Abstract
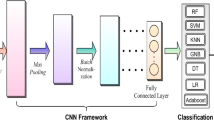
Artificial Intelligence uses statistical theory to generate mathematical models from samples. After a model is generated, its depiction and algorithmic solution for understanding require being competent as well. Biomedical data related to different diseases are recorded from a body, which can be at the organ level, cell level or molecular level. Biomedical data is mainly utilized to predict, diagnose or identify particular physiological or pathological conditions. The goal of biomedical data analysis is exact modelling of data by employing feature extraction, feature selection and dimension reduction for the prediction and detection of upcoming pathological problems by utilizing artificial intelligence algorithms. This chapter explains the steps of biomedical data analysis and how artificial intelligence techniques are utilized in disease prediction. An automated epileptic seizure prediction and detection approach based on deep learning is also presented. Since Deep Learning can automatically extract and learn features, the electroencephalography (EEG) time series are fed into the deep learning model. Deep Learning has been utilized in the prediction and detection of epileptic seizures. Since EEG recordings are high dimensional data, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is suitable for this use. The results show that CNN achieved a testing accuracy of 99.09% accuracy for the prediction of epileptic seizures from EEG signals.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Muthuswamy, Biomedical signal analysis, in Standard Handbook of Biomedical Engineering and Design, vol. 14, ed. by M. Kutz (McGraw-Hill Education, New York, 2004), pp. 18
L.T. Mainardi, A.M. Bianchi, S. Cerutti, Digital biomedical signal acquisition and processing, in Medical Devices and Systems (CRC Press, 2006), pp. 49–72
S. Palaniappan, R. Awang, Intelligent Heart Disease Prediction System Using Data Mining Techniques (2008), pp. 108–115
R. Wu, W. Peters, M.W. Morgan, The next generation of clinical decision support: linking evidence to best practice. J. Healthc. Inf. Manag. JHIM 16(4), 50 (2002)
S.D. Culler, M.L. Parchman, M. Przybylski, Factors related to potentially preventable hospitalizations among the elderly. Med. Care, 804–817 (1998)
N. Yiannakoulias, D. Schopflocher, L. Svenson, Using administrative data to understand the geography of case ascertainment. Chronic Dis. Can. 30(1), 20–28 (2009)
T. McCormick, C. Rudin, D. Madigan, A hierarchical model for association rule mining of sequential events: an approach to automated medical symptom prediction (2011)
E.S. Fisher, D.J. Malenka, J.E. Wennberg, N.P. Roos, Technology assessment using insurance claims: example of prostatectomy. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 6(2), 194–202 (1990)
M.E. Hossain, A. Khan, M.A. Moni, S. Uddin, Use of electronic health data for disease prediction: a comprehensive literature review. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (2019)
C. Zhang, L. Zhu, C. Xu, R. Lu, PPDP: an efficient and privacy-preserving disease prediction scheme in cloud-based e-Healthcare system. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 79, 16–25 (2018)
H. Yin, N.K. Jha, A health decision support system for disease diagnosis based on wearable medical sensors and machine learning ensembles. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 3(4), 228–241 (2017)
G. Bieber, M. Haescher, M. Vahl, Sensor requirements for activity recognition on smart watches (2013), pp. 1–6
D. Malathi, R. Logesh, V. Subramaniyaswamy, V. Vijayakumar, A.K. Sangaiah, Hybrid reasoning-based privacy-aware disease prediction support system. Comput. Electr. Eng. 73, 114–127 (2019)
A. Petrosian, D. Prokhorov, R. Homan, R. Dasheiff, D. Wunsch II, Recurrent neural network based prediction of epileptic seizures in intra-and extracranial EEG. Neurocomputing 30(1–4), 201–218 (2000)
Κ.Μ. Tsiouris, V.C. Pezoulas, M. Zervakis, S. Konitsiotis, D.D. Koutsouris, D.I. Fotiadis, A long short-term memory deep learning network for the prediction of epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 99, 24–37 (2018)
U.R. Acharya, S.L. Oh, Y. Hagiwara, J.H. Tan, H. Adeli, Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 100, 270–278 (2018)
H. Khan, L. Marcuse, M. Fields, K. Swann, B. Yener, Focal onset seizure prediction using convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65(9), 2109–2118 (2017)
R. San-Segundo, M. Gil-Martín, L.F. D’Haro-Enríquez, J.M. Pardo, Classification of epileptic EEG recordings using signal transforms and convolutional neural networks. Comput. Biol. Med. 109, 148–158 (2019)
R. Rosas-Romero et al., Prediction of epileptic seizures with convolutional neural networks and functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 111, 103355 (2019)
D. Jain, V. Singh, Feature selection and classification systems for chronic disease prediction: a review. Egypt. Inform. J. 19(3), 179–189 (2018)
S. Huda, J. Yearwood, H.F. Jelinek, M.M. Hassan, G. Fortino, M. Buckland, A hybrid feature selection with ensemble classification for imbalanced healthcare data: A case study for brain tumor diagnosis. IEEE Access 4, 9145–9154 (2016)
M. Chen, J. Yang, X. Zhu, X. Wang, M. Liu, J. Song, Smart home 2.0: Innovative smart home system powered by botanical IoT and emotion detection. Mob. Netw. Appl. 22(6), 1159–1169 (2017)
M. Chen, Y. Zhang, M. Qiu, N. Guizani, Y. Hao, SPHA: smart personal health advisor based on deep analytics. IEEE Commun. Mag. 56(3), 164–169 (2018)
K. He, J. Chen, R. Du, Q. Wu, G. Xue, X. Zhang, Deypos: deduplicatable dynamic proof of storage for multi-user environments. IEEE Trans. Comput. 65(12), 3631–3645 (2016)
M. Usama, B. Ahmad, W. Xiao, M.S. Hossain, G. Muhammad, Self-attention based recurrent convolutional neural network for disease prediction using healthcare data. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 190, 105191 (2020)
A.K. Verma, S. Pal, S. Kumar, Comparison of skin disease prediction by feature selection using ensemble data mining techniques. Inform. Med. Unlocked 16, 100202 (2019)
E. Alpaydin, Introduction to Machine Learning (MIT press, 2014)
N. Barakat, A.P. Bradley, M.N.H. Barakat, Intelligible support vector machines for diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 14(4), 1114–1120 (2010)
A. Ahlemeyer-Stubbe, S. Coleman, A Practical Guide to Data Mining for Business and Industry (Wiley, 2014)
Y. Bengio, Learning deep architectures for AI. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2(1), 1–127 (2009)
G.E. Hinton, R.R. Salakhutdinov, Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 313(5786), 504–507 (2006)
A. Subasi, Practical guide for biomedical signals analysis using machine learning techniques, a MATLAB based approach (Elsevier, First, 2019)
N. Fayyaz Khan, M. Kamil, A. Hussain, M. Sajjad, Detection and classification of vehicle-type by using convolution neural network. Presented at the The 4th International Conference on Next Generation Computing 2018 (2018)
S.N. Rakhade, F.E. Jensen, Epileptogenesis in the immature brain: emerging mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 5(7), 380 (2009)
M.J. England, C.T. Liverman, A.M. Schultz, L.M. Strawbridge, Epilepsy across the spectrum: promoting health and understanding.: a summary of the Institute of Medicine report. Epilepsy Behav. 25(2), 266–276 (2012)
K. Rasheed et al., Machine learning for predicting epileptic seizures using EEG signals: a review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng (2020), pp. 1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/rbme.2020.3008792
L. Sörnmo, P. Laguna, Bioelectrical Signal Processing in Cardiac and Neurological Applications, vol. 8 (Academic Press, San Diego, California, 2005)
A. Subasi, Biomedical signal analysis and its usage in healthcare, in Biomedical Engineering and its Applications in Healthcare (Springer, 2019), pp. 423–452
M.M.N. Mannan, M.A. Kamran, M.Y. Jeong, Identification and removal of physiological artifacts from electroencephalogram signals: A review. IEEE Access 6, 30630–30652 (2018)
H. Chu, C.K. Chung, W. Jeong, K.-H. Cho, Predicting epileptic seizures from scalp EEG based on attractor state analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 143, 75–87 (2017)
N.D. Truong et al., Convolutional neural networks for seizure prediction using intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram. Neural Netw. 105, 104–111 (2018)
Y. Gao, B. Gao, Q. Chen, J. Liu, Y. Zhang, Deep convolutional neural network-based epileptic electroencephalogram (EEG) signal classification. Front. Neurol. 11, 375 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00375
E. Alickovic, J. Kevric, A. Subasi, Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 39, 94–102 (2018)
X. Wei, L. Zhou, Z. Zhang, Z. Chen, Y. Zhou, Early prediction of epileptic seizures using a long-term recurrent convolutional network. J. Neurosci. Methods 327, 108395 (2019)
C.-L. Liu, B. Xiao, W.-H. Hsaio, V.S. Tseng, Epileptic Seizure prediction with multi-view convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 7, 170352–170361 (2019)
S. Rukhsar, Y. Khan, O. Farooq, M. Sarfraz, A. Khan, Patient-specific epileptic seizure prediction in long-term scalp eeg signal using multivariate statistical process control. IRBM 40(6), 320–331 (2019)
S. Sanei, Adaptive Processing of Brain Signals. The Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West Sussex, PO19 8SQ, (John Wiley & Sons, UK, 2013)
B.R. Bakshi, Multiscale PCA with application to multivariate statistical process monitoring. AIChE J. 44(7), 1596–1610 (1998)
B. Graimann, B. Allison, G. Pfurtscheller, Brain–computer interfaces: a gentle introduction, in Brain-Computer Interfaces (Springer, 2009), pp. 1–27
S. Siuly, Y. Li, Y. Zhang, EEG Signal Analysis and Classification (Springer, 2016)
A. Phinyomark, F. Quaine, S. Charbonnier, C. Serviere, F. Tarpin-Bernard, Y. Laurillau, EMG feature evaluation for improving myoelectric pattern recognition robustness. Expert Syst. Appl. 40(12), 4832–4840 (2013)
A. Wołczowski, R. Zdunek, Electromyography and mechanomyography signal recognition: Experimental analysis using multi-way array decomposition methods. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 37(1), 103–113 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2016.09.004
Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, G. Hinton, Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
J.-G. Lee et al., Deep learning in medical imaging: general overview. Korean J. Radiol. 18(4), 570–584 (2017)
C. Angermueller, T. Pärnamaa, L. Parts, O. Stegle, Deep learning for computational biology. Mol. Syst. Biol. 12(7), 878 (2016)
E. Asgari, M.R. Mofrad, Continuous distributed representation of biological sequences for deep proteomics and genomics. PLoS ONE 10(11), e0141287 (2015)
G. Li, C.H. Lee, J.J. Jung, Y.C. Youn, D. Camacho, Deep learning for EEG data analytics: a survey. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. e5199 (2019)
D. Hassabis, D. Kumaran, C. Summerfield, M. Botvinick, Neuroscience-inspired artificial intelligence. Neuron 95(2), 245–258 (2017)
V. Jain, H.S. Seung, S.C. Turaga, Machines that learn to segment images: a crucial technology for connectomics. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 20(5), 653–666 (2010)
I. Kiral-Kornek et al., Epileptic seizure prediction using big data and deep learning: toward a mobile system. EBioMedicine 27, 103–111 (2018)
A. Antoniades, L. Spyrou, C.C. Took, S. Sanei, Deep Learning for Epileptic Intracranial EEG Data (2016), pp. 1–6
N.D. Truong, A.D. Nguyen, L. Kuhlmann, M.R. Bonyadi, J. Yang, O. Kavehei, A generalised seizure prediction with convolutional neural networks for intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram data analysis. ArXiv170701976 (2017)
R. Begg, D.T. Lai, M. Palaniswami, Computational Intelligence in Biomedical Engineering (CRC Press, 2008)
M. Winterhalder, T. Maiwald, H. Voss, R. Aschenbrenner-Scheibe, J. Timmer, A. Schulze-Bonhage, The seizure prediction characteristic: a general framework to assess and compare seizure prediction methods. Epilepsy Behav. 4(3), 318–325 (2003)
A.H. Shoeb, Application of Machine Learning to Epileptic Seizure Onset Detection and Treatment (2009)
A.L. Goldberger et al., PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation, 101(23), Art. no. 23 (2000)
M. Hall, I. Witten, E. Frank, Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Kaufmann Burlingt. (2011)
M. Sokolova, N. Japkowicz, S. Szpakowicz, Beyond Accuracy, F-score and ROC: A Family of Discriminant Measures for Performance Evaluation (2006), pp. 1015–1021
J. Cohen, A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 20(1), 37–46 (1960)
Z. Yang, M. Zhou, Kappa statistic for clustered physician–patients polytomous data. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 87, 1–17 (2015)
N. LaPierre, C.J.-T. Ju, G. Zhou, W. Wang, MetaPheno: a critical evaluation of deep learning and machine learning in metagenome-based disease prediction. Methods 166, 74–82 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Subasi, A. (2021). Disease Prediction Using Artificial Intelligence: A Case Study on Epileptic Seizure Prediction. In: Marques, G., Kumar Bhoi, A., de la Torre Díez, I., Garcia-Zapirain, B. (eds) Enhanced Telemedicine and e-Health. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol 410. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70111-6_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-70111-6_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-70110-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-70111-6
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)