Abstract
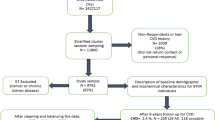
Metabolic dysfunctions are a set of metabolic risk factors that include abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, among others. Individuals with any of these metabolic dysfunctions are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Several parameters and anthropometric indices are used to detect metabolic dysfunctions, such as waist circumference and waist-height ratio (WHtR). The WHtR has an advantage over the body mass index (BMI) since the WHtR provides information on the distribution of body fat, particularly abdominal fat. Central fat distribution is associated with more significant cardio-metabolic health risks than total body fat. Machine learning techniques involve algorithms capable of predicting and analyzing data, increasing our understanding of the events being studied. k-means is a clustering algorithm that has been used in the detection of obesity. This research aims to apply the k-means grouping algorithm to study its capability as an impaired WHtR classifier. Accuracy (Acc), recall (Rec), and precision (P) were calculated. A database of 1863 subjects was used; the database consists of fifteen (15) anthropometric variables and two (2) indices; each anthropometric variable was measured for each participant. The results reported in this research suggest that the k-means clustering algorithm is an acceptable classifier of impaired WHtR subjects (\(Acc=0.81\), \(P=0.83\), and \(Rec=0.73\)). Besides, the k-means algorithm was able to detect subjects with overweight and fatty tissue deposits in the back and arm areas, suggesting that fat accumulation in these areas is directly related to abdominal fat accumulation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelsalam, H.A., Fayed, S.B., Mohamed, A.G.: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance in obese children as a predictor for metabolic syndrome. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 77(6), 5817–5824 (2019)
Anderberg, M.R.: Cluster Analysis for Applications: Probability and Mathematical Statistics: A Series of Monographs and Textbooks. Academic Press, Cambridge (2014)
Ashtary-Larky, D., Daneghian, S., Alipour, M., Rafiei, H., Ghanavati, M., Mohammadpour, R., Kooti, W., Ashtary-Larky, P., Afrisham, R.: Waist circumference to height ratio: better correlation with fat mass than other anthropometric indices during dietary weight loss in different rates. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab., 16(4) (2018)
Ashwell, M., Gunn, P., Gibson, S.: Waist-to-height ratio is a better screening tool than waist circumference and BMI for adult cardiometabolic risk factors: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 13(3), 275–286 (2012)
Basu, S., Yudkin, J.S., Kehlenbrink, S., Davies, J.I., Wild, S.H., Lipska, K.J., Sussman, J.B., Beran, D.: Estimation of global insulin use for type 2 diabetes, 2018–30: a microsimulation analysis. Lancet Diab. Endocrinol. 7(1), 25–33 (2019)
Browning, L.M., Hsieh, S.D., Ashwell, M.: A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0.5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr. Res. Rev. 23(2), 247–269 (2010)
Carr, M.C., Brunzell, J.D.: Abdominal obesity and dyslipidemia in the metabolic syndrome: importance of type 2 diabetes and familial combined hyperlipidemia in coronary artery disease risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89(6), 2601–2607 (2004)
Cho, N., Shaw, J., Karuranga, S., Huang, Y., da Rocha Fernandes, J., Ohlrogge, A., Malanda, B.: IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diab. Res. Clin. Pract. 138, 271–281 (2018)
Costello, Z., Martin, H.G.: A machine learning approach to predict metabolic pathway dynamics from time-series multiomics data. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 4(1), 1–14 (2018)
Dong, J., Wang, S.S., Chu, X., Zhao, J., Liang, Y.Z., Yang, Y.B., Yan, Y.X.: Optimal cut-off point of waist to height ratio in Beijing and its association with clusters of metabolic risk factors. Curr. Med. Sci. 39(2), 330–336 (2019)
Farina, P.V.R., Severeyn, E., Wong, S., Turiel, J.P.: Study of cardiac repolarization during oral glucose tolerance test in metabolic syndrome patients. In: 2012 Computing in Cardiology, pp. 429–432. IEEE (2012)
Fawcett, T.: An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 27(8), 861–874 (2006)
Fitzmaurice, C., Allen, C., Barber, R.M., Barregard, L., Bhutta, Z.A., Brenner, H., Dicker, D.J., Chimed-Orchir, O., Dandona, R., Dandona, L., et al.: Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 3(4), 524–548 (2017)
Ginsberg, H.N., MacCallum, P.R.: The obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus pandemic: Part i. increased cardiovascular disease risk and the importance of atherogenic dyslipidemia in persons with the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Cardiometabolic Syndr. 4(2), 113–119 (2009)
Goossens, G.H.: The metabolic phenotype in obesity: fat mass, body fat distribution, and adipose tissue function. Obes. Facts 10(3), 207–215 (2017)
Grundy, S.M., Cleeman, J.I., Daniels, S.R., Donato, K.A., Eckel, R.H., Franklin, B.A., Gordon, D.J., Krauss, R.M., Savage, P.J., Smith Jr., S.C., et al.: Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American heart association/national heart, lung, and blood institute scientific statement. Circulation 112(17), 2735–2752 (2005)
Hajian-Tilaki, K., Heidari, B.: Comparison of abdominal obesity measures in predicting of 10-year cardiovascular risk in an Iranian adult population using ACC/AHA risk model: a population based cross sectional study. Diab. Metab. Syndr.: Clin. Res. Rev. 12(6), 991–997 (2018)
Hansel, B., Giral, P., Nobecourt, E., Chantepie, S., Bruckert, E., Chapman, M.J., Kontush, A.: Metabolic syndrome is associated with elevated oxidative stress and dysfunctional dense high-density lipoprotein particles displaying impaired antioxidative activity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89(10), 4963–4971 (2004)
Hardiman, S.L., Bernanthus, I.N., Rustati, P.K., Susiyanti, E.: Waist circumference as a predictor for blood glucose levels in adults. Universa Medicina 28(2), 77–82 (2016)
Hartigan, J.A., Wong, M.A.: Algorithm as 136: a k-means clustering algorithm. J. Royal Stat. Soc. Ser. c (Appl. Stat.) 28(1), 100–108 (1979)
He, J., Ma, R., Liu, J., Zhang, M., Ding, Y., Guo, H., Mu, L., Zhang, J., Wei, B., Yan, Y., et al.: The optimal ethnic-specific waist-circumference cut-off points of metabolic syndrome among low-income rural Uyghur adults in far western China and implications in preventive public health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 14(2), 158 (2017)
Herrera, H., Rebato, E., Arechabaleta, G., Lagrange, H., Salces, I., Susanne, C.: Body mass index and energy intake in Venezuelan university students. Nutr. Res. 23(3), 389–400 (2003)
Hubert, H., Guinhouya, C.B., Allard, L., Durocher, A.: Comparison of the diagnostic quality of body mass index, waist circumference and waist-to-height ratio in screening skinfold-determined obesity among children. J. Sci. Med. Sport 12(4), 449–451 (2009)
Kontis, V., Cobb, L.K., Mathers, C.D., Frieden, T.R., Ezzati, M., Danaei, G.: Three public health interventions could save 94 million lives in 25 years: global impact assessment analysis. Circulation 140(9), 715–725 (2019)
Kuciene, R., Dulskiene, V.: Associations between body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio, and high blood pressure among adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–11 (2019)
Lee, J.E.: Simply the best: anthropometric indices for predicting cardiovascular disease. Diab. Metab. J. 43(2), 156–157 (2019)
Li, L., Song, Q., Yang, X.: Categorization of \(\beta \)-cell capacity in patients with obesity via ogtt using k-means clustering. Endocr. Connections 9(2), 135–143 (2020)
Lopes, H.F., Corrêa-Giannella, M.L., Consolim-Colombo, F.M., Egan, B.M.: Visceral adiposity syndrome. Diabetology Metab. Syndr. 8(1), 40 (2016)
MacQueen, J.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In: Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Statistics, vol. 1, pp. 281–297. University of California Press, Berkeley, Calif. (1967). https://projecteuclid.org/euclid.bsmsp/1200512992
Marusteri, M., Bacarea, V.: Comparing groups for statistical differences: how to choose the right statistical test? Biochemia Medica: Biochemia Medica 20(1), 15–32 (2010)
Moussa, H.N., Alrais, M.A., Leon, M.G., Abbas, E.L., Sibai, B.M.: Obesity epidemic: impact from preconception to postpartum. Future Sci. OA, 2(3), FSO137 (2016)
Niehues, J.R., Gonzales, A.I., Lemos, R.R., Bezerra, P.P., Haas, P.: Prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents from the age range of 2 to 19 years old in Brazil. Int. J. Pediatr. 2014, (2014)
Organization, W.H.: Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. World Health Organization (2000)
Pang, S.J., Man, Q.Q., Song, S., Song, P.K., Liu, Z., Li, Y.Q., Jia, S.S., Wang, J.Z., Zhao, W.H., Zhang, J.: Relationships of insulin action to age, gender, body mass index, and waist circumference present diversely in different glycemic statuses among Chinese population. J. Diab. Res. 2018, (2018)
Perpiñan, G., Severeyn, E., Altuve, M., Wong, S.: Classification of metabolic syndrome subjects and marathon runners with the k-means algorithm using heart rate variability features. In: 2016 XXI Symposium on Signal Processing, Images and Artificial Vision (STSIVA), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2016)
Powers, D.M.W.: Evaluation: from precision, recall and f-measure to roc, informedness, markedness and correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2(1), 37–63 (2011)
Ramírez-Vélez, R., López-Cifuentes, M.F., Correa-Bautista, J.E., González-Ruíz, K., González-Jiménez, E., Córdoba-Rodríguez, D.P., Vivas, A., Triana-Reina, H.R., Schmidt-RioValle, J.: Triceps and subscapular skinfold thickness percentiles and cut-offs for overweight and obesity in a population-based sample of schoolchildren and adolescents in Bogota. Colombia. Nutrients 8(10), 595 (2016)
Rivera-Soto, W.T., Rodríguez-Figueroa, L.: Is waist-to-height ratio a better obesity risk-factor indicator for puerto rican children than is BMI or waist circumference? Puerto Rico Health Sci. J. 35(1) (2016)
Rousseeuw, P.J.: Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 20, 53–65 (1987)
Sgambat, K., Clauss, S., Moudgil, A.: Comparison of BMI, waist circumference, and waist-to-height ratio for identification of subclinical cardiovascular risk in pediatric kidney transplant recipients. Pediatr. Transplant. 22(8), e13300 (2018)
Sgambat, K., Roem, J., Mitsnefes, M., Portale, A.A., Furth, S., Warady, B., Moudgil, A.: Waist-to-height ratio, body mass index, and cardiovascular risk profile in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 33(9), 1577–1583 (2018)
Shen, F., Wang, Y., Sun, H., Zhang, D., Yu, F., Yu, S., Han, H., Wang, J., Ba, Y., Wang, C., et al.: Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with triceps skin fold thickness and body fat percentage but not with body mass index or waist circumference in Han Chinese. Lipids Health Dis. 18(1), 97 (2019)
Stocks, T., Lukanova, A., Bjørge, T., Ulmer, H., Manjer, J., Almquist, M., Concin, H., Engeland, A., Hallmans, G., Nagel, G., et al.: Metabolic factors and the risk of colorectal cancer in 580,000 men and women in the metabolic syndrome and cancer project (me-can). Cancer 117(11), 2398–2407 (2011)
Swainson, M.G., Batterham, A.M., Tsakirides, C., Rutherford, Z.H., Hind, K.: Prediction of whole-body fat percentage and visceral adipose tissue mass from five anthropometric variables. PloS One 12(5), e0177175 (2017)
Tchkonia, T., Morbeck, D.E., Von Zglinicki, T., Van Deursen, J., Lustgarten, J., Scrable, H., Khosla, S., Jensen, M.D., Kirkland, J.L.: Fat tissue, aging, and cellular senescence. Aging Cell 9(5), 667–684 (2010)
Velásquez, J., Severeyn, E., Herrera, H., Encalada, L., Wong, S.: Anthropometric index for insulin sensitivity assessment in older adults from Ecuadorian highlands. In: 12th International Symposium on Medical Information Processing and Analysis, vol. 10160, p. 101600S. International Society for Optics and Photonics (2017)
Velásquez, J., Herrera, H., Encalada, L., Wong, S., Severeyn, E.: Análisis dimensional de variables antropométricas y bioquímicas para diagnosticar el síndrome metabólico. Maskana 8, 57–67 (2017)
Vintimilla, C., Wong, S., Astudillo-Salinas, F., Encalada, L., Severeyn, E.: An aide diagnosis system based on k-means for insulin resistance assessment in eldery people from the Ecuadorian highlands. In: 2017 IEEE Second Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2017)
Visscher, T.L., Seidell, J.C.: The public health impact of obesity. Ann. Rev. Public Health 22(1), 355–375 (2001)
Zerf, M., Atouti, N., Ben, F.A.: Abdominal obesity and their association with total body: fat distribution and composition. case of Algerian teenager male high school students. Phys. Educ. Stud. 21(3), 146–151 (2017)
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by the Research and Development Deanery of the Simón Bolívar University (DID) and the Research Direction of the Ibagué University. Full acknowledgment is given to David Powers, author of “Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Factor to ROC, Informedness, Markedness & Correlation" (BioInfo Publications™).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
La Cruz, A., Severeyn, E., Wong, S., Perpiñan, G. (2021). Classification of Impaired Waist to Height Ratio Using Machine Learning Technique. In: Botto-Tobar, M., S. Gómez, O., Rosero Miranda, R., Díaz Cadena, A. (eds) Advances in Emerging Trends and Technologies. ICAETT 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1302. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63665-4_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63665-4_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-63664-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-63665-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)