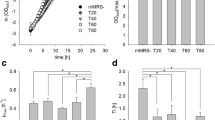
Abstract
E. coli K1060, a mutant defective in the synthesis and degradation of unsaturated fatty acids, was used to obtain membranes of different fatty acid composition without altering other growth parameters. The pressure resistance of the cells varied according to the different fatty acid supplement used in the growth medium. Cells grown on elaidic acid were the least pressure resistant in exponential phase and the most resistant in stationary phase. The fluidity of the membrane, as measured by differential scanning calorimetry of stationary-phase cell lipids, showed a secondary peak at high temperature (51.9 °C) for cells grown on elaidic acid. Cells with a more rigid membrane were more sensitive to pressure in exponential phase and more resistant in stationary phase confirming the results previously obtained with cells grown at different temperatures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shigehisa, T., Ohmori, T., Saito, A., Taji, S. and Hayashi, R. (1991) Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on characteristics of pork slurries and inactivation of microorganisms associated with meat and meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 12, 207–216.
Wouters, P.C., Galaasker, E. and Smelt, J.P.P.M. (1998) Effects of high pressure on inactivation kinetics and events related to proton efflux in Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 64, 509–514.
Casadei, M.A. and Mackey, B.M.M. (1997). The effect of growth temperature on pressure resistance of Escherichia coli. High Pressure Research in the Biosciences and Biotechnology, K. Heremans (Ed.) 281. Leuven, Belgium: Leuven University Press.
Miller, L. and Berger, T. (1985) Bacteria identification by gas chromatography of whole cell fatty acids. Hewlett Packard Gas Chromatography pub. no.43–5953–1838, 1–8.
Bligh, E.G. and Dyer, W.J. (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37, 911–917.
Overath, P., Schairer, H.U. and Stoffel, W. (1970) Correlation of in vivo and in vitro phase transitions of membrane lipids in Escherichia coli. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 67, 606–612.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Casadei, M.A., Mackey, B.M. (1999). Use of a Fatty Acid Auxotroph To Study the Role of Membrane Fatty Acid Composition on the Pressure Resistance of Escherichia coli . In: Ludwig, H. (eds) Advances in High Pressure Bioscience and Biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60196-5_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-60196-5_11
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-64300-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-60196-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive