Abstract
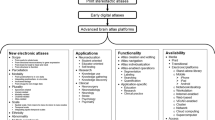
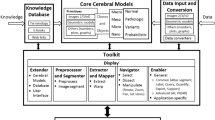
This chapter addresses the construction, features, applications, and potential of electronic brain atlases for neuroradiology and neuroeducation. An electronic brain atlas database with complementary atlases containing gross anatomy, subcortical structures, brain connections, and sulcal patterns was constructed. This database contains two-dimensional and three-dimensional, mutually coregistered atlases with about 1000 structures and 400 sulcal patterns.
Six commercial applications have been developed and described here based on this database suitable for neuroradiology, neuroeducation, human brain mapping, and stereotactic functional neurosurgery. Three applications are low-cost CD-ROMs: The Electronic Clinical Brain Atlas, Brain Atlas for Functional Imaging, and the Cerefy Student Brain Atlas. The Cerefy Neuroradiology Atlas is a web-enabled application.
The use of the electronic brain atlas as a tool for faster scan interpretation, facilitating communicating information, increasing confidence, and speeding up learning is illustrated. The atlas: (1) reduces time in image interpretation by providing interactive multiple labeling, triplanar display, higher panellation than the scan itself, multi-modal fusion, and display of underlying anatomy for functional images; (2) facilitates the communication of information about the interpreted scans from the neuroradiologist to other clinicians and medical students; (3) increases the neuroradiologist’s confidence; and (4) reduces time in learning neuroanatomy and scan interpretation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADAM (1994) A.D.A.M. Animated dissection of anatomy for medicine. User’s guide, ADAM Software.
Afshar E, Watkins ES, Yap JC (1978) Stereotactic atlas of the human brainstem and cerebellar nuclei. Raven Press, New York.
Andrew J, Watkins ES (1969) A stereotaxic atlas of the human thalamus and adjacent structures: a variability study. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Bohm C, Greitz T, Eriksson L (1983) A computerized adjustable brain atlas. Eur J Nucl Med 15:687–689.
DeArmond SJ, Fusco MM, Dewey MM (1989) Structure of the human brain: a photographic atlas, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York.
Dev P, Coppa GP, Tancred E (1992) BrainStorm: designing an interactive neuroanatomy atlas. Radiology 185:413.
Duvernoy HM (1988) The human hippocampus: an atlas of applied anatomy. Bergman, Munich.
Evans AC, Collins DL, Milner B (1992) An MRI-based stereotactic brain atlas from 300 young normal subjects. Proceedings of the 22nd symposium of the Society for Neuroscience, Anaheim, pp 407–408.
Fix JD (1987) Atlas of the human brain and spinal cord. Aspen, Rockville.
Greitz T, Bohm C, Holte S (1991) A computerized brain atlas: construction, anatomical content, and some applications. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:26–38.
Hardy TL, Deming LR, Harris-Collazo R (1999) Computerized stereotactic atlases. In: Alexander E III, Maciunas RJ (eds) Advanced neurosurgical navigation. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 115–124.
Hassler R (1959) Anatomy of the thalamus. In: Schaltenbrand G, Bailey W (eds) Introduction to stereotaxis with an atlas of the human brain. Thieme, Stuttgart.
Hohne KH (1995) Voxel-Man. I. Brain and skull. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Hohne KH, Bomans M, Riemer M (1992) A 3D anatomical atlas based on a volume model. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 12:72–78.
Kall BA (1992) Computer-assisted stereotactic functional neurosurgery. In: Kelly PJ, Kali BA (eds) Computers in stereotactic neurosurgery. Blackwell, Boston, pp 134–142.
Kazarnovskaya MI, Borodkin SM, Shabalov VA (1991) 3-D computer model of subcortical structures of human brain. Comput Biol Med 21:451–457.
Kikinis R, Shenton ME, Iosifescu DV (1996) A digital brain atlas for surgical planning, model-driven segmentation, and teaching. IEEE Trans Visualization Comput Graph 2:232–241.
Kraus GE, Bailey GJ (1994) Microsurgical anatomy of the brain: a stereo atlas. Wiliams and Wilkins, Baltimore.
Lehmann ED, Hawkes D, Hill D (1991) Computer-aided inter pretation of SPECT images of the brain using an MRI-derived neuroanatomic atlas. Med Inform 16:151–166.
Martin J (1989) Neuroanatomy. Text and atlas. Appleton and Lange, Norwalk.
Mazziotta JC, Toga AW, Evans AC (1995) A probabilistic atlas of the human brain: theory and rationale for its development. Neuroimage 2:89–101.
McMinn RMH, Hutchings RT, Pegington J (1993) Color atlas of human anatomy, 3rd edn. Mosby Year Book, St Louis.
Netter FH (1991) The CIBA collection of medical illustrations, vol 1. Nervous system. CIBA, New Jersey.
Niemann K, Naujokat C, Pohl G, Wollner C, von Keyserlingk D (1994) Verification of the Schaltenbrand and Wahren stereotactic atlas. Acta Neurochir 129:72–81.
Niemann K, van den Boom R, Haeselbarth K (1999) A brainstem stereotactic atlas in a three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging navigation system: first experiences with atlas-to-patient registration. J Neurosurg 90:891–901.
Nieuwennhuys R, Voogd J, van Huijzen C (1981) The human central nervous system: a synopsis and atlas, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Nowinski WL (1998a) Anatomical targeting in functional neurosurgery by the simultaneous use of multiple Schalten-brand-Wahren brain atlas microseries. Stereotac Funct Neurosurg 71:103–116.
