Abstract
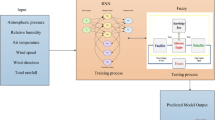
Forest fires that occurred in Portugal on June 18, 2017 caused several dozens of human casualties. The cause of their emergence, as well as many others that occurred in Western Europe at the same time, remained unknown. The heliocentric hypothesis has indirectly been tested, according to which charged particles are a possible cause of forest fires. We must point out that it was not possible to verify whether in this specific case the particles by reaching the ground and burning the plant mass create initial phase of the formation of flame. Therefore, we have tried to determine whether during the critical period, i.e. on June 15–19, there was a certain statistical connection between certain parameters of the solar wind (SW) and meteorological elements. Based on the hourly values of the charged particles flow, a correlation analysis was performed with hourly values of individual meteorological elements including time lag at Monte Real station. The application of the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems has shown that there is a high degree of connection between the flow of protons and the analyzed meteorological elements in Portugal. However, further verification of this hypothesis requires further laboratory testing.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/pub/lists/ace2/201706_ace_epam_1h.txt.
- 3.
ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/pub/lists/ace2/201706_ace_swepam_1h.txt.
References
Gomes, J.F.P., Radovanovic, M.: Solar activity as a possible cause of large forest fires a case study: analysis of the Portuguese forest fires. Sci. Total Environ. 394(1), 197–205 (2008)
Gomes, J.F.P., Radovanovic, M.: Solar Activity and Forest Fires, pp. 1–139. Nova Science Publishers, New York (2009). ISBN 978-1-60741-002-7
Hazewinkel, M.: Encyclopaedia of Mathematics: Monge - Ampère Equation - Rings and Algebras, 929 p. Springer, Dordrecht (2013). ISBN 978-0-7923-2976-3
Jang, J.-S.R.: ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(3), 665–685 (1993)
Milenković, M., Yamashkin, A.A., Ducić, V., Babić, V., Govedar, Z.: Forest fires in Portugal - the connection with the atlantic multidecadal oscillation (AMO). J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 67(1), 27–35 (2017)
Radovanović, M.: Forest fires in Europe from July 22nd to 25th 2009. Arch. Biolog. Sci. 62(2), 419–424 (2010)
Radovanović, M., Vyklyuk, Y., Jovanović, A., Vuković, D., Milenković, M., Stevančević, M., Matsiuk, N.: Examination of the correlations between forest fires and solar activity using Hurst index. J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 63(3), 23–32 (2013)
Radovanović, M.M., Vyklyuk, Y., Malinović Milićević, B.S., Jakovljević, M.D., Pecelj, R.M.: Modelling of forest fires time evolution in the USA on the basis of long term variations and dynamics of the temperature of the solar wind protons. Therm. Sci. 19(Suppl. 2), S437–S444 (2014)
Radovanović, M.M., Pavlović, T.M., Stanojević, G.B., Milanović, M.M., Pavlović, M.A., Radivojević, A.R.: The influence of solar activities an occurrence of the forest fires in south Europe. Therm. Sci. 19(2), 435–446 (2014)
Radovanović, M.M., Vyklyuk, Y., Milenković, M., Vuković, B.D., Matsiuk, N.: Application of ANFIS models for prediction of forest fires in the USA on the basis of solar activity. Therm. Sci. 19(5), 1649–1661 (2015)
Todorović, N., Vujović, D.: Effect of solar activity on the repetitiveness of some meteorological phenomena. Adv. Space Res. 54(11), 2430–2440 (2014)
Viegas, D.X.: A mathematical model for forest fires blowup. Combust. Sci. Technol. 177, 27–51 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Vyklyuk, Y., Radovanović, M.M., Pasichnyk, V., Kunanets, N., Petro, S. (2019). Forecasting of Forest Fires in Portugal Using Parallel Calculations and Machine Learning. In: Chertov, O., Mylovanov, T., Kondratenko, Y., Kacprzyk, J., Kreinovich, V., Stefanuk, V. (eds) Recent Developments in Data Science and Intelligent Analysis of Information. ICDSIAI 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 836. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97885-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-97885-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-97884-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-97885-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)