related to Solar Events, Reidel, Hingham, MA, pp. 53–89.
Von Rosenvinge, T.T., Barbier, L.M., Karsh, J., Liberman, R., Madden, M.P., Nolan, T., Reames, D.V., Ryan, L., Singh, S., Trexel, H. and Winkert, G. (1995). The Energetic Particles: Acceleration, Composition and Transport (EPACT) investigation on the Wind spacecraft. Space Science Reviews, 71, 155–206.
Von Rosenvinge T.T. and McDonald, F.B. (1975). IMP 6, 7, and 8 observations of the composition and time variations of low energy cosmic rays. In Proceedings of the 14th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Munich, Vol. 2, pp. 792–797.
Von Steiger, R., Schwadron, N.A., Fisk, L.A., Geiss, J., Gloeckler, G., Hefti, S., Wilken, B., Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F. and Zurbuchen, T.H. (2000). Composition of quasi-stationary solar wind flows from SWICS/Ulysses. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 27,217–27,238.
Wenzel, K.P., Marsden, R.G., Page, D.E. and Smith, E.J. (eds) (1992). Ulysses instruments. Astronomy and Astrophysics, Suppl., 92, 207–440.
Wild, J.P., Smerd, S.F. and Weiss, A.A. (1963). Solar bursts. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1, 291–366.
Williams, D.J., McEntire, R.W., Krimigis, S.M., Roelof, E.C., Jaskulek, S., Tossman, B., Wilken, B., Stüdemann, W., Armstrong, T.P., Fritz, T.A., Lanzerotti, L.J. and Roederer, J.G. (1991). Energetic particles at Venus: Galileo results. Science, 253, 1525–1528.
Witte, M., Rosenbauer, H., Banaszkiewicz, M. and Fahr, H. (1993). The Ulysses neutral gas experiment: Determination of the velocity and temperature of the interstellar neutral helium. Advances in Space Research, 13(6), 121–130.
Zirin, H. (1994). Solar storminess. Sky & Telescope, November, p. 9.
Further Reading
Balogh, A., Gosling, J.T., Jokipii, J.R., Kallenbach, R. and Kunow, H.(eds) (1999). Corotating interaction regions. Space Science Reviews, 89 (1-2).
Mewaldt, R.A., Jokipii, J.R., Lee, M.A., Möbius, E. and Zurbuchen, T.H. (eds) (2000). Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles observed in the Heliosphere, ACE-2000 Symposium. AIP Conference Proceedings, 528.
Simpson, J.A. (1995). The anomalous nuclear component in the three-dimensional heliosphere. Advances in Space Research, 16(9), 135–149.
Zank, G.P. and Gaisser, T.R. (eds) (1992). Particle Acceleration in Cosmic Plasmas. AIP Conference Proceedings, 264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gloeckler, G., Wenzel, KP. (2001). Acceleration processes of heliospheric particle populations. In: Bleeker, J.A.M., Geiss, J., Huber, M.C.E. (eds) The Century of Space Science. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0320-9_42
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0320-9_42
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-0-7923-7196-0
Online ISBN: 978-94-010-0320-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive