Abstract
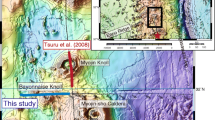
In September 1999, we collected seven high resolution seismic reflection profiles along the northern continental margin of Papua New Guinea, which targeted the source region of the 1998 tsunami that inundated Sissano Lagoon. We utilized swath bathymetry collected by the JAMSTEC/SOPAC groups in January 1999. The seismic profiles image several faults, bottom simulating reflectors, and a large rotational slump. The slump has a head scarp of 100 m vertical extent, coinciding with the headwall and tension cracks observed previously by submersible at the southern edge of the amphitheater. The central, back-rotated part of the slump is coherent with parallel reflections. The interpreted basal failure plane has a maximum depth of 760 m below the seafloor, and it crops out at a steep escarpment, about 100 meters high, located 4.5 km north of the head scarp. This escarpment separates the slide toe from a series of seafloor-parallel, coherent reflections that are top-lapped by basin deposits at the foot of the amphitheater to the north. The cross-sectional area of the displaced mass is 2.3 km2. From the bathymetry, the width is approximately 2.5–3 km, yielding a total volume (assuming parabolic shape) of 3.8–4.6 km3. Based on these interpretations, the slump was restored to its undeformed position. This technique yields a center of mass vertical drop of 380 m, horizontal movement of 840 m and slip of 980 m along the slide plane.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abers, G. and Mccaffrey, R. (1988), Active Deformation in the New Guinea Fold-and-thrust Belt: Seismological Evidence for Strike-slip Faulting and Basement-involved Thrusting, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 13,332–13,354.
Allen, P. A. and Allen, J. R., Basin Analysis Principles and Applications (Oxford, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1990), 451 pp.
Christie-Blick, N. and Biddle, K. T. (1985), Deformation and basin formation along strike-slip faults. In Strike-slip Deformation, Basin Formation and Sedimentation (eds., K. T. Biddle and N. Christie-Blick), Spec. Publ. Soc. Econ. Paleont. Mineral. 37, 1–34.
Clennell, M. B., Hovland, M., BOOTH, J. S., Henry, P., and Winters, W. J. (1999), Formation of Natural Gas Hydrates in Marine Sediments 1. Conceptual Model of Gas Hydrate Growth Conditioned by Host Sediment Properties, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 22,985–23,003.
Cooper, P. and Taylor, B. (1987), Seismotectonics of New Guinea, A Model for Arc Reversal Following Arc-continent Collision, Tectonics 6, 53–67.
Davies, H. L. (1998), The Sissano Tsunami, Univ. Papua New Guinea, Port Moresby.
Demets, C., Gordon, R. G., Argus, D. F., and Stein, S. (1994), Effect of Recent Revisions of the Geomagnetic Reversal Time Scale on Estimated of Current Plate Motions, Geophys. Res. Lett. 21, 2191–2194.
Fukao, Y. (1979), Tsunami Earthquakes and Subduction Processes near Deep-sea Trenches, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2303–2314.
Hamilton, W. (1979), Tectonics of the Indonesian Region, U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1078, 345 pp.
Henkart, P. (1981), SIOSEIS, Scripps Industrial Associates and National Science Foundation.
Henry, P., Thomas, M., and Clennell, M. B. (1999), Formation of Natural Gas Hydrates in Marine Sediments 2. Thermodynamic Calculations of Stability Conditions in Porous Sediments, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 23,005–23,022.
Imamura, A. Theoretical and Applied Seismology (Maruzen, Tokyo, 1937), 358 pp.
Kanamori, H. (1972), Mechanism of Tsunami Earthquakes, Phys. Earth Planet. Interiors 6, 346–359.
KAWATA, Y., Benson, B. C., Borrero, J. L., Davies, H. L., de Lange, W. P., Imamura, F., Letz, H., Nott, J., and Synolakis, C. (1999), Tsunami in Papua New Guinea was as Intense as First Thought, EOS. Trans. Am. Geophys. Un. 80, 101, 104–105.
Kreemer, C., Holt, W. E., Goes, S., and Govers, R. (2000), Active Deformation in Eastern Indonesia and the Philippines from GPS and Seismicity Data.,J. Geophys. Res. 105, 663–680.
Kvenvolden, K. A. and Barnard, L. A. (1983), Hydrates of natural gas in continental margins. In Future Petroleum Provinces of the United Stated (eds., J. S. Watkins and C. L. Drake), AAPG Memoir 34, 631–640.
Miall, A.D., Principles of Sedimentary Basin Analysis (New York, Springer-Verlag, 1984), 490 pp.
Newman, A. V. and Okal, E. A. (1998), Teleseismic Estimates of Radiated Seismic Energy: The El M, Discriminant for Tsunami Earthquakes, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 26,885–26,898.
Ripper, I., Seismicity, earthquake focal mechanisms and tectonics of the Indo-Aus/SolomonSea plate boundary (Dept. of Min. and Energy Rep. 1980), 8015, 55 pp. Geol. Surv, Papua New Guinea, Port Moresby.
Synolakis, C., Bardet, J., Borrero, J., Davies, H., Grilli, S., Okal, E., Silver, E., Sweet, S., and Tappin, D., (2001), The Splum Origin of the 1998 Papua New Guinea Tsunami, The Roy. Soc. Proc.: Math., Phys. and Engin. Sci. 458, 763–789.
Tappin, D.R. et al. (1999), Sediment Slmp Likely Caused 1998 Papua New Guinea Tsunami, EOS. Trans. Am. Geophys. Un., 80, 329, 334, 340.
Tregoning, P. et al. (1998), Estimation of Current Plate Motions in Papua New Guinea from Global Positioning System Observations, J. Geophys. Res. 103, 12,181–12,203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer Basel AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sweet, S., Silver, E.A. (2003). Tectonics and Slumping in the Source Region of the 1998 Papua New Guinea Tsunami from Seismic Reflection Images. In: Bardet, JP., Imamura, F., Synolakis, C.E., Okal, E.A., Davies, H.L. (eds) Landslide Tsunamis: Recent Findings and Research Directions. Pageoph Topical Volumes. Birkhäuser, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7995-8_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7995-8_9
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser, Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-7643-6033-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-7995-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive