Summary
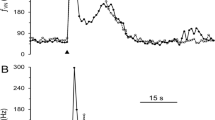
Voltage-clamped adult rabbit nodose ganglion (NG) neurones and murine NlE-115 neuroblastoma cells respond to locally applied 5-HT with an inward current response mediated by the opening of 5-HT3 receptor-linked cation selective ion channels. 5-HT-induced currents reversed in sign at a potential close to 0 mV and desensitized rapidly. The conductance of the 5-HT3 receptor ion channel complex in NlE-115 cells ( ~ 0.3 pS) was estimated to be approximately 155-fold lower than that found in rabbit NG neurones ( ~ 17.0 pS). Ondansetron and metoclopramide demonstrated similar IC50 values in blocking 5-HT-induced currents in the two cell types, but the antagonist potencies of (+)-tubocurarine and cocaine in NlE-115 cells (IC50 values 0.85 nM and 7.9 μM respectively) were different to those determined in rabbit NG neurones (160 nM and 80 nM) under similar recording conditions. The relative contributions of species and tissue differences to these discrepancies are discussed, together with preliminary data obtained from guinea-pig nodose ganglion neurones, which suggests the former to be an important variable.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burridge, J., Butler, A., and Kilpatrick, G. J. (1989). 5-HT3 receptors mediate depolarization of the guinea-pig isolated vagus nerve. Br. J. Pharmacol. 96: 269P.
Colquhoun, D., Dreyer, F., and Sheridan, R. E. (1979) The actions of tubocurarine at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Physiol. 293: 247–284.
Derkach, V., Surprenant, A., and North, R. A. (1989). 5-HT3 receptors are membrane ion channels. Nature 339: 706–709.
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., and Sigworth, F. J. (1981). Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recordings from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch. 391: 85–100.
Higashi, H., and Nishi, S. (1982). 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors of visceral primary afferent neurones on rabbit nodose ganglia. J. Physiol. 323: 543–567.
Hille, B. (1984). Ionic channels of excitable membranes. Sunderland, Massachusetts: Sinauer Associates, pp. 227–248.
Ikeda, S. R., Scholfield, G. G., and Weight, F. F. (1986). Na’ and Ca’ currents of acutely isolated adult rat nodose ganglion cells. J. Neurophysiol. 55: 527–539.
Kilpatrick, G. J., Butler, A., Hagan, R. M., Jones, B. J., and Tyers, M. B. (1990). [3H] GR67330, a very high affinity ligand for 5-HT3 receptors. Naunyn Schiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 342: 22–30.
Lambert, J. J., Peters, J. A., Hales, T. G., and Dempster, J. (1989). The properties of 5-HT3 receptors in clonal cell lines studied by patch-clamp techniques. Br. J. Pharmacol. 97: 27–40.
Lattimer, N., Rhodes, K. F., and Saville, V. L. (1989). Possible differences in 5-HT3 like receptors in the rat and guinea-pig. Br. J. Pharmacol. 96: 270P.
Newberry, N. R., Cheshire, S. H., and Gilbert, M. J. (1991). Evidence that the 5-HT3 receptors of the rat, mouse and guinea-pig superior cervical ganglion may be different. Br. J. Pharmacol. 102: 615–620.
Peters, J. A., Hales, T. G., and Lambert, J. J. (1988). Divalent cations modulate 5-HT3 receptor-induced currents in N 1 E-115 neuroblastoma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 151: 491–495.
Peters, J. A., and Lambert, J. J. (1989). Electrophysiology of 5-HT3 receptors in neuronal cell lines. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 10: 172–175.
Peters, J. A., Malone, H. M., and Lambert, J. J. (1990). Antagonism of 5-HT3 receptor mediated currents in murine NIE-115 neuroblastoma cells by (+)-tubocurarine. Neurosci. Lett. 110: 107–112.
Richardson, B. P., Engel, G., Donatsch, P., and Stadler, P. A. (1985). Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature, 316: 126–131.
Richardson, B. P., Engel, G. (1986). The pharmacology and function of 5-HT3 receptors. Trends Neurosci. 9: 424–428.
Robertson, B., and Bevan, S. (1991). Properties of 5-HT3 receptor-gated currents in adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. Br. J. Pharmcol. 102: 272–276.
Vanner, S., and Surprenant, A. (1990). Effects of 5-HT3 receptor antagonists on 5-HT and nicotinic depolarizations in guinea-pig submucosal neurones. Br. J. Pharmcol. 99: 840–844.
Wallis, D. I. (1989). Interaction of 5-hydroxytryptamine with autonomic and sensory neurones. In: Fozard, J. R. (ed.), The peripheral actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Oxford University Press, pp. 220–246.
Wallis, D. I., and Dun, N. J. (1988). A comparison of fast and slow depolarizations evoked by 5-HT in guinea-pig coeliac ganglion cells in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 93: 110–120.
Yakel, J. L., and Jackson, M. B. (1988). 5-HT3 receptors mediate rapid responses in cultured hippocampus and a clonal cell line. Neuron. 1: 615–621.
Yakel, J. L., Shao, X. M., and Jackson, M. B. (1990). The selectivity of the channel coupled to the 5-HT3 receptor. Brain Res. 533: 46–52.
Yang, J. (1990). Ion permeation through 5-HT-gated channels in neuroblastoma N18 cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 96: 1177–1198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Birkhäuser Verlag Basel/Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Peters, J.A., Malone, H.M., Lambert, J.J. (1991). Characterization of 5HT3 Receptor Mediated Electrical Responses in Nodose Ganglion Neurones and Clonal Neuroblastoma Cells Maintained in Culture. In: Fozard, J.R., Saxena, P.R. (eds) Serotonin: Molecular Biology, Receptors and Functional Effects. Birkhäuser Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7259-1_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-7259-1_8
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-0348-7261-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-7259-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive