Abstract
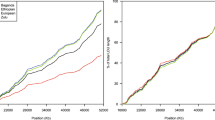
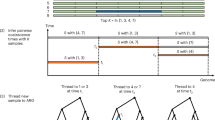
With the aim of developing a linkage disequilibrium (LD) SNP map to serve as a resource for candidate-gene, candidate-region and whole-genome association studies, we have genotyped >250,000 SNPs on 90 DNA samples (45 African-American, 45 Caucasian, unrelated) selected from the Coriell Human variation collection. The individual genotypes thus generated have enabled us to survey the patterns of LD and haplotype diversity across all gene regions of the human genome. Here I describe the empirical results of the first comparative study of the patterns of LD across three entire human autosomes: Chromosomes 6, 21, and 22. We selected for the study a total of 17,966 SNPs covering more than 209 Mb of chromosomal segments, and overlapping 2,266 predicted gene regions, with a minor allele frequency greater than 10% in either population, and that were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (p>0.01). Several methods to define ?haplotype blocks? were applied to this dataset, including several forms of the D? method and the 4-gamete rule. Haplotypes were then computationally inferred for the markers within each block by the EM algorithm to assess haplotype diversity. In addition, a subset of 277 SNPs spanning 4 Mb across the HLA region on chromosome 6 was genotyped on 550 DNA samples of unrelated individuals of European ancestry from north Germany, 93 samples from Norway, and 77 samples from UK. We analyze the robustness of the different haplotype block definitions, the differences between the population samples, and the effect of sample size on the generalization of haplotype blocks defined in one given population sample. Finally, I present the preliminary results of haplotype-based power calculations for case-control studies across the gene regions of these three chromosomes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
de la Vega, F. (2004). Patterns of Linkage Disequilibrium across Human Chromosomes 6, 21, AND 22. In: Istrail, S., Waterman, M., Clark, A. (eds) Computational Methods for SNPs and Haplotype Inference. RSNPsH 2002. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 2983. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24719-7_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-24719-7_30
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-21249-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-24719-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive