Abstract
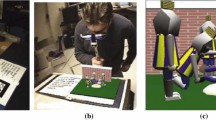
Augmented Reality (AR) has been recognized as one of the most promising technologies for the gaming industry. In this study, the designers intend to apply AR technology to developing an educational interactive game. This paper presents an AR featured educational game specifically designed for 4–6 years old pre-school children. The main objective of the game was to teach children knowledge about color mix, mathematics and 2D-3D geometrical shapes. This game allows user to interact with both in-screen and physical objects at same time, and different interaction forms like the touch screen (click) and AR game (rotate) for better interaction with real world and learning. This paper focuses in detail on the design and interactive behavior. Furthermore, beyond the needs of children, this game also serves for parents. Through the Token Economy method, parents can control kids’ playing time, and track and modify their everyday behavior.
Access provided by CONRICYT-eBooks. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Children learn from imitation and play before the age of seven, and games provide a fun way of learning serious ideas and important life skills [3]. According to studies, well designed digital educational games can play a significant role in early childhood education, being more efficient and effective than traditional toys [2, 4, 8], also enable ‘playful learning’ [1]. One of the challenges in recent child education is to enable them to think on an abstract level; such complex knowledge only can be transferred to children through unified/combined methods and manipulating tangible toys [6]. Under such context, augmented reality (AR) technology can significantly enhance early childhood education by providing exciting experiences of ‘playful’, as it can integrate virtual objects and additional information to real objects.
However, till recently, there are only limited successful cases to support 2D-3D geometrical shape, mathematic and color mix learning, since most of the existing ones are in-screen exercises or pure virtually interactive environments and objects. Also none of them focus on bridging theory and abstract concepts with real world feedbacks. In the design of this AR game, the following aspects have been specifically focused:
-
1.
Game design principles based on montessori education theory
-
2.
Physical object interaction with screen
-
3.
Learning and playing method
The following sections describe further details of this study: Sect. 2 illustrates research background information and design concept of the game. Section 3 describes technology and system structure. Section 4 organizes different interactive methods. Sections 5 and 6 detail discussion, future work and conclusions of this project.
2 Design Rationale
The aim of this augmented construction toy kit (AR BLOCK) is to base design on the Montessori education method, which considers that introducing children as young as four or five to mathematics can have long-lasting benefits. Montessori materials are designed to allow for auto-education and self-correction [5].
2.1 Integration of Tangibility and AR
Augmented Reality (AR) technology can enhance ‘playfulness’ and ‘abstract learnability’. In order to recognize the features of AR technology have been applied in children’s education, a series existing products have been analyzed. Table 1 presents the advantages and disadvantages of these products. NEOBEAR is a company that specializes in children education and technology. Most of their products use AR technology, such as Pocket Vehicles, Popup AR Paintings and Magnifier NEO. These products allow children to observe virtual 3D models through scanning different animals, vehicles or vocabulary cards. More importantly, NEOBEAR chooses soybean oil ink, which is a safe material for children. Disney Research also presents a texturing process, which uses AR technology. This product can track texture from 2D colored drawing and apply it on virtual 3D models in real time.
Comparing with existing products, AR BLOCK emphasizes on interactivity, playability and methods variations, which could enhance children’s experience when exploring the game. This no longer requires a common AR game with display card information but through manipulating tangible 3D objects.
In terms of the ideology of overall system, wide range interactive behaviors have been considered. How to transfer the plane graphics into abstract solid shape is the key of teaching geometrical shapes. Through researching the Montessori methods, we found that touching will be a good solution for bridging abstract concepts with physical objects. So our product will provide some tangible cards and blocks, which helps children observe differences between 2D and 3D shape through touching them. Furthermore, we want to discover a unique method to learn mathematic. And consider our product’s feature, we combine the math function with geometrical shape function. In terms of color mix function, our Color Blocks provide intuitionistic color mixing process. Touching two Color Blocks can become a new color.
2.2 Design of Tangible Components
The AR BLOCK game consists of tangible construction blocks/cards and intangible application for tablets. The tangible object component contains four main functions:
Through playing with distinctive blocks or cards, children can learn different concepts. For example, when children observe Foundation Cards, they can only see 2D geometrical shapes, but the screen will show the 3D geometrical shapes. These Foundation Cards can help children with 2D and 3D conversion ability. Children can learn mathematics from Number Blocks. Number Blocks have different shapes and numbers; if the Foundation Card shows a house frame with square and triangle shape and number 8, the user should choose a cube and a triangle Number Block. Then they calculate numbers on the cube block and triangle block, letting the result equal 8. Moreover, children can exercise their matching ability through comparing Building Cards with Foundation Cards. Same geometrical shape can complete the house. Lastly, each Color Block has three colors: yellow, red and blue. Children can rotate Color Blocks to change the house’s color and two Color Blocks color can mix to a new color.
At current product design process, timber was chosen to manufacture the tangible blocks for our original prototype. Timber comes from nature, and exposure to natural material is good for children. This material can be preserved for a long time, and is widely used in construction blocks toy market. Children are familiar with wooden toys. However, we also consider another material: silica gel, which is wildly used in medicine, toy business and other fields. Silica gel has many advantages, such as non-toxic, no pungent smell, chemical stability. In the future, we will continue to discover the differences between timber and silica gel. Considering the characteristics of AR BLOCK to finally choose a better solution. For the software, Vuforia-an open source AR platform was used to develop the AR features, also due to it’s cross-platform and game engines supporting features. Comparing with other open source platform, functions of Vuforia come closer to my requests, such as objects recognizing and tracking, user-defined images or frame markers, which are ideal for product and game creations.
As shown in Table 2, blocks and cards have different markers’ design. These markers will be printed on the timber, so it is very important to choose a safe printed material. Based on current research, we choose soybean oil ink. Soybean oil ink is an environment friendly material. It has many advantages, such as a more reasonable price than other materials, non-toxicity, recyclability, and is already widely used in children’s products. Because of the restrictions on the size of Vuforia markers (>30 mm), the size of cards is 55 mm square and blocks have different types, such as 55 mm cube and 55 mm triangle.
2.3 Design of Intangible Components
The intangible/in-screen component is designed for digital media devices, such as an iPad or Android tablet. AR BLOCK application has three modes:
-
1.
Parent Mode
-
2.
Kids’ Mode
-
3.
Family Mode
As well known, long period electronic equipment using brings negative impact to both children’s physical and mental health. Based on our user studies and demonstrating prototype to parents, the playing time issue has been raised by most of parents. It is important for parents to supervise their kids’ playing time. In Parent Mode, parents can choose different behavior medals and each medal has three stars. Bases on children’s everyday behavior, parents can provide stars for their kids; one star equals to five minutes playing time. Better behavior can earn longer playing time. This method is called the Token Economy, which is an excellent behavior modification tool. Through Parent Mode service, parents not only can control kids playing time but also can track their everyday behavior, in order to correct behavior problems immediately. Children can play game in Kids’ Mode or Family Mode. Kids’ Mode has time limited, which needs stars to unlock. Family Mode does not have time limits, but it needs parent’s password to unlock.
3 Technology
Though using Unity3D and Vuforia software, we designed an application. As we mentioned before, the system of AR BLOCK divides into three directions: Parent Mode, Kids’ Mode and Family Mode.
Figure 1 describes the different interactive behaviors, feedbacks and system of Kids’ Mode and Family Mode. If children already get playing stars in the Parent Mode, they can unlock Kids’ Mode and play, otherwise users have to go back to home page. When playing times out, users cannot continue to play the game. There are three buttons in the game interface. Clicking ‘Home’ button can go back to home page and ‘Screenshot’ button can save children’s work to the tablet’s gallery. The ‘Help’ button can help children learning independently, because self-directed learning is an important concept of the Montessori education method. ‘Help’ has different tips, such as 2D and 3D geometric shapes, the results of mixing two colors, and how to learn mathematics. When the game starts, children will choose a Foundation Card first and the screen will show a 3D frame of house. Next, children should click the yellow number button beside the house on the screen. If users forget to click the button but choose another cards directly, the system will present visual and audio feedbacks, in order to remind users to make the correct behavior. This method can help children to focus on their existing work. After they finish the existing work, they can go to next.
4 Interactivity
The concept of interaction of this project divides into two sections: a visual and auditory interactivity, and an operational interaction aspect. For instance, in terms of parents operation gesture, the main behavior focuses on the screen. The click gesture allows choice of different functions, and swipe choice of different medals. Conversely, in the play environment, the users’ main behavior will focus on the physical blocks/cards.
4.1 Visual and Auditory Interactivity
In most cases, the system provides feedback to users when they have operation behavior. These visual or audio feedbacks are crucial for guiding the user’s interactive behavior [7]. For example, suppose that after choosing a Foundation Card, instead of clicking the screen to choose the house, children just continue to choose another block. The system will show a visual feedback ‘Please click the number to choose which building you want to change’ and an audio feedback ‘Oops’. If the user chooses a Building Card with a shape different from the Foundation Card, the user will see a message ‘Please choose the right card’ and hear an audio feedback ‘Wrong card’.
4.2 Operational Interactivity
When the user interacts with application, Click is the most commonly used operation gesture. However, in the game environment, Rotate will become to the mainly gesture. Through rotating blocks, the tablet camera will recognize different markers and the screen will show different feedbacks. For instance, if the user wants to change the house color and learn color mix knowledge, the user can use Color Blocks. Camera recognized No. 1 Color Block marker was yellow and No. 2 Color Block marker was red, so the house’s color showed as orange. If the user rotated No. 2 Color Block and changed the marker to blue, the house color will change to green (Fig. 2).
5 Discussion and Future Work
This paper provides an overview of the design of AR BLOCK; we start our study with a survey of existing AR products and discover weaknesses of them. Then our prototype was tested in a MADA exhibition in 2015. In the exhibition, researchers, educators and parents have a trial with AR BLOCK. They provide different comments bases on their experiences. Through the observation and conversation with users, some features have been accomplished. For example, most of users consider that the interaction behavior of AR BLOCK is very interesting. Their playing method is no longer limited to the screen but return to the original operation behavior. Instead of Drag, Click or Swipe, they can assemble physical blocks, exactly the same as with traditional construction block toy’s operation mode. Moreover, rotating Color Blocks to change colors provide an intuitive and effective method for learning color mix knowledge. However, the prototype is lacking a better way of guidance, despite its tutorial function. The majority of users do not know how to start the game when they play for the first time. We designed a tutorial page in Parent Mode; we hope that after parents understand how to play, they can teach their children by themselves. In fact, children still do not know the game rule.
From these survey and user test, the prototype is different from other existing products in interactive operation methods. AR BLOCK pays more attention to interaction of physical objects with the screen. In terms of learning, AR BLOCK provides a unique color mix method. Users can choose different Color blocks and rotate any of them, which will produce a new color. Children can learn each color’s name and observe the result when two colors are combined.
As the next step, the future development of AR BLOCK will focus on building a more effective guidance system, in order to provide a better user experience. For example, in the playing environment, instead of ‘Tutorial’ function page, using a cartoon character guides users game process and provides visual/audio feedback of users operation. Moreover, the interface design of existing Foundation cards and Building cards are easy to mislead users, they do not know how to pair the right card. We should redesign them and display information more efficiently.
6 Conclusions
To sum up, the main contributions of this project are bonding Montessori education theory with real world feedbacks; allowing user to learn abstract concept through interacting with tangible blocks. According to Montessori theory, blocks and cards of AR BLOCK can transfer abstract information to children, such as addition, 2D or 3D geometrical shape and color mixing. Instead of in-screen exercises, children can assemble or rotate these blocks, and the screen will give feedback based on their operation gestures. AR BLOCK can provide a better interactive experience when children are playing and learning.
References
Bundy, A.: Play and playfulness: what to look for. In: Parham, L.D., Fazio, L.S., (eds.) Play in Occupational Therapy for Children, pp. 52–66. Mosby, St. Louis (1997)
David, F., González-Ganced, S., Juan, M.-C., Segui, I., Costa, M.: The effects of the size and weight of a mobile device on an educational game. Comput. Educ. 64, 24–42 (2013)
Deborah, P.: Focusing and Calming Games for Children: Mindfulness Strategies and Activities to Help Children to Relax Concentrate and Take Control. Jessica Kingsley Publishers, London (2012)
Rui, L., Rodrigues, J.M.F., Aderito, M.: Game-based learning: augmented reality in the teaching of geometric solids. Int. J. Art Cult. Des. Technol. 4(1), 63–75 (2014)
Stephanie, W.: Creating an amazing montessori toddler home environment. Montessori Life 26(2), 54–59 (2014). A Publication of the American Montessori Society
Vygotsky, L.S.: Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes. Harvard University Press, Cambridge (1978)
Wang, S.J.: Fields Interaction Design (FID): The Answer to Ubiquitous Computing Supported Environments in the Post-Information Age. Homa & Sekey Books, Paramus (2013)
Zaranis, N., Kalogiannakis, M., Papadakis, S.: Using mobile devices for teaching realistic mathematics in kindergarten education. Creative Educ. 04(07), 1–10 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 ICST Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhu, Y., Wang, S.J. (2017). A Tangible Augmented Reality Toy Kit: Interactive Solution for Early Childhood Education. In: Brooks, A., Brooks, E. (eds) Interactivity, Game Creation, Design, Learning, and Innovation. ArtsIT DLI 2016 2016. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering, vol 196. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55834-9_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55834-9_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-55833-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-55834-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)