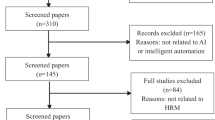
Abstract
The controversy over fairness and objectivity in the job market, due to hiring irregularities, has led to calls for transparent and fair recruitment procedures. Advances in IT technology have led to the emergence of a non-face-to-face “AI recruitment system” in which artificial intelligence (AI) conducts interviews, instead of human interviews. As the introduction of the non-face-to-face method is encouraged in the hiring process due to the COVID-19 virus pandemics, the number of companies introducing AI recruitment systems is steadily increasing. In this study, the factors affecting the intention of use of AI-based recruitment system were analyzed by utilizing TOE and TAM. As a result, it was shown that the reliability, security, suitability, new technology, partiality, readiness, and legal and policy environment of the TOE affected the intention of using the system. It was also identified to have the moderating effect of the number of employees in the firm.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park, S.H.: Everything About AI Competency Testing. EDUCE, Seoul, Korea (2020)
Lee, H.W., Lee, R.S., Jung, C.G.: The impact of artificial intelligence adoption in candidates screening and job interview on intentions to apply. J. Inf. Syst. 28(2), 25–52 (2019)
Hengstler, M., Enkel, E., Duelli, S.: Applied artificial intelligence and trust—the case of autonomous vehicles and medical assistance devices. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 105, 105–120 (2016)
Bae, W.Y., Maeng, S.G., Han, H.S.: Artificial intelligence is expanding into reality. KEIT PD Issue Report 2016-09. Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (2016). https://www.bioin.or.kr/board.do?num=264308&cmd=view&bid=tech
Van Esch, P., Black, J.S., Ferolie, J.: Marketing AI recruitment: the next phase in job application and selection. Comput. Hum. Behav. 90, 215–222 (2019)
Lee, S.W.: AI interviewers appear in U.S. corporate recruitment… Concerns about fairness in evaluation. Seoul (2018). http://m.seoul.co.kr/news/newsView.php?id=20180921500157&cp=seoul#csidx8724d62a156885fb0eaafdef95a2697
Tornatzky, L.G., Fleischer, M., Chakrabarti, A.K.: Processes of Technological Innovation. Lexington Books (1990)
Gangwar, H., Date, H., Raoot, A.D.: Review on IT adoption: insights from recent technologies. J. Enterp. Inf. Manage. (2014)
Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R.: User acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of two theoretical models. Manage. Sci. 35(8), 982–1003 (1989)
Legris, P., Ingham, J., Collerette, P.: Why do people use information technology? A critical review of the technology acceptance model. Inf. Manage. 40(3), 191–204 (2003)
Venkatesh, V., Davis, F.D.: A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manage. Sci. 46(2), 186–204 (2000)
Lee, H.Y., Ahn, H., Han, I.: VCR: virtual community recommender using the technology acceptance model and the user’s needs type. Expert Syst. Appl. 33(4), 984–995 (2007)
Schierz, P.G., Schilke, O., Wirtz, B.W.: Understanding consumer acceptance of mobile payment services: an empirical analysis. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 9(3), 209–216 (2010)
Tornatzky, L.G., Klein, K.J.: Innovation characteristics and innovation adoption-implementation: a meta-analysis of findings. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manage. 1, 28–45 (1982)
Kannan, P.K., Chang, A.M., Whinston, A.B.: Wireless commerce: marketing issues and possibilities. In: Proceedings of the 34th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 6 pp. IEEE (2001)
Ku, K.B., An, B.J.: An empirical study on important factors of ubiquitous commerce acceptance. Int. Account. Res. 18, 1–21 (2007)
Rogers, E.M., Shoemaker, F.F.: Communication of innovations: a cross-cultural approach (1971)
Dasgupta, S.: Supporting ideas with data. Econ. Pol. Wkly 34(50), 3513–3515 (1999)
Teo, T.S., Lim, G.S., Fedric, S.A.: The adoption and diffusion of human resources information systems in Singapore. Asia Pac. J. Hum. Resour. 45(1), 44–62 (2007)
Chin, W.W., Todd, P.A.: On the use, usefulness, and ease of use of structural equation modeling in MIS research: a note of caution. MIS Q. 237–246 (1995)
Bhattacherjee, A.: Understanding information systems continuance: an expectation-confirmation model. MIS Q. 351–370 (2001)
Nunnally, J.C., Berstein, I.H.: Psychometric Theory. McGraw-Hill, New York (1994)
Fornell, C., Larcker, D.F.: Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 18(1), 39–50 (1981)
Taylor, S., Todd, P.A.: Understanding information technology usage: a test of competing models. Inf. Syst. Res. 6(2), 144–176 (1995)
Gefen, D., Straub, D., Boudreau, M.C.: Structural equation modeling and regression: guidelines for research practice. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 4(1), 7 (2000)
Cangur, S., Ercan, I.: Comparison of model fit indices used in structural equation modeling under multivariate normality. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 14(1), 14 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Lee, J.H., Kim, J.H., Kim, Y.H., Song, Y.M., Gim, G.Y. (2021). Factors Affecting the Intention to Use Artificial Intelligence-Based Recruitment System: A Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) Approach. In: Lee, R. (eds) Computer and Information Science 2021—Summer . ICIS 2021. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 985. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79474-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79474-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-79473-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-79474-3
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)