Abstract
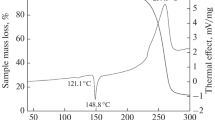
The thermal breakdown of several polybenzimidazoles, especially poly2,2′-(m-phenylene)-5,5′-bibenzimidazole has been studied in vacuum between 200 and 650°C. Formation of oxygen-containing products, such as water, carbon monoxide,and carbon dioxide led to an investigation about their origin. It was found that polybenzimidazoles have a strong tendency to adsorb water, and that this tendency may be traced to the C=N double bond and/or the imino group. In addition, the polymers must also contain intermediate amide, hydroxy imidazoline or imidazole-water complex structures from incomplete cyclization.
Based on these findings, and on the occurrence of volatiles such as hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, hydrogen and methane, as well as elemental analysis data and infrared spectra, a breakdown mechanism has been proposed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. F. L. Ehlers, K. R. Fisch and W. R. Powell, J. Polymer Sci., A-1, 7, 2931 (1969).
G. F. L. Ehlers, K. R. Fisch and W. R. Powell, J. Polymer Sci., A-1, 7, 2955 (1969).
G. F. L. Ehlers, K. R. Fisch and W. R. Powell, J. Polymer Sci., A-1, 7, 2969 (1969).
G. F. L. Ehlers, K. R. Fisch and W. R. Powell, J. Polymer Sci., A-1, 8, 3511 (1970).
G. P. Shulman and W. Lochte, J. Macromol. Sci. (Chem) Al, 413 (1967).
T. E. Helminiak, private communication.
W. R. Feairheller, Jr. and J. E. Katon, AFML-TR-67–102 (1967).
A. R. Katritzky, Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry, 4, Academic Press, New York and London 1965.
R. T. Conley, private communication.
H. L. Friedman, G. A. Griffith and H. W. Goldstein, ML-TDR-64–274, Part I II (1967).
H. L. Friedman, H. W. Goldstein and G. A. Griffith, AFML-TR-68–111, Part I I (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1972 Springer Basel AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ehlers, G.F.L., Fisch, K.R. (1972). Studies of the Thermal Breakdown of Polybenzimidazoles. In: Wiedemann, H.G. (eds) Thermal Analysis. Birkhäuser, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-5775-8_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-5775-8_16
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser, Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-0348-5777-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-5775-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive