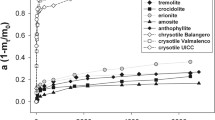
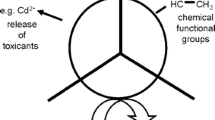
Abstract
The major properties of mineral fibres that relate to carcinogenesis are the length and diameter of the fibres, a fact known for many years, and their chemical composition that enables them to remain in tissues for long periods without dissolving. This has been appreciated more recently. In stating that carcinogenicity depends on length, diameter and durability, however, it is important to examine the evidence on which these suggestions are based and consider if other factors may also be involved.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baris, Y.I., Artvinli, M. and Sahin, A.A. (1979) Environmental mesothelioma in Turkey. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 330: 423–432.
Bolton, R.E., Davis, J.M.G., Donaldson, K. and Wright, A. (1982) Variations in the carcinogenicity of mineral fibres. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 26: 569–582.
Browne, K. (1986) Is asbestos or asbestosis the cause of increased risk of lung cancer in asbestos workers? Br.J. Indust. Med. 43: 145–149.
Chamberlain, M. and Tarmy, E.M. (1977) Asbestos and glass fibres in bacterial mutation tests. Mutat. Res. 43: 159–164.
Davis, J.M.G. (1974) An electron microscope study of the response of mesothelial cells to the intrapleural injection of asbestos dust. Br. J. Exp. Path. 55: 64–70.
Davis, J.M.G., Beckett, S.T., Bolton, R.E., Collings, P. and Middleton, A.P. (1978) Mass and number of fibres in the pathogenesis of asbestos-related lung disease in rats. Br. J. Cancer. 37: 673–688.
Davis, J.M.G., Addison, J., Bolton, R.E., Donaldson, K., Jones, A.D. and Wright, A. (1984) The pathogenic effects of fibrous ceramic aluminium silicate glass administered to rats by inhalation or peritoneal injection. In, “Biological Effects of Man-made Mineral Fibres”. Report of a WHO/IARC meeting. WHO, Copenhagen, pp. 303–323.
Davis, J.M.G., Addison, J., Bolton, R.E., Donaldson, K., Jones, A.D. and Smith, T. (1986) The pathogenicity of long versus short fibre samples of amosite asbestos administered to rats by inhalation and intraperitoneal injection. Br. J. Exp. Path. 67: 415–430.
Davis, J.M.G., and Jones, A.D. (1988) Comparisons of the pathogenicity of long and short fibres of chrysotile asbestos in rats. Br. J. Exp. Path. 69: 717–739.
Davis, J.M.G. (1989) Mineral fibre carcinogenesis: experimental data relating to the importance of fibre type, size, deposition, dissolution and migration. In, “Non-occupational exposure to mine fibres”, Bignon, J., Peto, J. and Saracci, R., eds. IARC Publication No. 90. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. pp. 33–34.
Davis, J.M.G. and Cowie, H. (1990) The relationship between fibrosis and cancer in experimental animals exposed to asbestos and other fibres. Environ. Hlth Perspect. 88: 305–309.
Davis, J.M.G., Jones, A.D. and Miller, B.G. (1990) Experimental studies in rats on the effects of asbestos inhalation coupled with the inhalation of titanium dioxide or quartz, (in press).
Forster, H. (1984) The behaviour of mineral fibres in physiological solutions. In, “Biological Effects of Man-made Mineral Fibres.” Report of a WHO/IARC meeting. WHO, Copenhagen, pp. 27–60.
Gylseth, B., Mowe, G. and Wannag, A. (1983) Fibre type and concentration in the lungs of workers in an asbestos cement factory. Br. J. Indust. Med. 40: 375–379.
Hansen, K. and Mossman, B.T. (1987) Generation of superoxide from alveolar macrophages exposed to asbestiform and non-fibrous particles. Cancer Res. 47: 1681–1686.
Hesterberg, T.W. and Barrett, J.C. (1985) Induction by asbestos fibres of anaphase abnormalities: mechanism for aneuploidy induction and possibly carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 6: 473–475.
King, E.J., Glegg, J.W. and Rae, V.M. (1946) Effect of asbestos and asbestos and aluminium on the lungs of rabbits. Thorax 1: 188–196.
Kipen, H.M., Lillis, R., Suzuki, Y., Valciukas, J.A. and Selikoff, J. (1987) Pulmonary fibrosis in asbestos insulation workers with lung cancer: a radiological and histopathological evaluation. Br. J. Indust. Med. 44: 96–100.
Klingholz, R. and Steinkopf, B. (1984) The reactions of MMMF in a physiological model fluid and in water. In, “Biological Effects of Man-made Mineral Fibres.” Report of a WHO/IARC meeting. Copenhagen pp. 60–87.
Klosterkotter, W. (1968) Experimentelle Untersuchunger uber die Bedeutung der Faserlange fier die Asbest-Fibrose sowie Untersuchunger uber die Beeinflussung der Fibrose durch Polyvinylpyridin-n-oxid. In, “Biologische Wirkungen des Asbestos ”, International Conference, Dresden. Deutches Zentralinstitut Fur Arbeitsmedizin, Berlin 1968, pp. 47–49.
Kolev, K. (1982) Experimentally-induced mesothelioma in white rats in response to intraperitoneal administration of amorphous crocidolite asbestos. Environ. Res. 29: 123–133.
Kuschner, M. (1987) The effects of MMMF on animal systems: some reflections on their pathogenesis. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 31: 791–797.
Le Bouffant, L., Daniel, H., Henin, J.P. and Martin, J.C. (1985) Carcinogenic potency of chrysotile fibres of the length 5 µm. Cahiers de Notes Documentaires 118: 83–90.
Le Bouffant, L., Daniel, H., Henin, J.P., Martin, J.C., Normand, C., Tichoux, G. and Trolard, F. (1987) Experimental study on long-term effects of inhaled MMMF on the lungs of rats. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 31: 765–791.
Lee, K.P., Kelly, D.P., O’Neal, F.O., Slader, J.C. and Kennedy, G.L. (1988) Lung response to ultrafine Kevlar aramid synthetic fibrils following 2-year inhalation exposure in rats. Fundamental Appl. Toxicol. 11: 1–14.
Leineweber, J.P. (1984) Solubility of fibres in vitro and in vivo. In, “Biological Effects of Manmade Mineral Fibres.” Report of a WHO/IARC meeting. WHO, Copenhagen, pp. 87–102.
McConnell, E.E., Wagner, J.C., Skidmore, J.W. and Moore, J.A. (1984) A comparative study of the fibrogenic and carcinogenic effects of UICC Canadian chrysotile B asbestos and glass microfibre (JM100). In, “Biological Effects of Man-made Mineral Fibres.” Report of a WHO/IARC meeting. WHO, Copenhagen, pp. 234–251.
Mikalsen, S., Rivedal, E. and Sanner, T. (1988) Morphological transformation of Syrian Hamster embryo cells induced by mineral fibres and the alleged enhancement of benzo[a]pyrene. Carcinogenesis 9: 891–899.
Morgan, A. and Holmes, A. (1986) Solubility of asbestos and man-made mineral fibres in vitro and in vivo. Its significance in lung disease. Environ. Res. 39: 475–484.
Mossman, B.T., Begin, R.O. (1989) Effects of mineral dusts on cells. Report of a NATO-sponsored workshop. NATO AS1 Series H Vol 30. Springer-verlag, Berlin, New York, London.
Pott, F. and Friedrichs, K.H. (1972) Tumours in rats after intraperitoneal injection of asbestos dusts. Naturwissenschaften 59: 318–332.
Pott, F. (1978) Some aspects on the doseometry of the carcinogenic potency of asbestos and other fibrous dusts. Staub-Reinholt der Luft 38: 486–490.
Pooley, F.D. (1976) An examination of the fibrous mineral content of asbestos lung tissue from the Canadian chrysotile mining industry. Environ. Res. 12: 281–298.
Robertson, A., Bolton, R.E., Miller, B.G., Chapman, J.S., Dodgson, J., Jones, A.D., Niven, K.J. and Davis, J.M.G. (1988) The effect of quartz content on the pathogenicity of coalmine dusts. In, “Inhaled particles Vi”, Dodgson, J., McCallum, R.I., Bailey, M.R., Fisher, D.R., eds. Pergamon Press, Oxford, New York.
Rowlands, N., Gibbs, G.W. and McDonald, A.D. (1982) Asbestos fibres in the lungs of chrysotile miners and millers. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 26: 411–417.
Scymczykiewicz, K. and Wiecek, E. (1960) The effect of fibrous and amorphous asbestos on the collagen content in the lungs of guinea pigs. In, “Proc. 13th Int. Conf. Occupational Hygiene,” New York, pp. 801 et seq.
Smith, D.M., Ortiz, L.W., Archuleta, R.F. and Johnson, N.F. (1987) Long-term health effects in hamsters and rats exposed chronically to man-made vitreous fibres. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 31: 731–755.
Stanton, M.F. and Wrench, C. (1972) Mechanisms of mesothelioma induction with asbestos and fibrous glass. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 48: 797–821.
Stanton, M.F., Layard, M., Tegeris, A., Miller, M. and Kent, E. (1977) Carcinogenicity of fibrous glass: pleural response in the rat in relation to fibre dimension. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 58: 587–603.
Stanton, M.F. and Layard, M. (1978) The carcinogenicity of fibrous minerals, National Bureau of Standards special publication 506, Proceedings of the workshop on asbestos, Gaithersburg, MD, pp. 143–151.
Suzuki, Y. (1974) Interaction of asbestos with alveolar cells. Environ. Hlth Perspect. 9: 241–252.
Timbrell, V. (1973) Physical factors as etiological mechanisms. In, “Biological Effects of Asbestos”, Bogovski, P., ed. IARC Scientific publication no. 8. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon. pp. 295–304.
Vorwald, A.J., Durkan, T.M. and Pratt, P.C. (1951) Experimental studies of asbestosis. AMA Arch. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Med. 3: 1–43.
Wagner, J.C., Berry, G. and Timbrell, V. (1973) Mesotheliomata in rats after inoculation with asbestos and other minerals. Br. J. Cancer 28: 173–185.
Wagner, J.C., Berry, G., Skidmore, J.W. and Timbrell, V. (1974) The effects of the inhalation of asbestos in rats. Br. J. Cancer 29: 252–269.
Wagner, J.C., Berry, G., Skidmore, J.W. and Pooley, F.D. (1980) The comparative effects of three chrysotiles by injection and inhalation in rats. In, “Biological Effects of Mineral Fibres”, Wagner, J.C., ed. IARC Scientific Publication No. 30. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, pp. 363–372.
Wagner, J.C., Berry, G.B., Hill, R.J., Munday, D.E. and Skidmore, J.W. (1984) Animal experiments with MMM(V)F. Effects of inhalation and intraperitoneal inoculation in rats. In, “Biological Effects of Man-made Mineral Fibres.” Report of A WHO/IARC meeting WHO, Copenhagen, pp. 209–234.
Wagner, J.C., Griffiths, D.M. and Hill, R.J. (1984) The effect of fibre size on the in vivo activity of UICC crocidolite. Br. J. Cancer 49: 455–458.
Wagner, J.C., Skidmore, J.W., Hill, R.J. and Griffiths, D.M. (1985) Erionite exposure and mesothelioma in rats. Br. J. Cancer 51: 727–730.
Wagner, J.C. (1988) Significance of the fibre size of erionite. Paper presented at VII International Pneumoconiosis Conference, Pittsburgh. (Conference report in press.)
Wright, G.W. and Kuschner, M. (1977) The influence of varying lengths of glass and asbestos fibres on tissue response in guinea pigs. In, “Inhaled particles IV.” Walton, H., ed. Pergamon Press, Oxford. pp. 455–474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Davis, J.M.G. (1991). Experimental Studies on Mineral Fibre Carcinogenesis: An Overview. In: Brown, R.C., Hoskins, J.A., Johnson, N.F. (eds) Mechanisms in Fibre Carcinogenesis. NATO ASI Series, vol 223. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-1363-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-1363-2_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-1365-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-1363-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive