Abstract
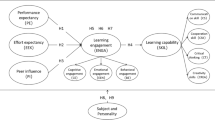
This study explores the effectiveness of online flipped learning for outstanding students in Jordan. It examines the factors influencing students’ acceptance and use of technology, such as performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating conditions. The findings show a positive relationship between these factors and students’ intention to utilize e-flipped learning, highlighting the efficacy of this approach for outstanding students in Jordan. The proposed model can guide the development of online flipped learning systems tailored to the needs of outstanding students.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alawamreh, A.R. and N.F. Elias, The Acceptance of e-Learning System for Gifted Students in Developing Country (Jordan Case Study). 2016.
Logan, R.M., Johnson, C.E., Worsham, J.W.: Development of an e-learning module to facilitate student learning and outcomes. Teach. Learn. Nurs. 16(2), 139–142 (2021)
Maatuk, A.M., et al.: The COVID-19 pandemic and E-learning: challenges and opportunities from the perspective of students and instructors. J. Comput. High. Educ. 1–18 (2021)
Obeidat, A.: IT adaption with knowledge conversion process (SECI)? Manag. Sci. Lett. 9(13), 2241–2252 (2019)
Mulyani, M., et al.: University students’ perceptions through e-learning implementation during COVID-19 pandemic: positive or negative features dominate? Stud. Engl. Lang. Educ. 8(1), 197–211 (2021)
Amarin, N., Al-Saleh, A.A.-S.: The effect of color use in designing instructional aids on learners’ academic performance. J. e-Learn. Knowl. Soc. 16(2), 42–50 (2020)
Kanan, M., Zerban, A., Abunar, S., El Harbi, A., Weheba, G., Ahmed, R.A., Abdultawwab, M., Haddad, T.: Online education and managing service quality with the challenges of COVID 19: the case of university of business and technology (UBT) Saudi Arabia. Appl. Math. 17(2), 201–207 (2023)
Musleh Al-Sartawi, A.M.A.: E-learning improves accounting education: case of the higher education sector of Bahrain. In: Themistocleous, M., Papadaki, M., Kamal, M.M. (eds.) Information systems. EMCIS 2020. Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing, vol. 402. Springer, Cham (2020)
Bakir, A., Dahlan, M.: Higher education leadership and curricular design in industry 5.0 environment: a cursory glance. Dev. Learn. Organ. Int. J. 37(3), 15–17 (2023)
Kamarudin, S., Shoaib, H.M., Jamjoom, Y., Saleem, M., Mohammadi, P.: Students’ behavioural intention towards e-learning practices through augmented reality app during COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia. Interact. Learn. Environ. 1–17 (2021)
Obeidat, A.M.: E-marketing and its impact on the competitive advantage. Ilkogretim Online 20(5) (2021)
Nash, S.S.: Moodle Course Design Best Practices: Design and Develop Outstanding Moodle Learning Experiences. Packt Publishing Ltd., (2018)
Al-Zu’bi, M.A., et al.: Motivating pre-school children to learn creative thinking in Jordan using iPad applications: a mixed-methods approach. In: 2022 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT). IEEE (2022)
Bognar, B., Sablić, M., Škugor, A.: Flipped learning and online discussion in higher education teaching. Didactics of Smart Pedagogy: Smart Pedagogy for Technology Enhanced Learning, pp. 371–392 (2019)
Hwang, G.-J., Lai, C.-L.: Facilitating and bridging out-of-class and in-class learning: an interactive e-book-based flipped learning approach for math courses. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 20(1), 184–197 (2017)
Al Mawadieh, R.S., Al-Badawi, M., Al-Sarairah, K.: The reality of risk management in private Jordanian universities from the viewpoint of faculty members. Int. J. High. Educ. 9(5), 274–282 (2020)
Venkatesh, V., et al.: User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q., 425–478 (2003)
Yi, M.Y., Davis, F.D.: Developing and validating an observational learning model of computer software training and skill acquisition. Inf. Syst. Res. 14(2), 146–169 (2003)
Al-Zoubi, S.M., Rahman, M.S.B.A.: the effects of a training program in improving instructional competencies for special education teachers in Jordan. Educ. Res. 2(3), 1021–1030 (2011)
Nederveld, A., Berge, Z.L.: Flipped learning in the workplace. J. Workplace Learn. (2015)
Kalogiannakis, M.: Training with ICT for ICT from the trainee’s perspective. A local ICT teacher training experience. Educ. Inf. Technol. 15(1), 3–17 (2010)
Musleh Al-Sartawi, A.M., Razzaque, A., Kamal, M.M. (eds.): Artificial Intelligence Systems and the Internet of Things in the Digital Era. EAMMIS 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 239. Springer, Cham (2021)
Musleh Al-Sartawi, A.M.A. (eds.): Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Finance and Sustainable Technology. ICGER 2021. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 423. Springer, Cham (2022)
Musleh Al-Sartawi, A.M.A., Razzaque, A., Kamal, M.M. (eds.): From the Internet of Things to the Internet of Ideas: The Role of Artificial Intelligence. EAMMIS 2022. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 557. Springer, Cham (2023)
Fatemeh, K., Mahmoud, A., Roman, K.: Using interactive E-based flipped learning to enhance EFL literature students’ critical reading. Sci. Educ. Today 10(1), 25–42 (2020)
Compeau, D.R., Higgins, C.A.: Computer self-efficacy: development of a measure and initial test. MIS Q. 189–211 (1995)
Murphy, C.A., Coover, D., Owen, S.V.: Development and validation of the computer self-efficacy scale. Educ. Psychol. Measur. 49(4), 893–899 (1989)
Wolverton, C.C., Hollier, B.N.G., Lanier, P.A.: The impact of computer self efficacy on student engagement and group satisfaction in online business courses. Electron. J. E-learn. 18(2), 175–188 (2020)
Maiyaki, A.A., Mohd Mokhtar, S.S.: Determinants of customer behavioural responses: A pilot study. Int. Bus. Res. 4(1), 193–197 (2011)
Wang, S.M., Sekaran, S.D.: Early diagnosis of Dengue infection using a commercial Dengue Duo rapid test kit for the detection of NS1, IGM, and IGG. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 83(3), 690 (2010)
Mugenda, O.M., Hira, T.K., Fanslow, A.M.: Assessing the causal relationship among communication, money management practices, satisfaction with financial status, and satisfaction with quality of life. Lifestyles 11(4), 343–360 (1990)
Al-Badawi, M., Aljaafreh, A., Al-Mawdieh, R.S.: The employment of listening teaching strategies in elementary classrooms by Jordanian Arabic teachers. Int. J. Instr. 13(2), 783–796 (2020)
Sarstedt, M., Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M.: Multigroup analysis in partial least squares (PLS) path modeling: Alternative methods and empirical results. In: Measurement and research methods in international marketing. Emerald Group Publishing Limited (2011)
Hair Jr, J.F., et al.: Identifying and treating unobserved heterogeneity with FIMIX-PLS: part I–method. Eur. Bus. Rev. (2016)
Ramayah, T., et al.: Factors influencing SMEs website continuance intention in Malaysia. Telematics Inform. 33(1), 150–164 (2016)
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.F.: Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. Sage Publications Sage CA, Los Angeles, CA (1981)
Henseler, J., Ringle, C.M., Sarstedt, M.: A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 43, 115–135 (2015)
ALMawadieh, R.S., The trends of implementing blended learning among Jordanian universities’ faculty members and the obstacles they face, Zarqa University-Jordan (2019)
Alawamreh, A.R., Elias, N.F.: Examining the effectiveness of using web-based learning for gifted students: Jordan as case study. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 76(2) (2015)
Venkatesh, V., Davis, F.D.: A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manage. Sci. 46(2), 186–204 (2000)
Davis, F.D.: Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 319–340 (1989)
Prachi, R., et al.: A study of knowledge, attitude and practice of family planning among the women of reproductive age group in Sikkim. Religion 35(44years), 34 (2008)
Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R.: User acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of two theoretical models. Manage. Sci. 35(8), 982–1003 (1989)
Gupta, B., Dasgupta, S., Gupta, A.: Adoption of ICT in a government organization in a developing country: an empirical study. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 17(2), 140–154 (2008)
Nahla Aljojo, B.A.: Investigating effort expectancy and facilitating conditions affecting behavioral intention to use mobile learning. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 55(5) (2020)
Al-Khatib, H., et al.: E-government Systems Success and User Acceptance in Developing Countries: The Role of Perceived Support Quality (2019)
Huang, D.-H., Chueh, H.-E.: Behavioral intention to continuously use learning apps: A comparative study from Taiwan universities. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 177, 121531 (2022)
Negi, N.S., Nasreen, R.: The effect of facilitating conditions on behavioral intention of farmers towards national agriculture market (eNAM). IUP J. Market. Manag. 20(2) (2021)
Abdelhamied, H.H.S.: The impact of training activities on quality of service, customer satisfaction and behavioral intention. J. Tour. Hospitality Manag. 7(1), 135–148 (2019)
De Vries, H., Dijkstra, M., Kuhlman, P.: Self-efficacy: the third factor besides attitude and subjective norm as a predictor of behavioural intentions. Health Educ. Res. 3(3), 273–282 (1988)
Maddux, J.E., Norton, L.W., Stoltenberg, C.D.: Self-efficacy expectancy, outcome expectancy, and outcome value: relative effects on behavioral intentions. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 51(4), 783 (1986)
Alharbi, S., Drew, S.: Using the technology acceptance model in understanding academics’ behavioural intention to use learning management systems. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 5(1), 143–155 (2014)
Kabra, G., et al.: Understanding behavioural intention to use information technology: Insights from humanitarian practitioners. Telematics Inform. 34(7), 1250–1261 (2017)
Al-Mawadieh, R.S., et al.: The degree of practicing electronic management by kindergarten principals in Karak Governorate in light of corona pandemic. In: 2022 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT). IEEE (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Alawamreh, A.R. et al. (2023). The Effectiveness of Online Flipped Learning Using the UTAUT Model for Outstanding Students in Jordan. In: Hannoon, A., Mahmood, A. (eds) Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, and Society 5.0. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1113. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43300-9_33
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-43300-9_33
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-43299-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-43300-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)