Abstract
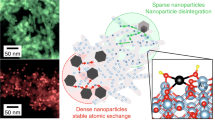
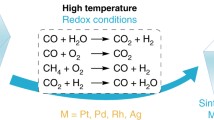
When noble metals are used as catalysts, the metal is generally dispersed on a high surface area support in the form of small crystallites (< 3 nm in diameter). One of the functions of the support is to physically separate the metal crystallites and thereby hinder the agglomeration of the metal crystallites. This agglomeration would decrease the metal surface area and therefore cause a loss of catalytic activity. This process of metal particle growth is generally called catalyst sintering or aging. It is in this context that the term sintering will be used throughout this paper.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruckenstein, E. and Pulvermacher, B., AIChE J. 19, 356 (1973).
Ruckenstein, E. and Pulvermacher, B., J. Catal. 29, 224 (1973).
Flynn, P.C. and Wanke, S.E., J. Catal. 34, 390 (1974).
Flynn, P.C. and Wanke, S.E., J. Catal. 34, 400 (1974).
Wanke, S.E. and Flynn, P.C., Catal. Rev. (in press).
Wynblatt, P. and Gjostein, N.A., Scr. Met. 7 969 (1973).
Wynblatt, P. and Gjostein, N.A., Progr. Solid State Chem. 9(in press).
Renouprez, A., Hoang-Van, C., and Compagnon, P.A., J. Catal. 34, 411 (1974).
Wynblatt, P. and Gjostein, N.A., Scr. Met. 8, 169 (1974).
McLean, N. and Hondros, E.D., J. Mat. Sci. 6, 19 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1975 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wanke, S.E. (1975). Sintering of Supported Metal Catalysts: Application of a Mechanistic Model to Experimental Data. In: Kuczynski, G.C. (eds) Sintering and Catalysis. Materials Science Research, vol 10. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-0934-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-0934-5_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-0936-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-0934-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive