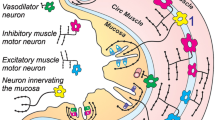
Abstract
The two morphological divisions of the afferent innervation of the upper gastrointestinal tract, the vagal and splanchnic nerves, are distinguishable in functional and in neurochemical terms. It has been known since the early part of the century that the vagal pathway mediates physiological reflexes involved in the normal control of gastric motility and secretion, and that the splanchnic pathway mediates the effects of noxious stimulation of the gut (Hertz, 1911). Peptides are involved in these functions in two ways — as mediators of some of the effects of nerve stimulation, and as modulators of afferent discharge by acting at peptide receptors expressed on afferent nerve fibres (Dockray, 1988). Splanchnic afferents are a rich source of neuropeptides and provide a good illustration of how peptides might mediate the function of some visceral afferents, while vagal fibres express receptors for several peptides and so illustrate modulatory functions. The present account will deal with the physiological significance of these actions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barthó, L., Holzer, P., Lembeck, F. and Szolcsány, J., 1982, Evidence that the contractile response of the guinea-pig ileum to capsaicin is due to release of substance P, J. Physiol., 332: 157.
Beglinger, C., Born, W., Hildebrand, P., Ensinck, J.W., Burkhardt, F., Fischer, J.A., and Gyr, K., 1988, Calcitonin gene-related peptides I and II and calcitonin: Distinct effects on gastric acid secretion in humans, Gastroenterology, 95: 958.
Bremner, A.J., Dockray, G.J., and Forster, E.R., 1990, The mechanism of action of liquid test meals on gastric emptying in rat, J. Physiol., 422: 63P.
Cottrell, D.F., and Iggo, A., 1984, The responses of duodenal tension receptors in sheep to pentagastrin, cholecystokinin and some other drugs, J. Physiol., 354: 477.
Davison, J.S., and Clarke G.D., 1988, Mechanical properties and sensitivity to CCK of vagal gastric slowly adapting mechano-receptors, Am. J. Physiol., 255: G55.
Debas, H.T., Farooq, O., and Grossman, M.I., 1975, Inhibition of gastric emptying is a physiological action of cholecystokinin, Gastroenterology, 68: 1211.
Delbro, D., Fändriks, L., Rosel, S., and Folkers, K., 1983, Inhibition of antidromically induced stimulation of gastric motility by substance P receptor blockade, Acta Physiol. Scand., 118: 309.
Dimaline, R., Dockray, G.J., and Green, T., 1988, The role of the coeliac ganglion in the control of gastric emptying in the rat, J. Physiol., 403: 53P.
Dockray, G.J., 1988, Regulatory peptides and the neuroendocrino-logy of gut-brain relations, Quart. J. Expl. Physiol., 73: 703.
Dunning, B.E., and Taborsky, G.J., 1987, Calcitonin gene-related peptide: A potent and selective stimulator of gastrointestinal somatostatin secretion, Endocrinology, 120: 1774.
Evangelista, S., Lippe, I.Th., Rovero, P., Maggi, C.A., and Meli, A., 1989, Tachykinins protect against ethanol-induced gastric lesions in rats, Peptides, 79: 81.
Fändriks, L., and Delbro, D., 1983, Neural stimulation of gastric bicarbonate secretion in the cat. An involvement of vagal axon-reflexes and substance P? Acta Physiol. Scand., 118: 301.
Flood, J.F., Smith, G.E., and Morley, J.E., 1989, Modulation of memory processing by cholecystokinin: Dependence on the vagus nerve, Science, 236: 832.
Forster, E.R., Green, T., Elliot, M., Bremner, A., and Dockray, G.J., 1990, The role of afferent neurons in the action of cholecystokinin, acid and hyperosmolal solutions on gastric emptying in the rat, Am. J. Physiol., in press.
Forster, E.R., 1990, The role of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the control of gastric emptying in the rat, J. Physiol., in press.
Freidinger, R.M., 1989, Cholecystokinin and gastrin antagonists, Med. Res. Rev., 9: 271.
Green, T., Dimaline, R., Peikin, S., and Dockray, G.J., 1988, Action of the cholecystokinin antagonist L364,718 on gastric emptying in the rat, Am. J. Physiol., 255: G685.
Green, T., and Dockray, G.J., 1988, Characterization of the peptidergic afferent innervation of the stomach in the rat, mouse and guinea pig, Neuroscience, 25: 181.
Hamamura, T., Kazahaya, Yl, and Otsuki, S., 1989, Ceruletide suppresses endogenous dopamine release via vagal afferent system, studied by in vivo intracerebral dialysis, Brain Res., 483: 78.
Hertz, A.F., 1911, “The sensibility of the alimentary canal”, Oxford University Press.
Hodson, C.A., Burden, H.W., and Lawrence, I.E. Jr., 1986, Intraperitoneal cholecystokinin administration inhibits prolactin release: an effect prevented by vagotomy, IRCS Medical Science, 14: 551.
Holzer, P., and Lippe, I.Th., 1988, Stimulation of afferent nerve endings by intragastric capsaicin protects against ethanol-induced damage of gastric mucosa, Neuroscience, 27: 981.
Holzer, P., Pabst, M.A., and Lippe, I.Th., 1989, Intragastric capsaicin protects against aspirin-induced lesion formation and bleeding in the rat gastric mucosa, Gastroenterology, 96: 1425.
Holzer, P., and Sametz, W., 1986, Gastric mucosal protection against ulcerogenic factors in the rat mediated by capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons, Gastroenterology, 91: 975.
Isenberg, J.I., and Csendes, A., 1972, Effect of octapeptide of cholecystokinin on canine pyloric pressure, Am. J. Physiol., 222: 428.
Janig, W., and Morrison, J.F.B., 1986, Functional properties of spinal visceral afferents supplying abdominal and pelvic organs, with special emphasis on visceral nociception, Progress in Brain Research, 67: 87.
Kessler, J.P., and Beaudet, A., 1989, Association of neurotensin binding sites with sensory and visceromotor components of the vagus nerve, J. Neurosci., 9: 466.
Kleibeuker, J.H., Beekhuis, H., Jansen, J.B.M.J., Piers, D.A., and Lamers, C.B.H.W., 1988, Cholecystokinin is a physiological hormonal mediator of fat-induced inhibition of gastric emptying in man, Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 18: 173.
Kawasaki, K., Kodama, M., and Matsushita, A., 1983, Caerulein, a cholecystokinin-related peptide, depresses somatic function via the vagal afferent system, Life Sciences, 33: 1045.
Liddle, R.A., Morita, E.T., Conrad, C.F., and Williams, J.A., 1986, Regulation of gastric emptying in humans by cholecystokinins, J. Clin. Invest., 77: 992.
Louis, S.M., Jamieson, A., Russell, N., and Dockray, G.J., 1989a, The role of substance P and CGRP in neurogenic plasma extravasation and vasodilatation in the rat, Neuroscience, 32: 581.
Louis, S.M., Johnstone, D., Russell, N.J.W., Jamieson, A., and Dockray, G.J., 1989b, Antibodies to calcitonin gene-related peptide reduce inflammation induced by topical mustard oil but not that due to carrageenin in the rat, Neurosci. Lett., 102: 257.
McCann, M.J., Verbalis, J.G., and Sticker, E.M., 1988, Capsaicin pretreatment attenuates multiple responses to cholecystokinin in rats, J. Autonomic Ner. System, 23: 265.
Maggi, C.A., Santicioli, P., Renzi, D., Patachini, R., Surrenti, G., and Meli, A., 1989, Release of substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity and motor response of the isolated guinea pig gallbladder to capsaicin, Gastroenterology, 96: 1093.
Meyer, B.M., Beglinger, C., Jansen, J.B.M.J., Rovati, L.C., Werth, B.A., Hildebrand, P., Zach, D., Stalder, G.A., 1989, Role of cholecystokinin in regulation of gastrointestinal motor functions, The Lancet, 1: 12.
Moran, T.H., Smith, G.P., Hostetier, A.M., and McHugh, P.R., 1987, Transport of cholecystokinin (CCK) binding sites in subdiaphragmatic vagal branches, Brain Research, 415: 149.
Morgan, K.G., Schmalz, P.F., Go, V.L.W., and Szurszewski, J.H., 1978, Electrical and mechanical effects of molecular variants of CCK on antral smooth muscle, Am. J. Physiol., 235: E324.
Mulderry, P.K., Ghatei, M.A., Spokes, R.A., Jones, P.M., Pierson, A.M., Hamid, Q.A., Kanse, S., Amara, S.G., Burrin, J.M., Legon, S., Polak, J.M. and Bloom, S.R., 1988, Differential expression of α-CGRP and β-CGRP by primary sensory neurons and enteric autonomic neurons of the rat, Neuroscience, 25: 195.
Niijima, A., 1981, Visceral afferents and metabolic function, Diabetologia 20: 325.
Niijima, A., 1983, Glucose-sensitive afferent nerve fibres in the liver and their role in food intake and blood glucose regulation, J. Aut. Nerv. System, 9: 207.
Paintal, A.S., 1953, Impulses in vagal afferent fibres from stretch receptors in the stomach and their role in the peripheral mechanism of hunger, Nature, 172: 1194.
Raybould, H.E., Roberts, M.E., and Dockray, G.J., 1987, Reflex decreases in intragastric pressure in response to cholecystokinin in rats, Am. J. Physiol., 253: G165.
Raybould, H.E., Gayon, R., and Dockray, G.J., 1985, CNS effects of circulating CCK8 — involvement of brainstem neurones responding to gastric distension, Brain Res., 342: 187.
Raybould, H.E., Gayton, R.J., and Dockray, G.J., 1988, Mechanisms of action of peripherally administered cholecystokinin octapeptide on brain stem neurones in the rat, J. Neurosci., 8: 3018.
Raybould, H.E., and Taché, Y., 1988, cholecystokinin inhibits gastric motilitiy and emptying via a capsaicin-sensitive vagal pathway in rats, Am. J. Physiol., 255: G242.
Renzi, D., Santicioli, P., Maggi, C.A., Surrenti, C., Pradelles, P., and Meli, A., 1988, Capsaicin-induced release of substance P-like immunoreactivity from the guinea pig stomach in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience Letters, 92: 254.
Ritter, R.C, Kalivas, P., and Bernier, S., 1986, Cholecystokinin-induced suppression of locomotion is attenuated in capsaicin pretreated rats, Peptides, 7: 587.
Schultz, H.D., Gardner, D.G., Deschepper, C.F., Coleridge, H.M., and Coleridge, J.C.G., 1988, Vagal C-fiber blockade abolishes sympathetic inhibition by atrial natriuretic factor, Am. J., Physiol., 255: R6.
Sharkey, K.A., Williams, R.G., Dockray, G.J., 1983, Sensory substance P innervation of the stomach and pancreas: Demonstration of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurones in the rat by combined immunohistochemistry and retrograde tracing, Gastroenterology, 87: 914.
Smith, G.P., Jerome, C., and Norgren, R., 1985, Afferent axons in abdominal vagus mediate satiety effect of cholecystokinin in rats, Am. J. Physiol., 249: R638.
Sternini, C., Reeve, J.R., Jr., and Brecha, N., 1987, Distribution and characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the digestive system of normal and capsaicin-treated rats, Gastroenterology, 93: 852.
Su, H.C., Bishop, A.E., Power, R.F., Hamada, Y, and Polak, J.M., 1987, Dual intrinsic and extrinsic origins of CGRP- and NPY-immunoreactive nerves of the rat gut and pancreas, J. Neurosci., 7: 2674.
Taché, Y., Pappas, T., Lauffenburger, M., Goto, Y., Walsh, J.H., and Debas, H., 1984, Calcitonin gene-related peptide; potent peripheral inhibitor of gastric acid secretion in rats and dogs, Gastroenterology, 87: 344.
Tsunoo, A., Konishi, S., and Otsuka, M., 1982, Substance P as an excitatory transmitter of primary afferent neurons in guinea-pig sympathetic ganglia, Neuroscience, 7: 2025.
Varro, A., Green, T., Holmes, S., and Dockray, G.J., 1988, Calcitonin gene-related peptides in visceral afferent nerve fibres: quantification by radioimmunoassay and transmission of axonal transport rates, Neuroscience, 26: 927.
Yamagishi, T., and Debas, H.T., 1978, Cholecystokinin inhibits gastric emptying by acting on both proximal stomach and pylorus, Am. J. Physiol., 234: E375.
Zarbin, M.A., Wamsley, J.K., Innis, R.B., and Kuhar, M.J., 1981, Cholecystokinin receptors; presence and axonal flow in the rat vagus nerve, Life Sciences, 29: 697..cp255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Dockray, G.J., Forster, E.R., Louis, S.M. (1991). Peptides and their Receptors on Afferent Neurons to the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. In: Costa, M., Surrenti, C., Gorini, S., Maggi, C.A., Meli, A. (eds) Sensory Nerves and Neuropeptides in Gastroenterology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 298. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-0744-8_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-0744-8_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4899-0746-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4899-0744-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive