Abstract
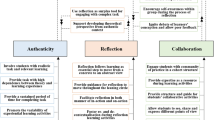
A moderate experiential learning is proposed as a framework to provide learners with significant experiences in data science. In this approach, the student learns through reflection on doing, abstract conceptualization, gamification and learning transferring; instead of being a recipient of already made content. Data science pedagogy has repeated a number of patterns that can be detrimental to the student. The proposed moderate experiential learning has been adopted together with other two learning approaches in a data science master subject for comparative purposes: a traditional learning approach, and a strict experiential learning adoption. Two evaluation studies have been conducted to compare these three different learning approaches. The results indicate that students do not actively support the strict experiential learning, but the moderate approach, where some guidelines are provided to face the realistic experience.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Association for Experiential Education: The principles of experiential education in practice (2018). http://www.aee.org/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=110:what-is-ee&catid=20:other&Itemid=260
Bennett, J., Lanning, S.: The Netflix prize. In: KDD Cup and Workshop in conjunction with KDD. ACM, San Jose (2007)
Kolb, D.A.: Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development, 2nd edn. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River (2015)
Kuhn, M.: Caret: classification and regression training (2018). https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=caret
Mayer-Schonberger, V., Cukier, K.: Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform How We Live, Work, and Think. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Boston (2013)
Qualters, D.M.: Making the most of learning outside the classroom. New Dir. Teach. Learn. 124, 95–99 (2010)
Reynolds, M., Vince, R.: Handbook of Experiential Learning and Management Education. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2008)
Serrrano, E., Manrique, D., Amador, E.: JupyterDS: a software tool for experiential learning in data science. Registration in the intellectual property registry of Madrid No. M-004029/2018 (2018)
Shiralkar, S.: IT Through Experiential Learning: Learn, Deploy and Adopt IT Through Gamification. Apress, New York (2016)
Silverman, M.L.: The Handbook of Experiential Learning. Pfeiffer, San Francisco (2007)
Witten, I.H., Frank, E., Hall, M.A.: Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington (2011)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Universidad Politécnica de Madrid under Grant IE1718.1003; Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad, Gobierno de España (ES) under Grant TIN2016-78011-C4-4-R, AEI/FEDER, UE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Serrano, E., Manrique, D. (2020). A Moderate Experiential Learning Approach Applied on Data Science. In: Gennari, R., et al. Methodologies and Intelligent Systems for Technology Enhanced Learning, 9th International Conference. MIS4TEL 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1007 . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23990-9_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23990-9_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-23989-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-23990-9
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)