Nowinski WL (1998b) Brain atlas: geometrical models. Thieme, New York/KRDL, Singapore (BAGM specification is available from www.cerefy.com).
Nowinski WL (2001a) Computerized brain atlases for surgery of movement disorders. Semin Neurosurg 12:183–194.
Nowinski WL (2001b) Modified Talairach landmarks. Acta Neurochir 143:1045–1057.
Nowinski WL, Benabid AL (2002) New directions in atlas-assisted stereotactic functional neurosurgery. Advanced techniques in image-guided brain and spine surgery. Thieme, New York.
Nowinski WL, Thirunavuukarasuu A (1998) Electronic brain atlas library. Thieme, New York/KRDL, Singapore (EBAL specification is available from www.cerefv.com).
Nowinski WL, Thirunavuukarasuu A (2000) Methods and apparatus for processing medical images. Patent application PCT/SG00/00185.
Nowinski WL, Thirunavuukarasuu A (2001) Atlas-assisted localization analysis of functional images. Med Image Anal 5:207–220.
Nowinski WL, Bryan RN, Raghavan R (1997a) The electronic clinical brain atlas. Multiplanar navigation of the human brain. Thieme, New York, Stuttgart.
Nowinski WL, Fang A, Nguyen BT (1997b) Multiple brain atlas database and atlas-based neuroimaging system. Comput Aided Surg 2:42–66.
Nowinski WL, Thirunavuukarasuu A, Kennedy DN (2000a) Brain atlas for functional imaging. Clinical and research applications. Thieme, New York.
Nowinski WL, Yang GL, Yeo TT (2000b) Computer-aided stereotactic functional neurosurgery enhanced by the use of the multiple brain atlas database. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19:62–69.
Nowinski WL, Thirunavuukarasuu A, Srinivasan R (2000c) Brain atlas for neuroradiology. Radiology 217 (Suppl) 217:S620.
Nowinski WL, Thirunavuukarasuu A, Belov D (2001a) Web-based atlas for neuroradiology. Proceedings of the American Society of Neuroradiology 39th annual meeting, ASNR2001,23–27 April 2001, Boston, Mass, USA, p 500 (the atlas is available from www.cerefv.com).
Nowinski WL, Bryan RN, Thirunavuukarasuu A (2001b) Cerefy student brain atlas. KRDL, Singapore.
Ono M, Kubik S, Abernathey CD (1990) Atlas of the cerebral sulci. Thieme/Thieme Medical, Stuttgart.
Schaltenbrand G, Bailey W (1959) Introduction to stereotaxis with an atlas of the human brain. Thieme, Stuttgart.
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W (1977) Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. Thieme, Stuttgart.
Schiemann T, Freudenberg J, Pflesser B (2000) Exploring the visible human using the VOXEL-MAN framework. Comput Med Imaging Graph 24:127–132.
Schmahmann JD, Doyon J, McDonald D (1999) Three-dimensional MRI atlas of the human cerebellum in proportional stereotaxic space. Neuroimage 10:233–260.
Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR (1980) Imaging anatomy of the head and spine. A photographic color atlas of MRI, CT, gross, and microscopic anatomy in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes, 2nd edn. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore.
Sramka M, Ruzicky E, Novotny M (1997) Computerized brain atlas in functional neurosurgery. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 69:93–98.
Sundsten JW, Brinkley JF, Eno K (1994) The digital anatomist. Interactive brain atlas. CD-ROM for the Macintosh. University of Washington, Seattle.
Szikla G, Bouvier G, Hori T (1977) Angiography of the human brain cortex: atlas of vascular patterns and stereotactic localization. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotactic atlas of the human brain. Thieme, Stuttgart.
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1993) Referentially oriented cerebral MRI anatomy: atlas of stereotaxic anatomical correlations for gray and white matter. Thieme, Stuttgart.
Talairach J, David M, Tournoux P (1957) Atlas d’anatomie stereotaxique des noyaux gris centraux. Masson, Paris.
Thompson PM, Woods RP, Mega MS (2000) Mathematical/ computational challenges in creating deformable and probabilistic atlases of the human brain. Hum Brain Mapp 9:81–92.
Toga AW (1998) Brain warping. Academic Press, San Diego.
Toga AW, Ambach KL, Schluender S (1994) High-resolution anatomy from in situ human brain. Neuroimage 1:334–344.
Van Buren JM, Borke RC (1972) Variations and connections of the human thalamus. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Van Essen DC, Drury HA (1997) Structural and functional analyses of human cerebral cortex using a surface-based atlas. J Neurosci 17:7079–7102.
Van Essen DC, Drury HA, Hadjikhani N (2000) A probabilistic surface-based atlas of human visual cortex. Proceedings of the human 6th brain mapping meeting, HBM 2000, June, San Antonio, Texas, USA. Neuroimage 11:S533.
Yoshida M (1992) Three-dimensional maps by interpolation from the Schaltenbrand and Bailey atlas. In: Kelly PJ, Kail BA (eds) Computers in stereotactic neurosurgery. Black-well, Boston, pp 143–152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Nowinski, W.L. (2002). Electronic Brain Atlases: Features and Applications. In: Caramella, D., Bartolozzi, C. (eds) 3D Image Processing. Medical Radiology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59438-0_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59438-0_9
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-63977-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-59438-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive