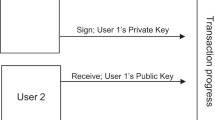
Abstract
Unified access to anonymous records through a trustworthy system is needed in our increasingly globalised world that still suffers from profoundly disconnected health care services. Emergencies are followed by redundant, costly and slow medical examinations without a global health data sharing mechanism. We establish the foundations of a decentralised healthcare ledger where patients decide what to share, with who, and with minimal costs. We review the state-of-the-art of transparent, auditable and interactive Blockchain-based healthcare studies, developing ClinicAppChain. Our solution features authentication, confidentiality and permissioned data sharing, considering the EU data protection regulation of 2018. ClinicAppChain is a cross-platform low-cost Blockchain prototype that empowers patients, hospitals, researchers, pharmaceuticals and insurance industries without crypto-currencies involved, and with a negligible energy foot-print (7.7 watts per node).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
Up to date, this was the only working effort that stopped to be compatible after Fabric 1.0 (2 years ago) https://github.com/Cleanshooter/hyperledger-pi-composer.
- 5.
References
Albeyatti, A.: White paper: medicalchain. MedicalChain self-publication (2018)
Andoni, M., Robu, V., Flynn, D., Abram, S., Geach, D., Jenkins, D., McCallum, P., Peacock, A.: Blockchain technology in the energy sector: a systematic review of challenges and opportunities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 100, 143–174 (2019)
Androulaki, E., Barger, A., Bortnikov, V., Cachin, C., Christidis, K., De Caro, A., Enyeart, D., Ferris, C., Laventman, G., Manevich, Y., et al.: Hyperledger fabric: a distributed operating system for permissioned blockchains. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth EuroSys Conference, p. 30. ACM (2018)
Brown, R.G., Carlyle, J., Grigg, I., Hearn, M.: Corda: An Introduction. CEV (2016)
Decker, C., Wattenhofer, R.: Bitcoin transaction malleability and MtGox. In: European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, pp. 313–326. Springer (2014)
Ekblaw, A., Azaria, A., Halamka, J.D., Lippman, A.: A case study for blockchain in healthcare: “medrec” prototype for electronic health records and medical research data. In: Proceedings of IEEE Open & Big Data Conference, vol. 13, p. 13 (2016)
Hintzman, Z.: Comparing blockchain implementations. In: Cable-Tec Expo (2017)
Iansiti, M., Lakhani, K.R.: The truth about blockchain. Harvard Bus. 95(1), 118–127 (2017)
Jiang, S., Cao, J., Wu, H., Yang, Y., Ma, M., He, J.: BlocHIE: a blockchain-based platform for healthcare information exchange. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), pp. 49–56. IEEE (2018)
Kolvart, M., Poola, M., Rull, A.: Smart contracts. In: The Future of Law and ETechnologies, pp. 133–147. Springer (2016)
Kombe, C., Ally, M., Sam, A.: A review on healthcare information systems and consensus protocols in blockchain technology. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Explor. 5(49), 473–483 (2018)
Kuo, T.T., Kim, H.E., Ohno-Machado, L.: Blockchain distributed ledger technologies for biomedical and health care applications. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 24(6), 1211–1220 (2017)
Mettler, M.: Blockchain technology in healthcare: the revolution starts here. In: 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), pp. 1–3. IEEE (2016)
Michael, J., Cohn, A., Butcher, J.R.: Blockchain technology. J. 1, 7 (2018)
O’Dwyer, K.J., Malone, D.: Bitcoin mining and its energy footprint. In: Proceedings of the 25th IET Irish Signals & Systems Conference, IET (2014)
Poon, J., Dryja, T.: The bitcoin lightning network: scalable off-chain instant payments. Lightning Network self-publication (2016)
Rouhani, S., Humphery, D.G., Butterworth, L., Deters, R., Simmons, A.D.: Medichain: a secure decentralized medical data asset management system. J., 1533–1538 (2018)
Stagnaro, C.: Innovative blockchain uses in health care. Freed Associates (2017)
Wood, G.: Ethereum: a secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger. Ethereum Proj. Yellow Pap. 151, 1–32 (2014)
Xia, Q., Sifah, E.B., Asamoah, K.O., Gao, J., Du, X., Guizani, M.: Medshare: trust-less medical data sharing among cloud providers b. IEEE Access 5, 14757–14767 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Work by Munoz and Fuentes is supported by the projects MAGIC P12-TIC1814 and HADAS TIN2015-64841-R (co-financed by FEDER funds). Work by Constantinescu and Asenjo is supported by the project TIN2016-80920-R, funded by the Spanish Government. ClinicAppChain has been supported by IMFAHE Foundation-Nodal Award of 2018. We are particularly grateful to other members of the awarded team that have guided us in the sanitary side and legal aspects: Esther Herrera, Laura Timanfaya, Patricia Rodríguez and Myriam Martínez.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Munoz, DJ., Constantinescu, DA., Asenjo, R., Fuentes, L. (2020). ClinicAppChain: A Low-Cost Blockchain Hyperledger Solution for Healthcare. In: Prieto, J., Das, A., Ferretti, S., Pinto, A., Corchado, J. (eds) Blockchain and Applications. BLOCKCHAIN 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1010 . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23813-1_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-23813-1_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-23812-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-23813-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)