Abstract
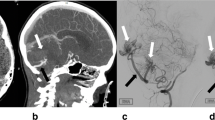
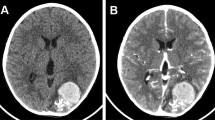
An 18-year-old male, who had two previous attacks of subarachnoid hemorrhage, presented asymptomatic and neurologically intact, after complete recovery from hemorrhage-associated severe headache. He was treated with upfront (primary); Linac-based SRS for right, frontal, large, diffuse, rare subtype of venous-predominant, parenchymal AVM, mimicking atypical arterialized developmental venous anomaly (DVA). The target volume of 12.5 cc received a marginal dose of 25.0 Gy normalized to 80% isodose line. The maximum dose to optic chiasm was 15.8 Gy. At 3 months post-SRS, the patient experienced moderate headache and vomiting, which resolved gradually over couple months with steroid and diuretic medications. Serial post-SRS follow-up imaging showed progressive reduction in the size of AVM nidus till its non-visualization at 11 months post-SRS. The follow-up images also showed perinidal high signal in T2 and FLAIR studies, denoting vasogenic edema, and perinidal large heterogeneously enhancing lesion, in T1 Gadolinium-enhanced study, denoting radiation-induced parenchymal changes. At last radiological follow-up (55 months post-SRS), conventional cerebral angiography documented complete obliteration of AVM nidus. The radiosurgery treatment was successful, and the patient was neurologically intact throughout the entire follow-up period of 64 months post-SRS.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
- Arteriovenous malformation
- Venous-predominant AVM
- Developmental venous anomaly
- Atypical arterialized DVA
- Linac-based radiosurgery
- Primary SRS
- Cerebral angiography
- Nidus obliteration
- Perinidal edema
- Radiation-induced changes
-
Demographics: Male; 18 years
-
Initial Presentation: Hemorrhage (subarachnoid), which occurred twice; at 8 months and 1 month before radiosurgery treatment
-
Diagnosis: A rare subtype of venous-predominant parenchymal AVM, mimicking atypical arterialized developmental venous anomaly (DVA)
-
Pre-radiosurgery Treatment: None
-
Pre-radiosurgery Presentation: Asymptomatic and neurologically intact, after complete recovery from severe hemorrhage-associated headache
-
Radiosurgery Treatment:
Upfront (primary); Linac-based SRS for right, frontal, large, diffuse, venous-predominant, parenchymal AVM
-
Radiosurgery Dosimetry:
-
Target volume: 12.5 cc
-
Marginal dose: 25.0 Gy
-
Marginal isodose: 80%
-
Maximum dose: 33.0 Gy
-
Minimum dose: 14.5 Gy
-
Average dose: 30.0 Gy
-
Number of isocenters: 1
-
Maximum dose to optic chiasm: 15.8 Gy
-
-
Follow-Up Period: 64 months post-SRS
-
Clinical Outcome:
-
3 months post-SRS: Experienced moderate headache and vomiting; started medications (steroids, diuretics)
-
5 months post-SRS: Improving headache and vomiting with gradual tapering of medications
-
7 months post-SRS: Recurrence of severe headache and vomiting; restarted medications (steroids, diuretics)
-
8 months post-SRS: Complete resolution of headache and vomiting; stopped medications
-
12 months post-SRS: Asymptomatic and neurologically intact
-
64 months post-SRS: Sustainable asymptomatic and intact neurological status
-
-
Complications: None
-
Radiological Outcome:
-
3 months post-SRS (CT):
-
Slight decrease in size of AVM nidus
-
Diffuse right frontal perinidal hypodensity, denoting severe vasogenic edema with focal mass effect and midline shift
-
-
7 months post-SRS (MRI):
-
Marked decrease in size of AVM nidus
-
Diffuse right frontal perinidal high signal in T2 study, denoting marked vasogenic edema
-
Appearance of right frontal perinidal large heterogeneously enhancing lesion, in T1 Gadolinium-enhanced study, denoting radiation-induced parenchymal changes
-
-
8 months post-SRS (CT):
-
Much more decrease in size of AVM nidus
-
Decreased right frontal perinidal hypodense vasogenic edema
-
-
9 months post-SRS (CTA):
-
Non-visualized AVM nidus
-
Persistent slightly dilated draining deep venous system
-
-
11 months post-SRS (CT):
-
Non-visualized AVM nidus
-
Markedly decreased right frontal perinidal hypodense vasogenic edema
-
-
12 months post-SRS (CTA):
-
Non-visualized AVM nidus
-
Evident decrease in number and size of draining deep veins
-
-
55 months post-SRS (Conventional angiography): Complete nidus obliteration
-
-
Post-radiosurgery Treatment: None
















Further Reading
Ilyas A, Chen CJ, Ding D, et al. Radiation-induced changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(3):365–76.
Im SH, Han MH, Kwon BJ, et al. Venous-predominant parenchymal arteriovenous malformation: a rare subtype with a venous drainage pattern mimicking developmental venous anomaly. J Neurosurg. 2008;108(6):1142–7.
Nabavizadeh SA. Intracranial arteriovenous shunting detection with arterial spin-labeling and susceptibility-weighted imaging: potential pitfall of a venous predominant parenchymal arteriovenous malformation. Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38(5):E32. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5108.
Van den Berg R, Buis DR, Lagerwaard FJ, et al. Extensive white matter changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations: a prognostic sign for obliteration? Neurosurgery. 2008;63(6):1064–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Abdelaziz, O.S., De Salles, A.A.F. (2023). Rare Subtype of Venous-Predominant Parenchymal Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM). In: NeuroRadiosurgery: Case Review Atlas. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16199-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16199-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-16198-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-16199-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)