Abstract
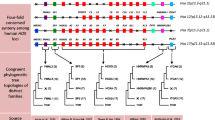
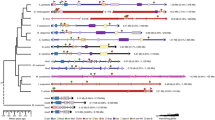
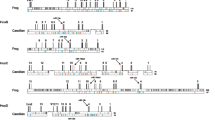
The non-coding intergenic regions of Hox genes are remarkably conserved among mammals. To determine the usefulness of this sequence for phylogenetic comparisons, we sequenced an 800-bp fragment of the Hoxc9-Hoxc8 intergenic region from several species belonging to different mammalian clades. Results obtained from the phylogenetic analysis are congruent with currently accepted mammalian phylogeny. Additionally, we found a TC mini satellite repeat polymorphism unique to felines. This polymorphism may serve as a useful marker to differentiate between mammalian species or as a genetic marker in feline matings. This study demonstrates usefulness of a comparative approach employing non-coding regions of Hox gene complexes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnason, U. and Gullberg, A. (1994) Relationship of baleen whales established by cytochrome b gene sequence comparison. Nature, 367, 726–728.
Arnason, U. and Gullberg, A. (1996) Cytochrome b nucleotide sequences and the identification of five primary lineages of extant cetaceans. Mol. Biol. Evol., 13, 407–417.
Belting, H.G., Shashikant, CS. and Ruddle, F.H. (1998) Multiple phases of expression and regulaiton of mouse Hoxc8 during early embryogenesis. J. Exp. Zool, 282, 196–222.
De Jong, W.W. (1998) Molecules remodel the mammalian tree. Trends Ecol. Evol., 13, 270–275.
Felsenstein, J. (1995) PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package). Version 3.5c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle.
Janke, A. and Arnason, U. (1997) The complete mitochondrial genome of Alligator mississippiensis and separation between recent archosauria (birds and crocodiles). Mol. Biol. Evol. 14, 1266–1272.
Janke, A., Xu, X. and Arnason, U. (1997) The complete mitochondrial genome of the wallaroo (Macropus robustus) and the phy-logenetic relationship among Monotremata, Marsupialia, and Eutheria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 1276–1281.
Jukes, T.H. and Cantor, CR. (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In Mammalian Protein Metabolism (Ed. H.N. Munro), Academic Press, New York, pp. 21–132.
Margarit, E., Gullen, A., Rebordosa, C, Vidal-Taboada, J., Sanchez, M., Ballesta, F. and Oliva, R. (1998) Identification of conserved potentially regulatory sequences of the SRY gene from 10 different species of mammals. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 245, 370–377.
Messenger, S.L. and McGuire, J.A. (1998) Morphological molecules, and phylogenetics of cetaceans. Syst. Biol., 47, 90–124.
Ohland, D.P., Harley, E.H. and Best, P.B. (1995) Systematics of cetaceans using restriction site mapping of mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol., 4, 10–19.
Olsen, G.J., Matsuda, H., Hagstrom, R. and Overbeek, R. (1994) FastDNAml: a tool for construction og phylogenetic trees of DNA sequences using maximum-likelihood. Comput. Appl. Biosci., 10, 41–48.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol., 4, 406–425
Shashikant, C.S. and Ruddle, F.H. (1996) Combinations of closely situated cis-acting elements determine tissue-specific patterns and anterior extent of early Hoxc8 expression. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 12364–12369.
Shashikant, CS., Bieberich, C.J., Belting, H.G., Wang, J.C., Bor-bely, M.A. and Ruddle, F.H. (1995) Regulation of Hoxc-8 during mouse embryonic development: identification and characterization of critical eleements involved in early neural tube expression. Development, 121, 4339–4347.
Shashikant, C.S., Kim, C.B., Borbely, M.A., Wang, W.C.H. and Ruddle, F.H. (1998) Comparative studies on mammalian Hoxc8 early enhancer sequence reveal a baleen whale-specific deletion of a cis-acting element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 15446–15451.
Shimamura, M., Yasue, H., Ohshima, K., Abe, H., Kato, H., Kish-iro, T., Goto, M., Munechika, I. and Okada, N. (1997) Molecular evidence from retroposons that whales form a clade within even-toed ungulates. Nature, 388, 666–670.
Spek, CA., Bertina, R.M. and Reitsma, P.H. (1998) Identification of evolutionarily invariant sequences in the protein C gene promoter. J. Mol. Evol., 47, 663–669.
Springer, M.S., Cleven, G.C., Madsen, O., De Jong, W.W., Wad-dell, V.G., Amrine, H.M. and Stanhope, M.J. (1997). Endemic African mammals shake the phylogenetic tree. Nature, 388, 61–64.
Sumiyama, K., Kim, C.B. and Ruddle, F.H. (2001) An efficient cis-element discovery method using multiple sequence comparisons based on evolutionary relationships. Genomics, 71, 260–262.
Swofford, D.L. (1998) PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (* and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F. and Higgins, D.G. (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res., 25, 4876–4882.
Yamamoto, H., Kudo, T., Masuko, N., Miura, H., Sato, S., Tanaka, M., Tanaka, S., Takeuchi, S., Shibahara, S. and Takeuchi, T. (1992) Phylogeny of regulatory regions of vertebrate tyrosinase genes. Pigment Cell Res., 5, 284–294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kim, CB., Shashikant, C.S., Sumiyama, K., Wang, W.C.H., Amemiya, C.T., Ruddle, F.H. (2003). Phylogenetic analysis of the mammalian Hoxc8 non-coding region. In: Meyer, A., Van de Peer, Y. (eds) Genome Evolution. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0263-9_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-010-0263-9_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-3957-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-010-0263-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive