Abstract
Adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL) is a distinct peripheral T-lymphocytic malignancy etiologically associated with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. The diversity in clinical features and prognosis of patients with this disease has led to its subtype classification into four categories, acute, lymphoma, chronic, and smoldering types. The chronic or smoldering subtypes are considered indolent and are usually managed with watchful-waiting until disease progression. Patients with acute or lymphoma subtypes generally have a very poor prognosis due to multidrug-resistance of ATL cells, a large tumor burden with multi-organ failure, hypercalcemia, and/or frequent infectious complications due to a profound T-cell immunodeficiency. A treatment strategy based on the clinical subtypes, prognostic factors, and response to initial therapy is suggested including watchful-waiting approach, intensive chemotherapy, interferon-α zidobudine therapy, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and targeted-therapies. Several new agent-trials for ATL are ongoing and in preparation, including a defucosylated humanized anti-CC chemokine receptor 4 monoclonal antibody, IL2-fused with diphtheria toxin, histone deacetylase inhibitors, a purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitor, a proteasome inhibitor, and lenalidomide.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
- Proviral Load
- Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase
- Japan Clinical Oncology Group
- Biweekly Chop
- Purine Nucleotide Phosphorylase
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Introduction
Adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL) was first described in 1977 by Uchiyama and Takatsuki as a distinct clinico-pathological entity with a suspected viral etiology because of the clustering of the disease in the southwest region of Japan [1]. Subsequently, a novel RNA retrovirus, human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-1), was isolated from a cell line established from leukemic cells of an ATL patient, and the finding of a clear association with ATL led to its inclusion among human carcinogenic pathogens [2–5]. In the mid-1980s and 1990s, several inflammatory diseases were reported to be associated with HTLV-1 [6–10]. At the same time, endemic areas for the virus and diseases have been found [reviewed in 11–13]. Diversity in ATL has been recognized and the subtype classification of the disease was proposed [14]. This chapter will characterize HTLV-1 and review the current recognition of ATL focusing on treatment of the disease.
HTLV-1 Structure and Biology
HTLV-1 is a C-type oncovirus in the RNA retrovirus family [12, 13, 15]. Its genome of approximately 9 kb encodes three structural proteins, group angigen (gag), reverse transcriptase (pol), and envelop (env), the genes for which are flanked by 5′ and 3′ long terminal repeats (LTRs). In the 3′portion of the genome is a pX region that encodes the Tax, Rex, p21, p12, p13, and p30 proteins in its various reading frames [16, 17] (Fig. 8.1). Both Rex, a post-transcriptional regulator of viral expression, and Tax, a viral transcription factor co-operate with other viral products and cellular proteins to mediate viral replication [18, 19]. Antisense transcripts of the HTLV-1 provirus were reported. The transcripts can encode a novel basic leucine zipper protein, named HBZ, which interacts with several host genes and suppresses the activity of Tax [20–22]. Various isoforms of HBZ were reported to be steadily expressed in HTLV-1-infected cells and ATL cells in contrast to other viral genes, suggesting an important role in the development of ATL.
Structure of HTLV-1. HTLV-1 encodes accessory and regulatory genes in the pXregion as well as viral structure genes. [Based on data from Satou Y, Matsuoka M. HTLV-1 and the host immune system: how the virus disrupts immune regulation, leading to HTLV-1-associated diseases. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2010; 50(1):1–8.]
Methods of Detecting HTLV-1
Serological, virological, and molecular examinations can detect an HTLV-1 infection. As with other human retroviruses, HTLV-1 causes a persistent life-long infection after it synthesizes copies of DNA by reverse transcriptase and integrates into the host’s genome as a provirus.
Specific antibodies against HTLV-1 can be detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), particle aggregation (PA), immunofluorescence microscopy, Western blotting (WB), or radioimmunoprecipitation. ELISA and PA are frequently used as screening assays [23–26]. To distinguish HTLV-1 from HTLV-2, which is less pathogenic, WB is usually necessary [27].
Fresh HTLV-1-infected cells from ATL patients or HTLV-1 carriers seldom express viral proteins except for HBZ [28, 29]. In contrast, in the presence of IL-2, short-term cultured HTLV-1-infected cells or established long-term T-cell lines usually produce viral particles and viral proteins, as demonstrated by electron microscopy and immunolabeling using antibodies to HTLV-1, respectively.
The clonal integration of HTLV-1 proviral DNA into infected T-cells can be demonstrated by Southern blot, inverse polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and/or ligation PCR assays [30–33]. Several investigators have analyzed the implications of the integration pattern of HTLV-I provirus in the progression of ATL [34, 35]. Neoplastic cells of ATL patients have only one complete copy of the HTLV-I provirus per cell in some cases (complete-type), but multiple complete copies in the others (multiple-type). The HTLV-I proviruses in the remaining patients have a defective genome (defective-type). The median survival times for patients were 7 months, 24 months, and 33 months for defective-type, complete-type, and multiple-type ATL, respectively (P = 0.006). Among the 52 patients examined, the HTLV-I integration patterns changed in four patients (8%). In three of these four, the rearrangements of the TCR-β gene changed concomitantly, suggesting the appearance of a new ATL clone. The researchers concluded that the frequent clonal change of ATL at crisis reflects the emergence of multiple premalignant clones in viral leukemogenesis. Tamiya and coworkers reported the presence of two types of defective virus. Among them, the type 2 defective virus with a deletion that includes the 5′ LTR was found more frequently in the acute and lymphoma types (39%, 21 of 54) than in the chronic type (6%, 1 of 18). It is postulated that the high frequency of the type 2 virus is caused by the genetic instability of the HTLV-I provirus and that the defective virus is selected because it escapes from the immune surveillance system in the host. Southern blotting and inverse PCR assays have sensitivity to detect the clonal disease, being able to identify the virus in a population with at least 5% and 1% of cells infected, respectively [33]. Also, about 20% of patients with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM)/tropical spastic paraparesis (TSP) and a small proportion of healthy HTLV-1 carriers have monoclonal HTLV-1 integration which can be detected by Southern blotting and/or inverse PCR [36, 37].
Epidemiology of HTLV-1
The three major routes of HTLV-1 transmission are mother-to-child infections via breast milk, sexual intercourses, and blood transfusions. Otherwise, HTLV-1 is not easily transmittable, since cell-to-cell contact is presumably required. Vertical transmission from mother to child is caused by breast-feeding beyond 4 to 6 months of age, after which time the protective IgG maternal antibodies decline [38]. HTLV-1-infected mononuclear cells are present in breast milk [39]. The overall rate of infection among breast-fed children from carrier mothers has been estimated at 10–30% [40]. Sexual transmission of HTLV-1 more frequently occurs from men to women than women to men. Infection by transfusion of contaminated cellular blood products is presumably the most efficient mode of transmission [41]. In contrast, fresh frozen plasma, which is acellular, is not infectious [42]. The transmission of HTLV-1 between intravenous drug abusers has been reported [43].
The Southwestern district of Japan has the highest prevalence of HTLV-1 infection in the world, but this infection is also endemic in the Caribbean basin, parts of Africa, Latin America, the Middle East, and the Pacific region [41, 44–48]. Many of the HTLV-1 carriers and ATL patients in the USA and Europe are immigrants from the above described endemic areas [49].
The seroprevalence of HTLV-1 in endemic areas is low and stable among children, but increases gradually with age, especially in women over 50 year of age [50]. In a cohort study in an endemic region of Japan, the seroprevalence of HTLV-1 in individuals between 16 and 39 years of age was 10% in both sexes; in contrast, the prevalence sky-rocketed to 30% in men and 50% in women over the age of 70 [51]. For several decades, the prevalence of HTLV-1 has declined drastically in endemic areas in Japan, probably because of birth cohort effects [52]. The elimination of HTLV-1 in endemic areas is now considered possible due to the natural decrease in the prevalence as well as intervention of transmission through blood transfusion and breast feeding.
HTLV-1-Related Diseases
HTLV-1 is associated with the development of ATL [1–5, 11–13], as well as HAM/TSP, a progressive form of chronic spastic myelopathy with demyelination of the spinal cord motor neurons, and HTLV-1-associated uveitis (HAU), a subacute inflammatory condition in which vitreous opacities are associated with mild iritis and mild retinal vasculitis [6, 7, 9]. Staphylococcal and streptococcal skin infections are common in the infective dermatitis (ID) syndrome described in Jamaica in association with HTLV-I infections in childhood [8]. Those individuals with ID were reported to be susceptible to ATL and HAM/TSP. ID was reported first in Jamaica and subsequently in Brazil and other countries of South America but rarely in Japan. In contrast, HAU was first reported in Japan and rarely occur in other countries. Other conditions reportedly associated with HTLV-1 include Sjogren’s syndrome, polymyositis, alveolitis, arthritis, thyroiditis, and immune suppression [53–56].
Adult T-Cell Leukemia-Lymphoma
ATL is a distinct peripheral T-lymphocytic malignancy associated with a retrovirus designated human T-cell leukemia virus type I or human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-1) [1, 11–13, 57, 58]. Major prognostic indicators for ATL, which have been elucidated in 854 patients with ATL in Japan, the Lymphoma Study Group (LSG) of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group (JCOG) by multivariate analysis, were advanced performance status (PS), high lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) level, age of 40 years or more, more than three involved lesions, and hypercalcemia [56]. Also, a subclassification was proposed based on prognostic factors and clinical features of the disease (Table 8.1) [14]. The leukemic subtypes include all of the acute and chronic types and most of the smoldering type. The acute type has a rapid course with leukemic manifestation (> = 2% ATL cells) with or without lymphocytosis (>4 × 109/L) including ATL cells and most of the characteristic features of ATL-generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, skin involvement, other organ infiltration as shown in Figure 8.2, a high LDH value, and hypercalcemia. The symptoms and signs include abdominal pain, diarrhea, ascites, jaundice, unconsciousness, dyspnea, pleural effusion, cough, sputum, and chest X-ray abnormalities because of organ involvement, hypercalcemia, and/or opportunistic infections. The smoldering type shows an indolent course and 5% or more of leukemic cells in the peripheral blood without leukocytosis, but may also include skin/lung involvement. The calcium level is less than the upper limit and LDH level is less than 1.5 times the upper limit in smoldering ATL. The chronic type, with absolute lymphocytosis (4 × 109/L) less frequently showing flower cell morphology than the acute type, is occasionally associated with skin involvement and lymphadenopathy and also usually shows a relatively indolent course. The calcium level is less than the upper limit and the LDH level is less than double the upper limit of the chronic type. The lymphoma type presents with the manifestations of a lymphoma without leukemic cells, frequently with high LDH/Ca levels, a rapid course, and symptoms and signs similar to the acute type. In case of ATL, clinical subtype is more important than Ann Arbor stage for predicting prognosis and deciding treatment.
(a) Leukemic cells (the so-called flower cells) showing characteristic polymorphic nuclei with condensed chromatin and agulanular and basophilic cytoplasm. (b) Photograph of skin lesion in a patient with acute-type ATL. (c) Histology of skin infiltration of ATL cells in the same patient; infiltrating ATL cells are present in the epidermis forming a Pautrer’s micro-abscess.
Additional factors associated with a poor prognosis include thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, bone marrow involvement, a high interleukin (IL)-5 serum-level, CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) expression, lung resistance-related protein, p53 mutation, and p16 deletion by multivariate analysis [59–65]. Specific for the chronic type of ATL, high LDH, high blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and low albumin levels were identified as factors for a poor prognosis by multivariate analysis [11]. Primary cutaneous tumoral type, although generally included among smoldering ATL, had a poor prognosis in one uni-variate analysis [66].
Epidemiology of ATL
The average age at onset of ATL in Japan is 57 years, which is about 15 years older than in the Caribbean, South America, and Africa [67–69]. This may reflect unknown environmental or ethnic cofactors in the multi-step leukemogenesis of this disease. The estimated annual incidence in Japan is about 1 per 1,000 HTLV-1 carriers over 40 years of age, with males affected about twice as often [70]. The cumulative life time risk for ATL among HTLV-1 carriers has been estimated at 1–5% in both sexes in Japan and in Jamaica [71, 72]. HTLV-1 infection early in life, presumably from breast feeding, is crucial in the development of ATL; 100% of mothers of ATL patients examined were HTLV-1 carriers as compared to about 30% of mothers of HAM/TSP patients [73]. HTLV-1infection by blood transfusion is associated with a higher risk for the development of HAM/TSP than infection by other routes [74]. In contrast, very few cases of ATL after HTLV-1 infection by blood transfusion have been reported [75, 76]. Interestingly, those affected had blood transfusions for a preceding hematological malignancy, and developed ATL within 11 years after HTLV-1infection. Factors reportedly associated with the onset of ATL include: HTLV-1 infection early in life, increase in age, male sex, family history of ATL, past history of infective dermatitis, smoking of tobacco, serum titers of antibody against HTLV-1, and several HLA subtypes [77–82].
Definitive risk factors for the development of ATL among asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers remain unclear. Recently, HTLV-1 proviral loads have been proposed as an important predictor of ATL, but only a few small prospective studies have been conducted. Recently, Iwanaga and colleagues evaluated 1,218 asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers (426 males and 792 females) who were enrolled during 2002–2008 for a prospective study on the development of ATL [83]. The proviral load at enrollment was significantly higher in males than females (median, 2.10 vs. 1.39 copies/100 peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC; P < 0.0001)), in those aged 40 or more years and in those with a family history of ATL. During the follow-up period, 14 participants developed acute ATL. Their baseline proviral loads were high (range, 4.17–28.58 copies/100 PBMC). Multivariate Cox regression analyses indicated that not only a higher proviral load but also advanced age, a family history of ATL, and the first opportunity for HTLV-1 testing during treatment for other diseases were independent risk factors for the progression of ATL from a carrier status.
Clinical Features
ATL patients show a variety of clinical manifestations because of various complications of organ involvement by ATL cells, opportunistic infections, and/or hypercalcemia [11–14]. These three often contribute to the extremely high mortality of the disease. Lymph node, liver, spleen, and skin lesions are frequently observed. Although less frequent, the digestive tract, the lungs, the central nervous system, bone, and/or other organs may be involved. Large nodules, plaques, ulcers, and erythroderma are common skin lesions [66 84]. Immune suppression is common. Approximately 26% of 854 patients with ATL had active infections at diagnosis in a prior nationwide study in Japan [14]. The incidence was highest in the chronic and smoldering types (36%) and lower in the acute (27%) and lymphoma types (11%). The infections were bacterial in 43%, fungal in 31%, protozoal in 18%, and viral in 8% of patients. The immunodeficiency at presentation in ATL patients can be exacerbated by cytotoxic chemotherapy. Individuals with indolent ATL might have no manifestation of the disease and are identified only by health check-ups and laboratory examinations.
Laboratory Findings
ATL cells are usually detected quite easily in the blood of affected individuals except for the smoldering type with mainly skin manifestations and lymphoma type [14]. These so called “flower cells” have highly indented or lobulated nuclei with condensed chromatin, small or absent nucleoli, and an agranular and basophilic cytoplasm (Figure 8.2A) [85]. In addition to polylobulated cells, some large blastoid cells with a basophilic cytoplasm are almost always observed in the blood film. Furthermore, the diversity of cell morphology in ATL is associated with prognostic factors, an aberrant immmunophenotype, and a defective HTLV-1 genotype [86]. Five percent or more abnormal T-lymphocytes in peripheral blood confirmed by cytology and immunophenotyping are required to diagnose ATL in cases without histologically proven tumor lesions [14].
The histological analysis of aberrant cutaneous lesions or lymph nodes is essential for the diagnosis of the smoldering type with mainly skin manifestations and lymphoma type of ATL, respectively. Because ATL cells in the skin and lymph node can vary in size from small to large and in form from pleomorphic to anaplastic and Hodgkin-like cell with no specific histological pattern of involvement, differentiating between Sezary syndrome, other peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), and Hodgkin lymphoma versus ATL can at times be difficult without examinations for HTLV-1 serotype/genotype [13, 87].
The white blood cell count ranges from normal to 500 × 109/L. Marked leukocytosis of >30 and lymphocytes of 15× have been observed in about 40% of acute ATLs and 25% of chronic ATLs, but not in the other two subtypes (lymphoma, smoldering) [14]. Granulocytosis of more than 8× is frequently observed (about 40% of acute type and 15% of the other three types) even in the absence of infection. Eosinophilia is frequent (21%) as compared to other T- or B-lymphomas. Neutrophilia and eosinophilia are presumably related to the release of cytokines {chiefly granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and Interleukin (IL)-5} by malignant cells. Anemia and thrombocytopenia are less frequently observed, probably because much of the bone marrow is spared by the leukemia. Some of the hematological abnormalities were associated with the prognosis of ATL as described previously.
Hypercalcemia is the most distinctive laboratory abnormality in ATL as compared to other lymphoid malignancies and is observed in 31% of patients (50% in acute type, 17% in lymphoma type, and 0% in the other two types) at onset [14]. Individuals with hypercalcemia do not usually have osteolytic bone lesions. Parathyroid hormone-related protein or receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand produced by ATL cells is considered the main factor causing hypercalcemia [88, 89].
Similar to serum LDH, β2-microglobulin, and serum thymidine kinase levels reflecting disease bulk/activity, the level of the soluble form of interleukin (IL)-2 receptor alpha-chain is elevated in the order acute/lymphoma-type ATL, smoldering/chronic-type ATL, and HTLV-1 carriers as compared with normal individuals, perhaps with better accuracy than the other markers [90–92]. These serum markers are useful for detecting the acute transformation of indolent ATL as well as the early relapse of ATL after achieving responses by therapy.
Prototypical ATL cells have a mature alpha–beta T-cell phenotype, that is, they are terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-negative, cluster of differentiation 1a-negative, T-cell receptor alpha–beta-positive, CD2-positive and CD5, CD45RO and CD29-positive, and frequently do not express CD7 and CD26. A decline in the CD3 level with the appearance of CD25 indicates that the ATL cells are in an activated state. Most ATL cells are CD52-positive, but some are negative and this may correlate with the co-expression of CD30. About 90% of cases are CD4-positive and CD8-negative, and in rare cases either co-express CD4 and CD8, are negative for both markers, or are only CD8-positive [93]. CCR4 is expressed in more than 90% of cases and associated with a poor prognosis. Recent studies have suggested that the cells of some ATL may be the equivalent of regulatory T-cells because of the high frequency of expression of CD25/CCR4 and about half of FoxP3 [62, 94].
Chromosomal abnormalities detected by cytogenetics or comparative genomic hybridization are often more complex and more frequent in aggressive ATL than in indolent ATL, with aneuploidy and several hot spots such as 14q and 3p [95, 96]. A more sensitive array-CGH revealed that the lymphoma type had significantly more frequent gains at 1q, 2p, 4q, 7p, and 7q, and losses at 10p, 13q, 16q, and 18p, whereas the acute type showed a gain at 3/3p, but no specific pattern of abnormality has been identified which is in contrast to Burkitt leukemia/lymphoma with a myc gene rearrangement induced by Epstein–Barr virus [97, 98].
DNA microarray analyses of the transcriptomes of ATL cells at the chronic and acute stages to elucidate the mechanism of stage progression in this disease revealed that several hundred genes were modulated in expression including those for MET, a receptor tyrosine kinase for hepatocyte growth factor, and cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1 [99, 100].
Diagnosis of ATL
The diagnosis of typical ATL is not difficult and is based on clinical features, ATL cell morphology, mature helper-T-cell phenotype, and ant-HTLV-1 antibody in most cases [13, 55]. Those rare cases which might be difficult to diagnose can be shown to have the monoclonal integration of HTLV-1 proviral DNA in the malignant cells as determined by Southern blotting. However, the monoclonal integration of HTLV-1 is also detected in some HAM/TSP patients and HTLV-1 carriers [35, 36]. After the diagnosis of ATL, subclassification of the disease is necessary for the selection of appropriate treatment [14, 57].
Clinical Course and Treatment of ATL
Treatment decisions should be based on the ATL subclassification and the prognostic factors at onset including those related with ATL and co-morbidity [57]. As mentioned above, subclassification of this disease has been proposed based on the prognosis and clinical manifestations. Without treatment, most patients with acute-/lymphoma/type ATL die of the disease or infections within weeks or months. More than half of patients with smoldering ATL survive for more than 5 years without chemotherapy and transformation to aggressive ATL. Chronic ATL has the most diverse prognosis among the subtypes and could be divided into favorable and unfavorable by clinical parameters (serum albumin, BUN, and LDH levels) after a multivariate analysis [11].
Current treatment options for ATL include watchful waiting until the disease progresses, interferon alpha (IFN) and zidobudine (AZT) therapy, multi-agent chemotherapy, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT), and a new agent [57].
Watchful Waiting
At present, no standard treatment for ATL exists. Therefore, patients with the smoldering or favorable chronic type, who may survive one or more years without chemotherapy, excluding topical therapy for cutaneous lesions, should be observed and therapy should be delayed until progression of the disease [57]. However, it was recently found that the long-term prognosis of such patients was poorer than expected. In a long-term follow-up study for 78 patients with indolent ATL (favorable chronic- or smoldering-type) with a policy of watchful waiting until disease progression at a single institution, the median survival time was 5.3 years with no plateau in the survival curve. Twelve patients remained alive for >10 years, 32 progressed to acute ATL, and 51 died [101]. These findings suggest that even “indolent” ATL patients should be carefully observed in clinical practice. Further study is required to establish appropriate management practices for indolent ATL.
Chemotherapy
Since 1978, chemotherapy trials have been consecutively conducted for patients newly diagnosed with ATL by JCOG’s LSG (Table 8.2) [102–107]. Between 1981 and 1983, JCOG conducted a phase III trial (JCOG8101) to evaluate LSG1-VEPA (vincristine, cyclophosphamide, prednisone, and doxorubicin) vs. LSG2-VEPA-M (VEPA plus methotrexate (MTX)) for advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), including ATL [102, 103]. The complete response (CR) rate of LSG2-VEPA-M for ATL (37%) was higher than that of LSG1-VEPA (17%; P = 0.09). However, the CR rate was significantly lower for ATL than for B-cell NHL and PTCL other than ATL (P < 0.001). The median survival time of the 54 patients with ATL was 6 months, and the estimated 4-year survival rate was 8%.
In 1987, JCOG initiated a multicenter phase II study (JCOG8701) of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy (LSG4) for advanced aggressive NHL (including ATL). LSG4 consisted of three regimens: (1) VEPA-B (VEPA plus bleomycin), (2) M-FEPA (methotrexate, vindesine, cyclophosphamide, prednisone, and doxorubicin), and (3) VEPP-B, (vincristine, etoposide, procarbazine, prednisone, and bleomycin) [104]. The CR rate for ATL patients was improved from 28% (JCOG8101) to 43% (JCOG8701); however, the CR rate was significantly lower in ATL than in B-cell NHL and PTCL (P < 0.01). Patients with ATL still showed a poor prognosis, with a median survival time of 8 months and a 4-year survival rate of 12%.
The disappointing results with conventional chemotherapies have led to a search for new active agents. Multicenter phase I and II studies of pentostatin (2′-deoxycoformycin, a inhibitor of adenosine deaminase) were conducted against ATL in Japan [108]. The phase II study revealed a response rate of 32% (10 of 31) in cases of relapsed or refractory ATL (two CRs and eight PRs).
These encouraging results prompted the investigators to conduct a phase II trial (JCOG9109) with a pentostatin-containing combination (LSG11) as the initial chemotherapy [105]. Patients with aggressive ATL—that is, of the acute, lymphoma, or unfavorable chronic type—were eligible for this study. Unfavorable chronic-type ATL, defined as having at least one of three unfavorable prognostic factors (low serum albumin level, high LDH level, or high BUN), has an unfavorable prognosis similar to that for acute- and lymphoma-type ATL. A total of 62 untreated patients with aggressive ATL (34 acute, 21 lymphoma, and 7 unfavorable chronic type) were enrolled. A regimen of 1 mg/m2 vincristine on days 1 and 8, 40 mg/m2 doxorubicin on day 1, 100 mg/m2 etoposide on days 1 through 3, 40 mg/m2 prednisolone (PSL) on days 1 and 2, and 5 mg/m2 pentostatin on days 8, 15, and 22 was administered every 28 days for ten cycles. Among the 61 patients evaluable for toxicity, four patients (7%) died of infections, two from septicemia, and two from cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Among the 60 eligible patients, there were 17 CRs (28%) and 14 partial responses (PRs) (overall response rate [ORR] = 52%). The median survival time was 7.4 months, and the estimated 2-year survival rate was 17%. The prognosis in patients with ATL remained poor, even though they were treated with a pentostatin-containing combination chemotherapy.
In 1994, JCOG initiated a phase II trial (JCOG9303) of an eight-drug regimen (LSG15) consisting of vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone, ranimustine, vindesine, etoposide, and carboplatin for untreated ATL [106]. Dose intensification was attempted with the prophylactic use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). In addition, non-cross-resistant agents such as ranimustine and carboplatin, and intrathecal prophylaxis with MTX and PSL were incorporated. Ninety-six previously untreated patients with aggressive ATL were enrolled: 58 acute, 28 lymphoma, and 10 unfavorable chronic types. Approximately 81% of the 93 eligible patients responded (75/93), with 33 patients obtaining a CR (35%). The overall survival rate of the 93 patients at 2 years was estimated to be 31%, with a median survival time of 13 months. Grade 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were observed in 65% and 53% of the patients, respectively, whereas grade 4 non-hematologic toxicity was observed in only one patient.
To confirm whether the LSG15 regimen is a new standard for the treatment of aggressive ATL, JCOG conducted a phase III trial comparing modified (m)-LSG15 with biweekly CHOP (cyclophosphamide, hydroxy-doxorubicin, vincristine [Oncovin], and prednisone), both supported with G-CSF and intrathecal prophylaxis [107].
mLSG15 in JCOG9801 was a modified version of LSG15 in JCOG9303, consisting of three regimens: VCAP [VCR 1 mg/m2 (maximum 2 mg), CPA 350 mg/m2, ADM 40 mg/m2, PSL 40 mg/m2] on day 1, AMP [ADM 30 mg/m2, MCNU 60 mg/m2, PSL 40 mg/m2] on day 8, and VECP [VDS 2.4 mg/m2 on day 15, ETP 100 mg/m2 on days 15–17, CBDCA 250 mg/m2 on day15, PSL 40 mg/m2 on days 15–17] on days 15–17, and the next course was to be started on day 29 (Figure 8.3). The modifications in mLSG15 as compared to LSG15 were as follows; (1) the total number of cycles was reduced from seven to six because of progressive cytopenia, especially thrombocytopenia, after repeating the VCAP-AMP-VECP therapy, (2) cytarabine 40 mg was used with MTX 15 mg and PSL 10 mg for prophylactic intrathecal administration, at the recovery phases of courses 1, 3, and 5 because of the high frequency of central nervous system relapse in the JCOG9303 study. Untreated patients with aggressive ATL were assigned to receive either six courses of LSG15 every 4 weeks or eight courses of biweekly CHOP. The primary endpoint was overall survival. A total of 118 patients were enrolled. The CR rate was higher in the LSG15 arm than in the biweekly CHOP arm (40% vs. 25%, respectively; P = 0.020). As illustrated in Figure 8.4, the median survival time and OS rate at 3 years were 12.7 months and 24% in the LSG15 arm and 10.9 months and 13% in the biweekly CHOP arm [two-sided P = 0.169, and the hazard ratio was 0.75; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.50 10 1.13]. A Cox regression analysis with performance status (PS 0 vs. 1 vs. 2–4) as the stratum for baseline hazard functions was performed to evaluate the effect on overall survival of age, B-symptoms, subtypes of ATL, LDH, BUN, bulky mass, and treatment arms. According to this analysis, the hazard ratio and two-sided P value for the treatment arms were 0.62 (95% CI, 0.38–1.01) and 0.056, respectively. The difference between the crude analysis and this result was because of unbalanced prognostic factors, such as PS 0 vs. 1, and the presence or absence of bulky lesions between the treatment arms. The progression-free survival rate at 1 year was 28% in the LSG15 arm compared with 16% in the biweekly CHOP arm (two-sided P = 0.200).
Regimen of VCAP-AMP-VECP MCNU and VDS are nitrosourea and vinca alkaloid, respectively, developed in Japan. A previous study on myeloma described that carmustine (BCNU), another nitrosourea, at 1 mg/kg is equivalent to MCNU at 0.8–1.0 mg/kg. VDS at 2.4 mg/m2 can be substituted for VCR, another vinca alkaloid used in this regimen, at 1 mg/m2 with possibly less myelosuppression and more peripheral neuropathy which can be managed by dose modification. VCAP = vincristine (VCR), cyclophosphamide (CPA), doxorubicin (ADM), prednisone (PSL); AMP = ADM, ranimustine (MCNU), PSL; VECP = vindesine (VDS), etoposide (ETP), carboplatin (CBDCA) and PSL. [Based on data from Tsukasaki K, Utsunomiya A, Fukuda H, et al.: VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG9801. J Clin Oncol 25:5,458–5,564, 2007.]
Kaplan-Meier Estimate of Overall Survival for all Randomly Assigned Patients in JCOG9801. CI = confidential interval; VCAP = vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, prednisone; AMP = doxorubicin, ranimustine, prednisone; VECP = vindesine, etoposide, carboplatin, prednisone; MST = median survival time; OS = overall survival; [Based on data from Tsukasaki K, Utsunomiya A, Fukuda H, et al.: VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG9801. J Clin Oncol 25:5,458–5,564, 2007.]
In VCAP-AMP-VECP vs. biweekly CHOP, rate of grade 4 neutropenia, grade 4 thrombocytopenia, and grade 3/4 infection were 98% vs. 83%, 74% vs. 17%, and 32% vs. 15%, respectively. There were three toxic deaths in the former. Three treatment-related deaths (TRDs), two from sepsis and one from interstitial pneumonitis related to neutropenia, were reported in the VCAP-AMP-VECP arm. Two cases of myelodysplastic syndrome were reported, one each in both arms.
The longer survival at 3 years and higher CR rate with LSG15 compared with biweekly CHOP suggest that LSG15 is a more effective regimen at the expense of higher toxicity, providing the basis for future investigations in the treatment of ATL [107]. The superiority of VCAP-AMP-VECP to biweekly CHOP may be explained by the more prolonged, dose dense schedule of therapy in addition to four more drugs. In addition, agents such as carboplatin and ranimustine not affected by multidrug-resistance related genes, which were frequently expressed in ATL cells at onset, were incorporated [109]. Intrathecal prophylaxis, which was incorporated in both arms of the phase III study, should be considered for patients with aggressive ATL even in the absence of clinical symptoms because a previous analysis revealed that more than half of relapses at new sites after chemotherapy occurred in the CNS [110]. However, the median survival time of 13 months still compares unfavorably to other hematological malignancies, requiring further effort to improve the outcome.
Interferon-Alpha and Zidovudine
A small phase II trial in Japan of IFN alpha against relapsed/refractory ATL showed a response rate (all PR) of 33% (8/24), including five out of nine (56%) chronic type ATL [111]. In 1995, Gill and associates reported that 11 of 19 patients with acute- or lymphoma-type ATL showed major responses (five CR and six PR) to a combination of interferon-alpha (IFN) and zidovudine (AZT) [112]. The efficacy of this combination was also observed in a French study; major objective responses were obtained in all five patients with ATL (four with acute type and one with smoldering type) [113]. Although these results are encouraging, the OS of previously untreated patients with ATL was relatively short (4.8 months) compared with the survival of those in the chemotherapy trials conducted by the JCOG-LSG (7–8 months) [114]. After that, numerous small phase II studies using AZT and IFN have shown responses in ATL patients [115–117]. High doses of both agents are recommended: 6–9 million units of IFN in combination with daily divided AZT doses of 800–1,000 mg/day.
Recently, the results of a “meta-analysis” on the use of IFN and AZT for ATL were reported [118]. A total of 100 patients received interferon-alpha and AZT as initial treatments. The ORR was 66%, with a 43% CR rate. In this worldwide retrospective analysis, the median survival time was 24 months and the 5-year survival rate was 50% for first-line IFN and AZT, vs. 7 months and 20% for 84 patients who received first-line chemotherapy. The median survival time of patients with acute-type ATL treated with first-line IFN/AZT and chemotherapy was 12 and 9 months, respectively. Patients with lymphoma-type ATL did not benefit from this combination. In addition, first-line IFN/AZT therapy in chronic- and smoldering-type ATL resulted in a 100% survival rate at a median follow-up of 5 years. While the results for IFN/AZT in indolent ATL appear to be promising compared to those with watchful-waiting policy until disease progression, recently reported from Japan [101], the possibility of selection bias cannot be ruled out. A prospective multicenter phase III study evaluating the efficacy of IFN/AZT as compared to watchful-waiting for indolent ATL is to be initiated in Japan.
Recently, a phase II study of the combination of arsenic trioxide, IFN, and AZT for chronic ATL revealed an impressive response rate and moderate toxicity [119]. Although the results appeared promising, the addition of arsenic trioxide to IFN/AZT, which might be sufficient for the treatment of chronic ATL as described above, caused more toxicity and should be evaluated with caution.
Allergenic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation (allo-HSCT)
Allo-HSCT is now recommended for the treatment of young patients with aggressive ATL. Despite higher treatment-related mortality in a retrospective multicenter analysis of myeloablative allo-HSCT, the estimated 3-year OS of 33% is promising, possibly reflecting a graft versus ATL effect [120]. To evaluate the efficacy of allo-HSCT more accurately, especially in view of a comparison with intensive chemotherapy, a prospective multicenter phase II study of LSG15 chemotherapy followed by allo-HSCT will be initiated in Japan.
Feasibility studies of allo-HSCT with reduced intensity conditioning for ATL also revealed promising results, and a subsequent multicenter trial of RIST is being conducted in Japan [121, 122]. The minimal residual disease after allo-HSCT detected as HTLV-1 proviral load was much less extensive than that after chemotherapy or AZT/IFN therapy, suggesting the presence of a graft-versus-ATL effect as well as graft-versus-HTLV-1 activity [121]. It remains unclear which type of allo-HSCT (myeloablative or reduced intensity conditioning) is more suitable for the treatment of ATL. Furthermore, selection criteria with respect to responses to previous treatments, sources of stem cells, and HTLV-1 viral status of the donor remain to be determined. However, several other retrospective studies as well as those mentioned above on allo-HSCT showed a promising long-term survival rate of 20–40% with an apparent plateau phase despite significant treatment-related mortality.
Supportive Care
The prevention of opportunistic infections is essential in the management of ATL patients, nearly half of whom develop severe infections during chemotherapy. Some patients with indolent ATL develop infections during watchful waiting. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim and antifungal agents have been recommended as prophylaxes for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia and fungal infections, respectively, in the JCOG trials [105–107]. While cytomegalovirus infections are not infrequent among ATL patients, ganciclovir is not usually recommended as a prophylaxis [55]. In addition, in patients not receiving chemotherapy, antifungal prophylaxis may not be critical. An anti-strongyloides agent, such as ivermectin or albendazole, should be considered to avoid systemic infections in patients with a history of exposure to the parasite in the tropics. Treatment with steroids and proton pump inhibitors may precipitate a fulminant strongyloides infestation and warrants testing before these agents are used in endemic areas [55]. Hypercalcemia associated with aggressive ATL can be corrected using chemotherapy in combination with hydration and bisphosphonate even when the PS of the patient is poor.
Response Criteria in ATL
The complex nature of ATL, often with both leukemic and lymphomatous components, makes response assessment difficult. A modification of the JCOG response criteria was suggested reflecting those for CLL and NHL which had been published later [55, 123, 124]. Recently, revised response criteria were proposed for lymphoma. New guidelines were presented incorporating positron emission tomography (PET), especially for the assessment of CR. It is well known and described in the criteria that several kinds of lymphoma including PTCLs were variably [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose avid [125]. Meanwhile, PET or PET/CT is recommended for evaluations of response when the tumorous lesions are FDG-avid at diagnosis [57].
New Agents for ATL
Topoisomerase Inhibitors
MST-16, a new orally administered bis(2,6-dioxopiperazine) analogue and an inhibitor of topoisomerase II, showed some activity with little cross resistance toward lymphoid malignancies in vitro and in vivo. MST-16 at 1,200–2,800 mg/day was given orally daily for 7 days, with courses repeated at intervals of 2–3 weeks to 24 patients with relapsed or refractory ATL in a phase I–II study [126]. Two CRs and eight PRs were obtained in 23 (13 acute, 8 lymphoma, and 2 chronic ATL) evaluable patients. Remissions were obtained at 7–232 (median, 23) days and lasted 43–374 (median, 68) days. The major toxic effects were leukopenia (68%), anemia (52%), thrombocytopenia (35%), and gastrointestinal disorders (22%). Although this agent showed promising activity against ATL as a single agent, no further study in combination with other agents has been reported.
Irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) is a semi-synthetic camptothecin with inhibitory activity against topoisomerase I. Preclinical studies of CPT-11 have suggested a lack of cross-resistance between topoisomerase I inhibitors and other anticancer agents. Multicenter phase II studies of CPT-11 have been conducted against relapsed or refractory NHL [127]. In this study, 9 patients achieved a CR, and 17 patients achieved a PR (response rate 38%: 26 of 69), using a weekly intravenous administration of 40 mg/m2/day for three consecutive days. Within this group, 5 of 13 patients with ATL (38%) responded to CPT-11 (one CR and four PR) [127]. The major toxic effects of CPT-11 were leukopenia, diarrhea, and nausea and/or vomiting. Subsequently, to develop a new chemo therapy regimen effective against NHL and ATL, two kinds of phase I/II studies of CPT-11 in combination with CBDCA or ETP were conducted for relapsed or refractory NHL. In both studies, however, dose escalation was halted because of hematologic toxicity (in combination with CBDCA) and hepatotoxicity (in combination with ETP).
Purine Analogs
Several purine analogs have been evaluated for ATL. Among them, pentostatin (deoxycoformycin) has been most extensively evaluated as a single agent and in combination as described above [105, 108]. Other purine analogs clinically studied for ATL are fludarabine and cladribine. Fludarabine is among standard treatments for B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other lymphoid malignancies. In a phase I study of fludarabine in Japan, five ATL patients and ten B-CLL patients with refractory or relapsed-disease were enrolled [128]. Six grade 3 non-hematological toxicities were only observed in the ATL patients. PR was achieved only in one of the five ATL patients and the duration was short. Cladribine is among standard treatments for hairy cell leukemia and other lymphoid malignancies. A phase II study of cladribine for relapsed/refractory aggressive-ATL in 15 patients revealed only one PR [129].
Forodesine, a purine nucleotide phosphorylase (PNP) inhibitor, is among purine nucleotide analogs. PNP is an enzyme in the purine salvage pathway that phosphorolysis 2′deoxyguanosine (dGuo). Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) deficiency in humans results in a severe combined immunodeficiency phenotype and the selective depletion of T cells associated with high plasma deoxyguanosine (dGuo) and high intracellular deoxyguanosine triphosphate levels in those cells with high deoxynucleoside kinase activity such as T cells, leading to cell death. Inhibitors of PNP, such as forodesine, mimic SCID in vitro and in vivo, suggesting a new targeting agent specific for T-cell malignancies [130]. A dose escalating phase I study of forodesine is being conducted for T-cell malignancies including ATL.
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
Gene expression governed by epigenetic changes is crucial to the pathogenesis of cancer. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are enzymes involved in the remodeling of chromatin and play a key role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Deacetylase inhibitors (DACi) induce the hyperacetylation of non-histone proteins as well as nucleosomal histones resulting in the expression of repressed genes involved in growth arrest, terminal differentiation, and/or apoptosis among cancer cells. Several classes of HDACi have been found to have potent anticancer effects in preclinical studies. HDACis such as vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid), romidepsin (depsipeptide), and panobinostat (LBH589) have also shown promise in preclinical and/or clinical studies against T-cell malignancies including ATL [131]. Vorinostat and romidepsin have been approved for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) by the Food and Drug Administration in the USA. LBH589 has a significant anti-ATL effect in vitro and in mice [132]. However, a phase II study for CTCL and indolent ATL was terminated because of severe infections associated with the shrinkage of skin tumors and formation of ulcers in patients with ATL. Further study is required to evaluate the efficacy of HDACIs for PTCL/CTCL including ATL.
Monoclonal Antibodies and Toxin Fusion Proteins
Monoclonal antibodies (MoAb) and toxin fusion proteins targeting several molecules expressed on the surface of ATL cells and other lymphoid malignant cells, such as CD25, CD2, CD52 and CCR4, have shown promise in recent clinical trials. Because most ATL cells express the alpha-chain of IL-2R (CD25), Waldmann et al. treated patients with ATL using monoclonal antibodies to CD25 [133]. Six (32%) of 19 patients treated with anti-Tac showed objective responses lasting from 9 weeks to longer than 3 years. One impediment to this approach is the quantity of soluble IL-2R shed by the tumor cells into the circulation. Another strategy for targeting IL-2R is conjugation with an immunotoxin (Pseudomonas exotoxin) or radioisotope (yttrium-90). Waldmann et al. developed a stable conjugate of anti-Tac with yttrium-90. Among the 16 patients with ATL who received 5- to 15-mCi doses, 9 (56%) showed objective responses. The response lasted longer than that obtained with unconjugated anti-Tac antibody [134, 135].
LMB-2, composed of the anti-CD25 murine MoAb fused to the truncated form of Pseudomonas toxin, was cytotoxic to CD25-expressing cells including ATL cells in vitro and in mice. Phase I/II trials of this agent showed some effect against hairy cell leukemia, CTCL, and ATL [136]. Six of thirty-five patients in the phase I study had significant levels of neutralizing antibodies after the first cycle. This drug deserves further clinical trials including in combination with cytotoxic agents.
Denileukin diftitox (DD; DAB(389)-interleukin-2 [IL-2]), an interleukin-2-diphtheria toxin fusion protein targeting IL-2 receptor-expressing malignant T lymphocytes, shows efficacy as a single agent against CTCL and PTCL [137]. Also, the combination of this agent with multi-agent chemotherapy, CHOP, was promising for PTCL [138]. ATL cells frequently and highly express CD25 as described above and several ATL cases successfully treated with this agent have been reported [139].
CD52 antigen is present on normal and pathologic B and T cells. In PTCL, however, CD52 expression varies among patients, with an overall expression rate lower than 50% in one study but not in another [140, 141]. ATL cells frequently express CD52 as compared to other PTCLs. The humanized anti-CD52 monoclonal antibody alemtuzumab is active against CLL and PTCL as a single agent. The combination of alemtuzumab with a standard-dose cyclophosphamide/doxorubicin/vincristine/prednisone (CHOP) regimen as a first-line treatment for 24 patients with PTCL showed promising results with CR in 17 (71%) patients, 1 had a partial remission, with an overall median duration of response of 11 months and was associated with mostly manageable infections but including CMV reactivation [142]. Major infections were Jacob–Creutzfeldt virus reactivation, pulmonary invasive aspergillosis, and Staphylococcus sepsis.
ATL cells express CD52, the target of alemtuzumab, which was active in a preclinical model of ATL and toxic to p53-deficient cells, and several ATL cases successfully treated with this agent have been reported [143–145].
Siplizumab is a humanized MoAb targeting CD2 and showed efficacy in a murine ATL model. P1 dose-escalating study of this agent in 22 patients with several kinds of T/NK-cell malignancy revealed six responses (two CR in LGL leukemia, three PR in ATL and one PR in CTCL). However, four patients developed EBV-associated LPD [146]. The broad specificity of this agent may eliminate both CD4- and CD8-positive T cells as well as NK cells without affecting B cells and predispose individuals to the development of EBV lymphoproliferative syndrome.
CCR4 is expressed on normal T helper type 27 and regulatory T (Treg) cells and on certain types of T-cell neoplasms [63, 94]. KW-0761, a next generation humanized anti-CCR4 mAb, with a defucosylated Fc region, exerts strong antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity due to increased binding to the Fcγ receptor on effecter cells [147]. A phase I study of dose escalation with four weekly intravenous infusions of KW-0761 in 16 patients with relapsed CCR4-positive T-cell malignancy (13 ATL and 3 PTCL) revealed that one patient, at the maximum dose (1.0 mg/kg), developed grade (G) three dose-limiting toxic effects, namely skin rashes and febrile neutropenia, and G4 neutropenia [148]. Other treatment-related G3-4 toxic effects were lymphopenia (n = 10), neutropenia (n = 3), leukopenia (n = 2), herpes zoster (n = 1), and acute infusion reaction/cytokine release syndrome (n = 1). Neither the frequency nor severity of these effects increased with dose escalation or the plasma concentration of the agent. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached. No patients had detectable levels of anti-KW-0761 antibody. Five patients (31%; 95% CI, 11–59%) achieved objective responses: two complete (0.1; 1.0 mg/kg) and three partial (0.01; 2 at 1.0 mg/kg) responses. Three out of thirteen patients with ATL (31%) achieved a response (two CR and one PR). Responses in each lesion were diverse, that is, good in PB (six CR and one PR/seven evaluable cases), intermediate in skin (three CR and one PR/eight evaluable cases), and poor in LN (1 CR and 2 PR/11 evaluable cases). KW-0761 was well tolerated at all the doses tested, demonstrating potential efficacy against relapsed CCR4-positive ATL or PTCL. Recently, results of subsequent phase II studies at the 1.0 mg/kg in relapsed ATL, showing 50% of response rate with acceptable toxicity profiles, were reported [149]. Also, a phase II trial of single agent KW-0761 at the 1.0 mg/kg in relapsed PTCL/CTCL and a phase II trial of VCAP-AMP-VECP combined with KW-0761 for untreated aggressive ATL are ongoing.
Other Novel Agents
Pralatrexate (Folotyn) is a new agent with potent preclinical and clinical activity in T-cell malignancies including ATL [150–152]. The agent is a novel anti-folate with improved membrane transport and polyglutamylation in tumor cells and high affinity for the reduced folate carrier highly expressed in malignant cells. Other potential drugs for ATL under investigation include a proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib (Velcade), and an immunomodulatory agent, lenalidomide (Revlimid) [153–155].
Prevention of ATL
Two steps should be considered for the prevention of HTLV-1-associated ATL. The first is the prevention of HTLV-1 infections. This has been achieved in some endemic areas in Japan by screening for HTLV-1 among blood donors and asking mothers who are carriers to refrain from breast feeding. The second step is the prevention of ATL among HTLV-1 carriers. This has not been achieved partly because only about 5% of HTLV-1 carriers develop the disease in their life time, although several risk factors have been identified by a cohort study of HTLV-1 carriers (Joint Study of Predisposing Factors for ATL Development) [81]. Also, no agent has been found to be effective in preventing the development of ATL among HTLV-1 carriers.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
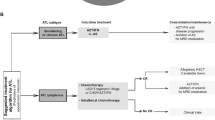
Clinical trials have been paramount to the recent advances in ATL treatment, including assessments of chemotherapy, AZT/IFN, and allo-HSCT. Recently, a strategy for ATL treatment, stratified by subclassification, prognostic factors, and the response to initial treatment as well as response criteria was proposed (Table 8.3) [57]. The recommended treatment algorithm for ATL is shown in Fig. 8.2. However, as described in this chapter, ATL still has a worse prognosis than the other T-cell malignancies [156]. There is no plateau with an initial steep slope and subsequent gentle slope without a plateau in the survival curve for aggressive or indolent ATL treated by watchful waiting and with chemotherapy, respectively, although the prognosis is much better in the latter [14, 61]. A prognostic model for each subgroup should be elucidated to properly identify the candidate for allo-HSCT which can achieve a cure of ATL despite considerable treatment-related mortality. Although several small phase II trials suggested IFN/AZT therapy to be promising, no confirmative phase III study has been conducted. Furthermore, as described in the other chapters in detail, more than ten promising new agents for PTCL/CTCL including ATL are now in clinical trials or preparation. Future clinical trials on ATL as described above should be incorporated to ensure that the consensus is continually updated to establish evidence-based practical guidelines.
References
Uchiyama T, Yodoi J, Sagawa K, et al. Adult T-cell leukemia: clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood. 1977;50:481–92.
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, et al. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980;77:7415–9.
Hinuma Y, Nagata K, Hanaoka M, Nakai M, Matsumoto T, Kinoshita KI, et al. Adult T-cell leukemia: antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1981;78(10):6476–80.
Miyoshi I, Kubonishi I, Yoshimoto S, Akagi T, Ohtsuki Y, Shiraishi Y, et al. Type C virus particles in a cord T-cell line derived by co-cultivating normal human cord leukocytes and human leukaemic T cells. Nature. 1981;294(5843):770–1.
Yoshida M, Miyoshi I, Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:2031–5.
Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, Gout O, Maurs L, Calender A, et al. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985;2(8452):407–10.
Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Igata A, et al. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986;1(8488):1031–2.
LaGrenade L, Hanchard B, Fletcher V, Cranston B, Blattner W. Infective dermatitis of Jamaican children: a marker for HTLV-I infection. Lancet. 1990;336(8727):1345–7.
Mochizuki M, Watanabe T, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K, Yoshimura K, Shirao M, et al. HTLV-I uveitis: a distinct clinical entity caused by HTLV-I. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992;83(3):236–9.
Terada K, Katamine S, Eguchi K, Moriuchi R, Kita M, Shimada H, et al. Prevalence of serum and salivary antibodies to HTLV-1 in Sjögren’s syndrome. Lancet. 1994;344(8930):1116–9.
Takatsuki K. Adult T-cell Leukemia. Oxford: Oxford University Press, New York; 1994.
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Human immunodeficiency viruses and human T-cell lymphotropic viruses. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, Geneva: IARCPress 1996
Ohshima K, Jaffe ES, Kikuchi M. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumour of haemaopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press; 2008. p. 281–4.
Shimoyama M. Diagnostic criteria and classification of clinical subtypes of adult T- cell leukaemia-lymphoma: a report from the lymphoma study group (1984–87). Br J Haematol. 1991;79:428–37.
Matsuoka M, Jeang KT. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(4):270–80.
Satou Y, Matsuoka M. HTLV-1 and the host immune system: how the virus disrupts immune regulation, leading to HTLV-1 associated diseases. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2010;50(1):1–8.
Seiki M, Hattori S, Hirayama Y, Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1983;80(12):3618–22.
Sodroski JG, Goh WC, Rosen CA, Salahuddin SZ, Aldovini A, Franchini G, et al. trans-Activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus long terminal repeat correlates with expression of the x-lor protein. J Virol. 1985;55(3):831–5.
Kiyokawa T, Seiki M, Iwashita S, Imagawa K, Shimizu F, Yoshida M. p27x-III and p21x-III, proteins encoded by the pX sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985;82(24):8359–63.
Gaudray G, Gachon F, Basbous J, et al. The complementary strand of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 RNA genome encodes a bZIP transcription factor that down-regulates viral transcription. J Virol. 2002;76:12813.
Satou Y, Yasunaga J, Yoshida M, et al. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:720.
Murata K, Hayashibara T, Sugahara K, Uemura A, Yamaguchi T, Harasawa H, et al. A novel alternative splicing isoform of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor (HBZ-SI) targets distinct subnuclear localization. J Virol. 2006;80(5):2495–505.
Kline RL, Brothers T, Halsey N, Boulos R, Lairmore MD, Quinn TC. Evaluation of enzyme immunoassays for antibody to human T-lymphotropic viruses type I/II. Lancet. 1991;337(8732):30–3.
Ikeda M, Fujino R, Matsui T, Yoshida T, Komoda H, Imai J. A new agglutination test for serum antibodies to adult T-cell leukemia virus. Gann. 1984;75(10):845–8.
Aoki T, Miyakoshi H, Koide H, Yoshida T, Ishikawa H, Sugisaki Y, et al. Seroepidemiology of human T-lymphotropic retrovirus type I (HTLV-I) in residents of Niigata Prefecture, Japan. Comparative studies by indirect immunofluorescence microscopy and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Int J Cancer. 1985;35(3):301–6.
Aboulafia DM, Feigal E, Vranzian K, Bennett C, Blattner W, Moss A, et al. Human T cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I/II) serodiagnostic testing: disparate results among a cohort of intravenous drug users. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993;9(10):1043–50.
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Proposed WHO criteria for interpreting results from western blot assays for HIV-1, HIV-2, and HTLV-I/HTLV-II. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 1990 Sep 14;65(37):281–3.
Franchini G, Wong-Staal F, Gallo RC. Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) transcripts in fresh and cultured cells of patients with adult T-cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81:6207.
Kinoshita T, Shimoyama M, Tobinai K, Ito M, Ito S, Ikeda S, et al. Detection of mRNA for the tax1/rex1 gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukemia patients and viral carriers by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86(14):5620–4.
Yoshida M, Seiki M, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81(8):2534–7.
Takemoto S, Matsuoka M, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K. A novel diagnostic method of adult T-cell leukemia: monoclonal integration of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I provirus DNA detected by inverse polymerase chain reaction. Blood. 1994;84(9):3080–5.
Wattel E, Vartanian JP, Pannetier C, Wain-Hobson S. Clonal expansion of human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected cells in asymptomatic and symptomatic carriers without malignancy. J Virol. 1995;69(5):2863–8.
Yamaguchi K, Seiki M, Yoshida M, Nishimura H, Kawano F, Takatsuki K. The detection of human T cell leukemia virus proviral DNA and its application for classification and diagnosis of T cell malignancy. Blood. 1984;63(5):1235–40.
Tamiya S, Matsuoka M, Etoh K, Watanabe T, Kamihira S, Yamaguchi K, et al. Two types of defective human T-lymphotropic virus type I provirus in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 1996;88(8):3065–73.
Tsukasaki K, Tsushima H, Yamamura M, et al. Integration patterns of HTLV-I provirus in relation to the clinical course of ATL: frequent clonal change at crisis from indolent disease. Blood. 1997;89:948–56.
Furukawa Y, Fujisawa J, Osame M, Toita M, Sonoda S, Kubota R, et al. Frequent clonal proliferation of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-infected T cells in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM-TSP). Blood. 1992;80(4):1012–6.
Ikeda S, Momita S, Kinoshita K, Kamihira S, Moriuchi Y, Tsukasaki K, et al. Clinical course of human T-lymphotropic virus type I carriers with molecularly detectable monoclonal proliferation of T lymphocytes: defining a low- and high-risk population. Blood. 1993;82(7):2017–24.
Takahashi K, Takezaki T, Oki T, Kawakami K, Yashiki S, Fujiyoshi T, et al. Inhibitory effect of maternal antibody on mother-to-child transmission of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. The Mother-to-Child Transmission Study Group. Int J Cancer. 1991;49(5):673–7.
Kinoshita K, Hino S, Amagaski T, Ikeda S, Yamada Y, Suzuyama J, et al. Demonstration of adult T-cell leukemia virus antigen in milk from three sero-positive mothers. Gann. 1984;75(2):103–5.
Hino S, Katamine S, Miyata H, Tsuji Y, Yamabe T, Miyamoto T. Primary prevention of HTLV-1 in Japan. Leukemia. 1997;11 Suppl 3:57–9.
Tajima K, Tominaga S, Suchi T, Kawagoe T, Komoda H, Hinuma Y, et al. Epidemiological analysis of the distribution of antibody to adult T-cell leukemia-virus-associated antigen: possible horizontal transmission of adult T-cell leukemia virus. Gann. 1982;73(6):893–901.
Okochi K, Sato H, Hinuma Y. A retrospective study on transmission of adult T cell leukemia virus by blood transfusion: seroconversion in recipients. Vox Sang. 1984;46(5):245–53.
Schwebke J, Calsyn D, Shriver K, Saxon A, Kleyn J, Oluoch-Mitchell E, et al. Prevalence and epidemiologic correlates of human T cell lymphotropic virus infection among intravenous drug users. J Infect Dis. 1994;169(5):962–7.
Schaffar-Deshayes L, Chavance M, Monplaisir N, Courouce AM, Gessain A, Blesonski S, et al. Antibodies to HTLV-I p24 in sera of blood donors, elderly people and patients with hemopoietic diseases in France and in French West Indies. Int J Cancer. 1984;34(5):667–70.
Hunsmann G, Bayer H, Schneider J, Schmitz H, Kern P, Dietrich M, et al. Antibodies to ATLV/HTLV-1 in Africa. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1984;173(3):167–70.
Ohtsu T, Tsugane S, Tobinai K, Shimoyama M, Nanri S, Watanabe S. Prevalence of antibodies to human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I and human immunodeficiency virus in Japanese immigrant colonies in Bolivia and Bolivian natives. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987;78(12):1347–53.
Achiron A, Pinhas-Hamiel O, Doll L, Djaldetti R, Chen A, Ziv I, et al. Spastic paraparesis associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I: a clinical, serological, and genomic study in Iranian-born Mashhadi Jews. Ann Neurol. 1993;34(5):670–5.
Yanagihara R, Jenkins CL, Alexander SS, Mora CA, Garruto RM. Human T lymphotropic virus type I infection in Papua New Guinea: high prevalence among the Hagahai confirmed by western analysis. J Infect Dis. 1990;162(3):649–54.
Cruickshank JK, Rudge P, Dalgleish AG, Newton M, McLean BN, Barnard RO, et al. Tropical spastic paraparesis and human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1 in the United Kingdom. Brain. 1989;112(Pt 4):1057–90.
Tajima K, Kamura S, Ito S, Ito M, Nagatomo M, Kinoshita K, et al. Epidemiological features of HTLV-I carriers and incidence of ATL in an ATL-endemic island: a report of the community-based co-operative study in Tsushima, Japan. Int J Cancer. 1987;40(6):741–6.
Mueller N, Okayama A, Stuver S, Tachibana N. Findings from the Miyazaki Cohort Study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996;13 Suppl 1:S2–7.
Iwanaga M, Chiyoda S, Kusaba E, Kamihira S. Trends in the seroprevalence of HTLV-1 in Japanese blood donors in Nagasaki Prefecture, 2000–2006. Int J Hematol. 2009;90(2):186–90.
Morgan OS, Rodgers-Johnson P, Mora C, Char G. HTLV-1 and polymyositis in Jamaica. Lancet. 1989;2(8673):1184–7.
Sugimoto M, Nakashima H, Watanabe S, Uyama E, Tanaka F, Ando M, et al. T-lymphocyte alveolitis in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Lancet. 1987;2(8569):1220.
Nishioka K, Maruyama I, Sato K, Kitajima I, Nakajima Y, Osame M. Chronic inflammatory arthropathy associated with HTLV-I. Lancet. 1989;1(8635):441.
Tachibana N, Okayama A, Ishizaki J, Yokota T, Shishime E, Murai K, et al. Suppression of tuberculin skin reaction in healthy HTLV-I carriers from Japan. Int J Cancer. 1988;42(6):829–31.
Tsukasaki K, Hermine O, Bazarbachi A, et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: a proposal from an international consensus meeting. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:453–9.
Major prognostic factors of patients with adult T-cell leukemia- lymphoma: a cooperative study. Lymphoma Study Group (1984–1987): Leuk Res 1991;15:81–90.
Yamada Y, Hatta Y, Murata K, et al. Deletions of p15 and/or p16 genes as a poor-prognosis factor in adult T-cell leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:1778–85.
Utsunomiya A, Ishida T, Inagaki A, et al. Clinical significance of a blood eosinophilia in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a blood eosinophilia is a significant unfavorable prognostic factor. Leuk Res. 2007;31:915–20.
Takasaki Y, Iwanaga M, Tsukasaki K, et al. Impact of visceral involvements and blood cell count abnormalities on survival in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL). Leuk Res. 2007;31:751–7.
Inagaki A, Ishida T, Ishii T, et al. Clinical significance of serum Th1-, Th2- and regulatory T cells-associated cytokines in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: high interleukin-5 and −10 levels are significant unfavorable prognostic factors. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:3054–61.
Ishida T, Utsunomiya A, Iida S, et al. Clinical significance of CCR4 expression in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: its close association with skin involvement and unfavorable outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:3625–34.
Ohno N, Tani A, Uozumi K, et al. Expression of functional lung resistance–related protein predicts poor outcome in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 2001;98:1160–5.
Tawara M, Hogerzeil SJ, Yamada Y, et al. Impact of p53 aberration on the progression of Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma. Cancer Lett. 2006;234:249–55.
Bittencourt AL, da Graças Vieira M, et al. Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in Bahia, Brazil: analysis of prognostic factors in a group of 70 patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 2007;128:875–82.
Statistical analyses of clinico-pathological, virological and epidemiological data on lymphoid malignancies with special reference to adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a report of the second nationwide study of Japan. The T- and B-Cell Malignancy Study Group. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1985 Sep;15(3):517–35.
Bartholomew C, Charles W, Saxinger C, Blattner W, Robert-Guroff M, Raju C, et al. Racial and other characteristics of human T cell leukemia/lymphoma (HTLV-I) and AIDS (HTLV-III) in Trinidad. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1985;290(6477):1243–6.
Gérard Y, Lepere JF, Pradinaud R, Joly F, Lepelletier L, Joubert M, et al. Clustering and clinical diversity of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma associated with HTLV-I in a remote black population of French Guiana. Int J Cancer. 1995;60(6):773–6.
Tajima K, Kuroishi T. Estimation of rate of incidence of ATL among ATLV (HTLV-I) carriers in Kyushu, Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1985;15(2):423–30.
Kondo T, Kono H, Nonaka H, Miyamoto N, Yoshida R, Bando F, et al. Risk of adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma in HTLV-I carriers. Lancet. 1987;2(8551):159.
Murphy EL, Hanchard B, Figueroa JP, Gibbs WN, Lofters WS, Campbell M, et al. Modelling the risk of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in persons infected with human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Int J Cancer. 1989;43(2):250–3.
Wilks R, Hanchard B, Morgan O, Williams E, Cranston B, Smith ML, et al. Patterns of HTLV-I infection among family members of patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and HTLV-I associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Int J Cancer. 1996;65(2):272–3.
Osame M, Janssen R, Kubota H, Nishitani H, Igata A, Nagataki S, et al. Nationwide survey of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy in Japan: association with blood transfusion. Ann Neurol. 1990;28(1):50–6.
Chen YC, Wang CH, Su IJ, Hu CY, Chou MJ, Lee TH, et al. Infection of human T-cell leukemia virus type I and development of human T-cell leukemia lymphoma in patients with hematologic neoplasms: a possible linkage to blood transfusion. Blood. 1989;74(1):388–94.
Kanno M, Nakamura S, Matsuda T. Adult T-cell leukemia with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy after complete remission of acute myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1998;338(5):333.
Kondo T, Kono H, Miyamoto N, Yoshida R, Toki H, Matsumoto I, et al. Age- and sex-specific cumulative rate and risk of ATLL for HTLV-I carriers. Int J Cancer. 1989;43(6):1061–4.
Kawano F, Tsuda H, Yamaguchi K, Nishimura H, Sanada I, Matsuzaki H, et al. Unusual clinical courses of adult T-cell leukemia in siblings. Cancer. 1984;54(1):131–4.
Tokudome S, Shimamoto Y, Sumida I. Smoking and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1993;2(1):84–5.
Tsukasaki K, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Tomonaga M. Infective dermatitis among patients with ATL in Japan. Int J Cancer. 1994;57(2):293.
Hisada M, Okayama A, Shioiri S, Spiegelman DL, Stuver SO, Mueller NE. Risk factors for adult T-cell leukemia among carriers of human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Blood. 1998;92(10):3557–61.
Usuku K, Sonoda S, Osame M, Yashiki S, Takahashi K, Matsumoto M, et al. Igata A HLA haplotype-linked high immune responsiveness against HTLV-I in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: comparison with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Ann Neurol. 1988;23(Suppl):S143–50.
Iwanaga M, Watanabe T, Utsunomiya A, Okayama A, Uchimaru K, Koh KR, et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1) proviral load and disease progression in asymptomatic HTLV-1 carriers: a nationwide prospective study in Japan. Blood. 2010 [Epub ahead of print].
Amano M, Kurokawa M, Ogata K, Itoh H, Kataoka H, Setoyama M. New entity, definition and diagnostic criteria of cutaneous adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 proviral DNA load can distinguish between cutaneous and smoldering types. J Dermatol. 2008;35(5):270–5.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, et al. Proposals for the classification of chronic (mature) B and T lymphoid leukaemias. French-American-British (FAB) Cooperative Group. J Clin Pathol. 1989;42:567–84.
Tsukasaki K, Imaizumi Y, Tawara M, et al. Diversity of leukaemic cell morphology in ATL correlates with prognostic factors, aberrant immunophenotype and defective HTLV-1 genotype. Br J Haematol. 1999;105:369–75.
Lennert K, Kikuchi M, Sato E, Suchi T, Stansfeld AG, Feller AC, et al. HTLV-positive and -negative T-cell lymphomas. Morphological and immunohistochemical differences between European and HTLV-positive Japanese T-cell lymphomas. Int J Cancer. 1985;35(1):65–72.
Watanabe T, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K, Osame M, Yoshida M. Constitutive expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein gene in human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) carriers and adult T cell leukemia patients that can be trans-activated by HTLV-1 tax gene. J Exp Med. 1990;172(3):759–65.
Nosaka K, Miyamoto T, Sakai T, Mitsuya H, Suda T, Matsuoka M. Mechanism of hypercalcemia in adult T-cell leukemia: overexpression of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand on adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood. 2002;99(2):634–40.
Tsuda H, Sawada T, Sakata KM, Takatsuki K. Possible mechanisms for the elevation of serum beta 2-microglobulin levels in adult T-cell leukemia. Int J Hematol. 1992;55(2):179–87.
Sadamori N, Ikeda S, Yamaguchi K, et al. Serum deoxythymidine kinase in adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and its related disorders. Leuk Res. 1991;15:99–103.
Kamihira S, Atogami S, Sohda H, et al. Significance of soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels for evaluation of the progression of adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer. 1994;73:2753–8.
Kamihira S, Sohda H, Atogami S, Toriya K, Yamada Y, Tsukazaki K, et al. Phenotypic diversity and prognosis of adult T-cell leukemia. Leuk Res. 1992;16(5):435–41.
Kohno T, Yamada Y, Akamatsu N, Kamihira S, Imaizumi Y, Tomonaga M, et al. Possible origin of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells from human T lymphotropic virus type-1-infected regulatory T cells. Cancer Sci. 2005;96(8):527–33.
Kamada N, Sakurai M, Miyamoto K, Sanada I, Sadamori N, Fukuhara S, et al. Chromosome abnormalities in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a karyotype review committee report. Cancer Res. 1992;52(6):1481–93.
Itoyama T, Chaganti RS, Yamada Y, et al. Cytogenetic analysis and clinical significance in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a study of 50 cases from the human T-cell leukemia virus type-1 endemic area, Nagasaki. Blood. 2001;97:3612–20.
Tsukasaki K, Krebs J, Nagai K, Tomonaga M, Koeffler HP, Bartram CR, et al. Comparative genomic hybridization analysis in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: correlation with clinical course. Blood. 2001;97(12):3875–81.
Oshiro A, Tagawa H, Ohshima K, Karube K, Uike N, Tashiro Y, et al. Identification of subtype-specific genomic alterations in aggressive adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 2006;107(11):4500–7.
Choi YL, Tsukasaki K, O’Neill MC, Yamada Y, Onimaru Y, Matsumoto K, et al. A genomic analysis of adult T-cell leukemia. Oncogene. 2007;26(8):1245–55.
Sasaki H, Nishikata I, Shiraga T, Akamatsu E, Fukami T, Hidaka T, et al. Overexpression of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1, as a possible molecular marker for acute-type adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 2005;105(3):1204–13.
Takasaki Y, Iwanaga M, Imaizumi Y, Tawara M, Joh T, Kohno T, et al. Long-term study of indolent adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Blood. 2010;115(22):4337–43.
Shimoyama M, Ota K, Kikuchi M, et al. Chemotherapeutic results and prognostic factors of patients with advanced non-Hodgkins lymphoma treated with VEPA or VEPA-M. J Clin Oncol. 1988;6:128–41.
Shimoyama M, Ota K, Kikuchi M, et al. Major prognostic factors of adult patients with advanced T-cell lymphoma/leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1988;6:1088–97.
Tobinai K, Shimoyama M, Minato K, et al. Japan Clinical Oncology Group phase II trial of second-generation LSG4 protocol in aggressive T- and B-lymphoma: a new predictive model for T- and B-lymphoma (abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 1994;13:378a.
Tsukasaki K, Tobinai K, Shimoyama M, et al. Deoxycoformycin-containing combination chemotherapy for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group study (JCOG9109). Int J Hematol. 2003;77:164–70.
Yamada Y, Tomonaga M, Fukuda H, et al. A new G-CSF-supported combination chemotherapy, LSG15, for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (ATL): Japan Clinical Oncology Group (JCOG) Study 9303. Br J Haematol. 2001;113:375–82.
Tsukasaki K, Utsunomiya A, Fukuda H, et al. VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG9801. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5458–564.
Tobinai K, Shimoyama M, Inoue S, et al. Phase I study of YK-176 (2-deoxycoformycin) in patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1992;22:164–71.
Kuwazuru Y, Hanada S, Furukawa T, et al. Expression of p-glycoprotein in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood. 1990;76:2065–71.
Tsukasaki K, Ikeda S, Murata K, et al. Characteristics of chemotherapy-induced clinical remission in long survivors with aggressive adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Leuk Res. 1993;17:157–66.
Ichimaru M, Kamihira S, Moriuchi Y, Kuraishi Y, Usui N, Toki H, et al. Clinical study on the effect of natural alpha-interferon (HLBI) in the treatment of adult T-cell leukemia. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1988;15(10):2975–81. Japanese.
Gill PS, Harrington W, Kaplan MH, et al. Treatment of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with a combination of interferon alfa and zidovudine. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1744–8.
Hermine O, Blouscary D, Gessain A, et al. Treatment of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma with zidovudine and interferon alfa. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1749–51.
Tobinai K, Kobayashi Y, Shimoyama M, et al. Interferon alfa and zidovudine in adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma (correspondence). N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1285–6.
White JD, Wharfe G, Stewart DM, et al. The combination of zidovudine and interferon alpha-2B in the treatment of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;40:287–94.
Matutes E, Taylor GP, Cavenagh J, et al. Interferon alpha and zidovudine therapy in adult T-cell leukaemia lymphoma: response and outcome in 15 patients. Br J Haematol. 2001;113:779–84.
Hermine O, Allard I, Levy V, et al. A prospective phase II clinical trial with the use of zidovudine and interferon-alpha in the acute and lymphoma forms of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Hematol J. 2002;3:276–82.
Bazarbachi A, Plumelle Y, Ramos JC, Tortevoye P, Otrock Z, Taylor G, et al. Meta-analysis on the use of zidovudine and interferon-alfa in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma showing improved survival in the leukemic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4177–83.
Kchour G, Tarhini M, Kooshyar M-M, et al. Phase 2 study of the efficacy and safety of the combination of arsenic trioxide, interferon alpha, and zidovudine in newly diagnosed chronic adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL). Blood. 2009;113:6528–32.
Hishizawa M, Kanda J, Utsunomiya A, Taniguchi S, Eto T, Moriuchi Y, et al. Transplantation of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells for adult T-cell leukemia: a nationwide retrospective study. Blood. 2010 [Epub ahead of print].
Okamura J, Utsunomiya A, Tanosaki R, et al. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation with reduced conditioning intensity as a novel immunotherapy and antiviral therapy for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 2005;105:4143–5.
Tanosaki R, Uike N, Utsunomiya A, Saburi Y, Masuda M, Tomonaga M, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using reduced-intensity conditioning for adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma: impact of antithymocyte globulin on clinical outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(6):702–8.
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, et al. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1244.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, et al. National Cancer Institute-sponsored Working Group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1996;87:4990–7.
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, et al. The International Harmonization Project on Lymphoma. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:579–86.
Ohno R, Masaoka T, Shirakawa S, Sakamoto S, Hirano M, Hanada S, et al. Treatment of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with MST-16, a new oral antitumor drug and a derivative of bis(2,6-dioxopiperazine). The MST-16 Study Group. Cancer. 1993;71(7):2217–21.
Tsuda H, Takatsuki K, Ohno R, et al. A late phase II trial of a potent topoisomerase inhibitor, CPT-11, in malignant lymphoma [abstract]. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 1992;11:316.
Arima N, Mizoguchi H, Shirakawa S, Tomonaga M, Takatsuki K, Ohno R. Phase I clinical study of SH L573 (fludarabine phosphate) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1999;26(5):619–29 [Article in Japanese].
Tobinai K, Uike N, Saburi Y, Chou T, Etoh T, Masuda M, et al. Cladribine/ATL Study Group, Japan. Phase II study of cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine) in relapsed or refractory adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2003;77(5):512–7.
Duvic M, Forero-Torres A, Foss F, et al: Long-term treatment of CTCL with the oral PNP inhibitor, forodesine. ASCO annual meeting, Jun 2009; No. 8552.
O’Connor OA, Heaney ML, Schwartz L, et al. Clinical experience with intravenous and oral formulations of the novel histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(1):166–73.
Hasegawa H, Yamada Y, Tsukasaki K, et al. LBH589, a deacetylase inhibitor, induces apoptosis in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells via activation of a novel RAIDD-caspase-2 pathway. Leukemia. 2011;25(4):575–87.
Waldmann TA. Multichain interleukin-2 receptor: a target for immunotherapy in lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989;81:914–23.
Waldmann TA, White JD, Carrasquillo JA, et al. Radioimmunotherapy of interleukin-2Ra-expressing adult T-cell leukemia with yttrium-90-labeled anti-Tac. Blood. 1985;86:4063–75.
Berkowitz JL, Janik JE, Stewart DM, Fioravanti S, Jaffe ES, Fleisher TA, et al. Phase II trial of daclizumab in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 (HTLV-1)-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL). J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:7s (suppl; abstr 8043).
Kreitman RJ, Wilson WH, White JD, Stetler-Stevenson M, Jaffe ES, Giardina S, et al. Phase I trial of recombinant immunotoxin anti-Tac(Fv)-PE38 (LMB-2) in patients with hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(8):1622–36.
Dang NH, Pro B, Hagemeister FB, et al. Phase II trial of denileukin diftitox for relapsed/refractory T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2007;136(3):439–47.
Foss FM, Sjak-Shie NN, Goy A, Advani R, Jacobsen ED. Phase II study of denileukin diftitox with CHOP chemotherapy in newly-diagnosed PTCL: CONCEPT trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:15s (suppl; abstr 8045).
Di Venuti G, Nawgiri R, Foss F. Denileukin diftitox and hyper-CVAD in the treatment of human T-cell lymphotropic virus 1-associated acute T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma. 2003;4(3):176–8.
Rodig SJ, Abramson JS, Pinkus GS, Treon SP, Dorfman DM, Dong HY, et al. Heterogeneous CD52 expression among hematologic neoplasms: implications for the use of alemtuzumab (CAMPATH-1H). Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(23):7174–9.
Jiang L, Yuan CM, Hubacheck J, Janik JE, Wilson W, Morris JC, et al. Variable CD52 expression in mature T cell and NK cell malignancies: implications for alemtuzumab therapy. Br J Haematol. 2009;145(2):173–9.
Gallamini A, Zaja F, Patti C, Billio A, Specchia MR, Tucci A, Levis A, Manna A, Secondo V, Rigacci L, Pinto A, Iannitto E, Zoli V, Torchio P, Pileri S, Tarella C. Alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) and CHOP chemotherapy as first-line treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma: results of a GITIL (Gruppo Italiano Terapie Innovative nei Linfomi) prospective multicenter trial. Blood. 2007 Oct 1;110(7):2316–23. Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 1;12(23):7174–9.
Zhang Z, Zhang M, Goldman CK, Ravetch JV, Waldmann TA. Effective therapy for a murine model of adult T-cell leukemia with the humanized anti-CD52 monoclonal antibody, Campath-1H. Cancer Res. 2003;63(19):6453–7.
Mone A, Puhalla S, Whitman S, Baiocchi RA, Cruz J, Vukosavljevic T, et al. Durable hematologic complete response and suppression of HTLV-1 viral load following alemtuzumab in zidovudine/IFN-[alpha]-refractory adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 2005;106(10):3380–2.
Ravandi F, Faderl S. Complete response in a patient with adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) treated with combination of alemtuzumab and pentostatin. Leuk Res. 2006;30(1):103–5.
O’Mahony D, Morris JC, Stetler-Stevenson M, Matthews H, Brown MR, Fleisher T, et al. EBV-related lymphoproliferative disease complicating therapy with the anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody, siplizumab, in patients with T-cell malignancies. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(7):2514–22.
Niwa R, Shoji-Hosaka E, Sakurada M, Shinkawa T, Uchida K, Nakamura K, Matsushima K, Ueda R, Hanai N, Shitara K.: Defucosylated chimeric anti-CC chemokine receptor 4 IgG1 with enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity shows potent therapeutic activity to T-cell leukemia and lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;64(6):2127–33. Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;64(6):2127–33.
Yamamoto K, Utsunomiya A, Tobinai K, et al. Phase I study of KW-0761, a defucosylated humanized anti-CCR4 antibody, in relapsed patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(9):1591–8.
Ishida T, Joh T, Uike N, et al. Defucosylated anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody (KW-0761) for relapsed adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012 [Epub ahead of print].
O’Connor OA, Horwitz S, Hamlin P, et al. Phase II-I-II study of two different doses and schedules of pralatrexate, a high-affinity substrate for the reduced folate carrier, in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma reveals marked activity in T-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(26):4357–64.
O’Connor OA, Pro B, Pinter-Brown L, et al. PROPEL: a multi-center phase 2 open-label study of pralatrexate (PDX) with vitamin B12 and folic acid supplementation in patients with replapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 2008;112:261.
Marneros AG, Grossman ME, Silvers DN, Husain S, Nuovo GJ, MacGregor-Cortelli B, et al. Pralatrexate-induced tumor cell apoptosis in the epidermis of a patient with HTLV-1 adult T-cell lymphoma/leukemia causing skin erosions. Blood. 2009;113(25):6338–41.
Lee J, Suh C, Kang HJ, Ryoo BY, et al. Phase I study of proteasome inhibitor bortezomib plus CHOP in patients with advanced, aggressive T-cell or NK/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 2008;19(12):2079–83.
Satou Y, Nosaka K, Koya Y, et al. Proteasome inhibitor, bortezomib, potently inhibits the growth of adult T-cell leukemia cells both in vivo and in vitro. Leukemia. 2004;18:1357–63.
Dueck GS, Chua N, Prasad A, et al. Activity of lenalidomide in a phase II trial for T-cell lymphoma: report on the first 24 cases. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:15s (suppl; abstr 8524).
Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4124–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Tsukasaki, K., Tobinai, K. (2013). HTLV-1-Associated T-cell Diseases. In: Foss, F. (eds) T-Cell Lymphomas. Contemporary Hematology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-170-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-170-7_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-169-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-170-7
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)