Abstract
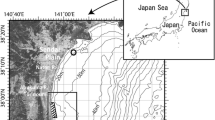
The epicentral area of the 1998 Papua New Guinea Earthquake and Tsunami off Sissano Lagoon, northern coast of Papua New Guinea (M = 7.1; 17 July, 1998) was surveyed by the Research Vessel Kairei in January 1999. Precise bathymetric survey by use of SEABEAM-2112 and other geophysical surveys (bottom reflectivity, sub-bottom profiling, surface ship gravity and geomagnetic surveys) were carried out and four piston core samples were collected during the nine days’ survey. The area was also surveyed by use of the Japanese deep sea research ROV Dolphin-3K and research submersible Shinkai-2000 after the regional geophysical survey, in order to locate the possible seismic faults and/or underwater landslides as the source of tsunami and to study the process which took place off Sissano Lagoon and the driving force of the event.
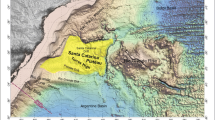
The study area is characterised by substantial fan sediment supply from Sissano Lagoon. Straight small-scale submarine canyons and valleys are eroding the shelf slope constructed by the fan sediment. Topographic features of arcuate slumps caused by landslides are recognised at numerous sites of the study area. Most of them are old and the most recent is located 25 km northeast off the Sissano Lagoon. Two major topographic depressions on the shelf were located off Sissano Lagoon. The western is a depression of about 10-km width and the eastern is a meandering deep-sea canyon.
Amphitheatre topographic features with slumps caused by landslides that were discovered by Kairei’s cruise were extensively surveyed in the study area. Six dives by Dolphin-3K and seven dives by Shinkai-2000 revealed that a fresh crack of about 15 km in total length is located along the slope of the amphitheatre. The crack is apparently the upper slope of a large-scale slumping on the amphitheatre, characterised by tensional stress on it.
The easternmost part of the fresh crack is accompanied by living chemosynthetic organisms such as mussels and tube worms. The chemosynthetic community is apparently associated with cold seepage along the crack suggesting that the crack was constructed very recently. The areas other than the crack were rather old with bioturbation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper, P., and Taylor, B. (1987), Seismotectonics of New Guinea: A Model for the Arc Reversal Following Arc-continent Collision, Tectonics 6, 53–67.
Tregoning, P., Lambeck, K., Stolz, A., Morgan, P., Mcclusky, S. C., Van Der Beek, P., Mcqueen, H., Jackson, R. J., Little, R. P., Laing, A., and Murphy, B. (1998), Estimation of Current Plate Motions in Papua New Guinea from Global Positioning System Observations,J. Geophys. Res. 103, 12,181–12,203.
Kawata, Y., Benson, B. C., Borrero, J. C., Borrero, J. L., Davies, H. L., De Lange, W. P., Imamura, F., Letz, H., Nott, J., and Synolakis, C. (1999), Tsunami in Papua New Guinea Was Intense as First Thought, EOS, Trans. Am. Geophys. Un. 80, 101 and 104–105.
Ripper, I. D., Letz, H., and Moihoi, M. (1998), Pre-tsunami Large Earthquakes of the Aitape Region North Coast Mainland of Papua New Guinea, Papua New Guinea Geolog. Survey Rep. 98/7, Port Moresby.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2003 Springer Basel AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Matsumoto, T., Tappin, D.R., SOS Onboard Scientific Party. (2003). Possible Coseismic Large-scale Landslide off the Northern Coast of Papua New Guinea in July 1998: Geophysical and Geological Results from SOS Cruises. In: Bardet, JP., Imamura, F., Synolakis, C.E., Okal, E.A., Davies, H.L. (eds) Landslide Tsunamis: Recent Findings and Research Directions. Pageoph Topical Volumes. Birkhäuser, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7995-8_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7995-8_8
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser, Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-7643-6033-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-7995-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive