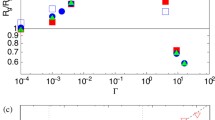
Abstract
The equilibrium and kinetic swelling properties of polymer gels are of considerable interest in the pharmaceutical field. Gels have been proposed as size selective extraction solvents1 and environmentally sensitive permeability barriers for a variety of pharmacologic agents.2,3 The use of gel mechanochemistry to drive an insulin pump is also under investigation.4
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. L. Cussler, M. R. Stokar and J. E. Varberg, Gels as Size Selective Extraction Solvents, A.ICh.E. J., 30:578 (1984).
J. H. Kou, G. L. Amidon and P. L Lee, pH-Dependent Swelling and Solute Diffusion Characteristics of Poly(Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-co-Methacrylic Acid) Hydrogels, Pharm. Res., 5:592 (1988).
K. Ishihara, M. Kobayashi and I. Shinohara, Insulin Permeation through Amphiphilic
Polymer Membranes Having 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate Moiety, Polym. J., 16:647 (1984).
R. A. Siegel and B. A. Firestone, Mechanochemical Approaches to Self-Regulated Insulin Delivery, J. Controlled Release, in press (1990).
R. A. Siegel and B. A. Firestone, pH-Dependent Equilibrium Swelling Properties of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolyte Copolymer Gels, Macromolecules, 21:3254 (1988).
R. A. Siegel, M. Falamarzian, B. A. Firestone, and B. C. Moxley, pH-Controlled Release from Hydrophobic/Polyelectrolyte Hydrogels, J. Controlled Release 8:179 (1988).
K. D. Collins and M.W. Washabaugh, The Hofmeister Effect and the Behavior of Water at Interfaces, O. Rev. Biophys., 18:323 (1985).
P. J. Flory, “Principles of Polymer Chemistry,” Cornell, Ithaca (1953).
J. Ricka and T. Tanaka, Swelling of Ionic Gels: Quantitative Performance of the Donnan Theory. Macromolecules. 17:2916 (1984).
J. Th. G. Overbeek, The Donnan Equilibrium, Prog. Biophys. Biophys. Chem., 6:57 (1956).
A. Shatkay and I. Michaeli, Potentiometrie Titrations of Polyelectrolytes with Separation of Phases, J. Phvs. Chem., 70:3777 (1966).
B. Erman and P.J. Flory, Critical Phenomena and Transitions in Swollen Polymer Networks and in Linear Macromolecules, Macromolecules, 19:2342 (1986).
B. Schwarz and R. A. Siegel, in preparation.
A. A. Rashin and B. Honig, Réévaluation of the Born Model of Ion Hydration, J. Phvs. Chem., 89:5588 (1985).
B. A. Firestone, Swelling and Transport Properties of Hydrophobic Polyelectrolyte Gels. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Francisco (1989).
I. Ohmine and T. Tanaka, Salt Effects on the Phase Transition of Ionic Gels, J. Chem. Phvs., 77,5725 (1982).
A. Katchalsky, Polyelectrolyte Gels,” Prog. Biophvs., 4:1 (1954).
A. Katchalsky and I. Michaeli, Polyelectrolyte gels in salt solutions, J. Polym. Sci., 15:69 (1955).
I. Michaeli and A. Katchalsky, Potentiometrie Titration of Polyelectrolyte Gels, J. Polvm. Sci.,23:683 (1957).
A. J. Grodzinsky. Electromechanical and Physicochemical Properties of Connective Tissue, CRC Grit. Rev. Bioeng. 9:133 (1984).
J. Hasa, M. Ilavsky, and K. Dusek, Deformational, Swelling, and Potentiometric
Behavior of Ionized Poly (methacrylic Acid) Gels. I. Theory, J. Polym. Sci., 13:253 (1975).
M. W. Washabaugh and K. D. Collins, The Systematic Characterization by Aqueous Column Chromatography of Solutes Which Affect Protein Stability, J. Biolog. Chem. 261:12477 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Siegel, R.A., Firestone, B.A., Bravo, J.C., Schwarz, B. (1991). Hydrophobic Weak Polybasic Gels: Factors Controlling Swelling Equilibria. In: DeRossi, D., Kajiwara, K., Osada, Y., Yamauchi, A. (eds) Polymer Gels. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5892-3_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5892-3_23
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5894-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5892-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive