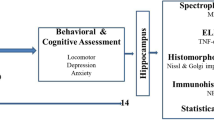
Summary
Background Tartrazine is an artificial coloring widely used in Moroccan gastronomy. Some utensils may contain a significant content of lead. Aims to study Tartrazine’s effects alone and in combination with lead on the central nervous system (CNS) in Sprague Dawley rats. Methods We randomized female Sprague Dawley rats (n = 60) into G1 received Tartrazine at 500 mg/kg by gavage, G2 received the same protocol in combination with lead nitrate at 100 mg/kg per peritoneal route and G3 (control group) received Nacl at 9% at 0.5 ml/d. We evaluated the cognitive and behavioral functions: memory, motor coordination, anxiety and locomotor capacities; and an immunohistochemical study of the hippocampus (Ca1, Ca2, Ca3 and the dentate gyrus) and the cerebellum using GFAP. Results: G1 showed a significant increase in latency time in the passive avoidance test (p < 0.001), a significant increase in hold time on the Rotarod and speed and distance traveled on the openfield (p = 0.003), and an increase in Closed Arms (BF) exploration time in the raised plus maze test (p < 0.001). Immunohistochemistry revealed that Tartrazine causes astrocyte loss associated with reduced branching and cellular hypotrophy in the hippocampus. In G2, moderate to severe astrogliosis was noted especially in the cerebellum. Conclusion this is the first study that focuses on the association of Tartrazine with lead. Several neurotoxic effects have been raised after consumption of Tartrazine alone and in combination with lead.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Elhakim, Y.M., et al.: Comparative haemato-immunotoxic impacts of longterm exposure to tartrazine and chlorophyll in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol.Immunopharmacol. 63, 145–154 (2018)
Achour, S., Iken, I., Amarti, A.: L’intoxication au plomb: caractéristiques toxicologiques et clinicobiologiques. Toxicologie Maroc 21, 9–12 (2014)
Albasher, G., et al.: Perinatal exposure to tartrazine triggers oxidative stress and neurobehavioral alterations in mice offspring. Antioxidants. 9(1), 53 (2020)
Alsalman, N., Aljafari, A., Wani, TA., Zargar, S.: High-dose aspirin reverses tartrazine-induced cell growth dysregulation independent of p53 signaling and antioxidant mechanisms in rat brain. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 9096404 (2019)
Amchova, P., Kotolova, H., Ruda-Kucerova, J.: Health safety issues of synthetic food colorants. Regulatory toxicology and pharmacology. Regulatory Toxicol. Pharmacol. 73(3), 1–9 (2015)
Antunes, M., Biala, G.: The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 13(2), 93–110 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-011-0430-z. Epub 9 December 2011. PMID: 22160349; PMCID: PMC3332351
Axon, A., May, F.E., Gaughan, L.E., Williams, F.M., Blain, P.G., Wright, M.C.: Tartrazine and sunset yellow are xenoestrogens in a new screening assay to identify modulators of human oestrogen receptor transcriptional activity. Toxicology 298, 40–51 (2012)
Beatriz Virgolini, M., Aschner, M.: Chapter Five - Molecular mechanisms of lead neurotoxicity. In: Aschner, M., Costa, L.G. (eds.) Advances in Neurotoxicology, vol. 5, pp. 159–213. Academic Press (2021). ISSN 2468-7480, ISBN 9780128237755. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ant.2020.11.002
Beausoleil, M., Brodeur, J.: Mesures Des Concentrations De Plomb Lessivable De La Glaçure De Cinq Tajines Marocains Disponibles A Montréal (2005)
Beutler, C.: Les colorants artificiels dans les denrées alimentaires destinées aux enfants (2011)
Bohlen, M., Cameron, A., Metten, P., Crabbe, J.C., Wahlsten, D.: Calibration of rotational acceleration for the rotarod test of rodent motor coordination. J. Neurosci. Methods 178, 10–14 (2009)
Bondan, E.F., Monteiro, M.F., Viani, F.C.: Decreased astrocytic GFAP expression in streptozotocin induced diabetes after gliotoxic lesion in the rat brainstem. Arquivos brasileiros de endocrinologia metabologia 57(6), 431–436 (2013)
Bratthauer, G.L.: The Peroxidase-Antiperoxidase (PAP) method. In: Javois, L.C. (eds.) Immunocytochemical Methods and Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 34. Humana Press (1994). https://doi.org/10.1385/0-89603285-X:165
Carobrez, A.P., Bertoglio, L.J.: Ethological and temporal analyses of anxiety-like behavior: the elevated plus-maze model 20 years on. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.. Biobehav. Rev. 29(8), 1193–1205 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.04.017
Demirkol, O., Zhang, X., Ercal, N.: Oxidative effects of Tartrazine (CAS No. 1934–21-0) and New Coccin (CAS No. 2611–82-7) azo dyes on CHO cells. J. Verbr. Lebensm.Verbr. Lebensm. 7, 229–236 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-012-0782-z
Doguc, D.K., Deniz, F., İlhan, İ., Ergonul, E., Gultekin, F.: Prenatal exposure to artificial food colorings alters NMDA receptor subunit concentrations in rat hippocampus. Nutr. Neurosci. 24, 1–11 (2019)
Dubois, B., Michon, A.: Démences. Traité De Neurologie. Editeur Doin - John Libbey Eurotext, p. 480 (2015)
Essawy, A.E., Mohamed, A.I., Ali, R.G., et al.: Analysis of Melatonin-modulating effects against tartrazine-induced neurotoxicity in male rats: biochemical, pathological and immunohistochemical markers. Neurochem. Res.. Res. 48, 131–141 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03723-9
Eubig, P.A., Aguiar, A., Schantz, S.L.: Lead and PCBS as risk factors for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Environ. Health Perspect. 118(12), 1654–1667 (2010)
Filgueiras, G.B., Carvalho-Netto, E.F., Estanislau, C.: Aversion in the elevated plus-maze: role of visual and tactile cues. Behav. Processes. Processes 107, 10611 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2014.08.005
Gao, Y., Li, C., Shen, J., Yin, H., An, X., Jin, H.: Effect of food azo dye tartrazine on learning and memory functions in mice and rats, and the possible mechanisms involved. J. Food Sci. 76(6), 125–126 (2011)
Gouget, C.: Le Guide Indispensable Pour Ne Plus Vous Empoisonner: Additifs Alimentaires Danger. Editions Chariot D’or, p. 30 (2008)
Guillarda, C., Lachheba, H., Houasb, A., Ksibib, M., Elalouib, E., Herrmanna, J.M.: Influence of chemical structure of dyes, of PH and of inorganic salts on their photocatalytic degradation by TIO2 comparison of the efficiency of powder and supported TIO2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 158, 27–36 (2003)
Himri, I., et al.: A 90-day oral toxicity study of Tartrazine, a synthetic food dye, in Wistar rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 3(3), 159–169 (2011)
Kamel, M.M., El-Lethey, H.S.: The potential health hazard of tartrazine and levels of hyperactivity, anxiety-like symptoms, depression and anti-social behaviour in rats. J. Am. Sci. 7(6), 1211–1218 (2011)
Kolb, B., Whishaw, I.Q.: Cerveau & Comportement. Neurosciences & Cognition. De Boeck Supérieur, pp. 55–59 (2002)
Lüllmann-Rauch, R.: Histologie. De Boeck Supérieur, pp. 204–205 (2008)
Marwa, G.B., Magdy, M.M., Maha, M.K., Omayma, H.: Effect of synthetic coloring dye erythrosine (E127) in rats. J. Environ. Sci. 46(1), 21–34 (2019)
Merinas-Amo, R., Martínez-Jurado, M., Jurado-Güeto, S., Alonso-Moraga, Á., Merinas-Amo, T.: Biological effects of food coloring in in vivo and in vitro model systems. Foods 8, 176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8050176
Mehedi, N., et al.: A thirteen week ad libitum administration toxicity study of Tartrazine in Swiss mice. Afr. J. Biotech. 12(28), 4519–4529 (2013)
Mpountoukas, P., et al.: Cytogenetic evaluation and DNA interaction studies of the food colorants amaranth, erythrosine and tartrazine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 48(10), 2934–2944 (2010)
Olewinska, E., et al.: Level of DNA damage in lead-exposed workers. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 17, 231–236 (2010)
Park, M., et al.: Risk assessment for the combinational effects of food color additives: neural progenitor cells and hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Toxicol. Environ. HealthToxicol. Environ. Health 2(21–22), 141–223 (2009)
Sasakia, Y.F., et al.: The comet assay with 8 mouse organs: results with 39 currently used food additives. Mutat. Res.. Res. 519, 103–119 (2002)
Sabouraud, B., et al.: Intoxication Environnementale Par Le Plomb Liée A La Consommation De Boisson Conservée Dans Une Cruche Artisanale En Céramique Vernissée. La Revue De Médecine Interne 30, 1038–1043 (2009)
Saxena, B., Sharma, S.: Food color induced hepatotoxicity in Swiss Albino Rats Rattus norvegicus. Toxicol. Int.. Int. 22(1), 152–157 (2015)
Sanders, T., Liu, Y., Buchner, V., Tchounwou, P.B.: Neurotoxic effects and biomarkers of lead exposure: a review. Rev. Environ. Health 24(1), 15–45 (2009)
Schrader, A.J., Taylor, R.M., Lowery-Gionta, E.G., Moore, N.L.T.: Repeated elevated plus maze trials as a measure for tracking within-subjects behavioral performance in rats (Rattus norvegicus). PLoS One 26; 13(11), e0207804 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0207804. PMID: 30475877; PMCID: PMC6257936
Seifert, G., Schilling, K., Steinhauser, C.: Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: a molecular perspective. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.Neurosci. 7, 194–206 (2006)
Sofroniew, M.V., Vinters, H.V.: Astrocytes: biology & pathology. Acta Neuropathol. Neuropathol. 119, 7–35 (2010)
Soulaymani-Bencheikh, R.: Les lourdes nuisances des métaux lourds. Toxicologie Maroc 21, 2 (2014)
Tanaka, T., Takahashi, O., Oishi, S., Ogata, A.: Effects of tartrazine on exploratory behavior in a three generation toxicity study in mice. Reprod. Toxicol.. Toxicol. 26(2), 156–163 (2008)
Tillement, J.P., Hauw, J.J., Papadopoulos, V.: Vieillissement Et Démences. Edition Lavoisier, p. 99 (2014)
Yazbeck, C., et al.: Maternal blood lead levels and the risk of pregnancy-induced hypertension: the EDEN cohort study. Environ. Health Perspect.Perspect. 117, 1526–1530 (2009)
Wopara, I., et al.: Anxiogenic and memory impairment effect of food color exposure: upregulation of oxido-neuroinflammatory markers and acetyl-cholinestrase activity in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Heliyon 7(3), e06378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06378.PMID:33748463;PMCID:PMC7970276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ait Belcaid, H. et al. (2024). The Neurotoxic and Neurobehavioral Effects of “Tartrazine E102” Alone and in Combination with Lead Nitrate on the Sprague Dawley Rat. In: Ezziyyani, M., Kacprzyk, J., Balas, V.E. (eds) International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems for Sustainable Development (AI2SD’2023). AI2SD 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 904. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52388-5_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-52388-5_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-52387-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-52388-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)