Summary
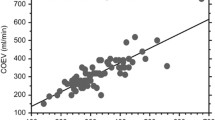
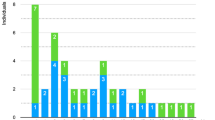
Using a reliable non-invasive technique for ICP monitoring, we realized 93 continuous anterior fontanelle pressure (AFP) recordings in 86 healthy infants aged from 29 to 85 post-conceptional (PC) weeks. For each recording, we calculated the mean and extremes values of AFP, cerebral pulse amplitude, and pressure waves rate and amplitude. We observed the occurrence of plateau-waves of relatively low amplitude and duration in most infants aged of more than 49 PC weeks. We postulate that PW represents a physiological phenomenon which is amplified under pathological conditions. All AFP parameters are correlated to PC age and vary during early infancy according to an ascending sigmoidal relation (this variation may be explained by a connection between several cranio-cerebral characteristics of the young infant). We conclude that the interpretation of AFP recordings must take into account [1] PC age rather than postnatal age, [2] variation of AFP parameters with age, and [3] occurrence of physiological plateau-waves.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Jong DA, Maas A, van de Voort E (1984) Non-invasive intracranial pressure monitoring. A technique for reproducible fontanelle pressure measurements. Z Kinderchir 39: 274–276
Di Rocco C, Mc Lone DG, Shimoji T, Raimondi AJ (1975) Continuous intraventricular cerebrospinal fluid pressure recording in hydrocephalic children during wakefulness and sleep. J Neurosurg 42: 683–689
Griicer G, Viernstein LJ (1979) Intracranial pressure in the normal monkey while awake and asleep. J Neurosurg 51: 206–210
Ishii H, Handa Y, Kobayashi H, Kawano H, Nogushi Y, Hayashi M (1989) Role of the medullary vasomotor centre in development of plateau waves. Neurol Res 11: 186–190
Lundberg N (1960) Continuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand 36 [Suppl 149]: 7–193
Marmarou A, Shulman K, LaMorgese J (1975) Compartmental analysis of compliance and outflow resistance of the cerebrospinal fluid system. J Neurosurg 43: 523–534
Minns RA (1991) Infectious and parainfectious encephalopathies. In: Minns RA (ed) Problems of intracranial pressure in childhood. Mc Keith, London, pp 170–282
Mises J, Gabersek V, Lacombe J, Hirsch JF, Pierre-Kahn A, Zouaoui A, Barrivault L, N’Geh R (1979) Polygraphie du sommeil avec enregistrement de la pression intracrânienne et mesure du volume sanguin cérébral chez le nourrisson hydrocéphale. Rev EEG Neurophysiol 9: 228–235
Paraicz E (1978) A-waves in infantile and children’s hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Sci 22: 169–171
Philip AGS, Long JG, Donn SM (1981) Intracranial pressure. Sequential measurements in full-term and preterm infants. Am J Dis Child 135: 521–524
Raftopoulos C, Chaskis C, Delecluse F, Cantraine F, Bidaut L, Brotchi J (1992) Morphological quantitative analysis of intracranial pressure waves in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurol Res 14: 389–395
Renier D, Sainte-Rose C, Marchac D, Hirsch JF (1982) Intracranial pressure in craniostenosis. J Neurosurg 57: 370–377
Rosner MJ, Becker DP (1984) Origin and evolution of plateau waves. Experimental observations and a theoretical model. J Neurosurg 60: 312–324
Wayenberg JL, Raftopoulos C, Vermeylen D, Pardou A (1993) Non invasive ICP monitoring in neonates and infants: the Rotterdam Teletransducer. Arch Dis Child 69: 493–497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer-Verlag Wien
About this paper
Cite this paper
Massager, N., Wayenberg, JL., Vermeylen, D., Brotchi, J. (1998). Anterior Fontanelle Pressure Recording with the Rotterdam Transducer: Variation of Normal Parameters with Age. In: Marmarou, A., et al. Intracranial Pressure and Neuromonitoring in Brain Injury. Acta Neurochirurgica Supplements, vol 71. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6475-4_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-6475-4_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Vienna
Print ISBN: 978-3-7091-7331-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-7091-6475-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive