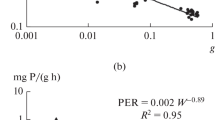
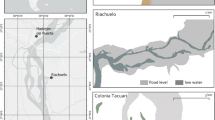
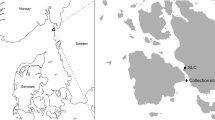
Abstract
From the biologist’s point of view the benthic boundary marks the lower limit of pelagic organisms, receives material dropping out of the pelagic phase, provides a substratum for the activities of epibenthos, and constitutes a habitat for burrowing forms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Key References
Fenchel, T., 1969, The ecology of marine microbenthos. IV. Structure and function of the benthic ecosystem, Ophelia 6: 1–182.
Hessler, R. R., 1974, The structure of deep benthic communities from central ocean waters, in: The Biology of the Oceanic Pacific, Oregon State University Press, pp. 79–93.
Hood, D. W., (ed.), 1970, Organic matter in natural waters. Institute of Marine Science, University of Alaska, Occasional Publication No. 1., 625 pp.
Jorgensen, C. B., 1966, Biology of Suspension Feeding, Pergamon, Oxford, 357 pp.
Mann, K. H., 1969, The dynamics of aquatic ecosystems, Advances in Ecological Research 6: 1–81.
Melchiori, and Hopkins, J., (Ed.), 1972, The role of detritus in the aquatic environment, Memorie dell’lnstituto Italiano di Idrobiologia 29 (Suppl.)
Pamatmat, M. M., and Bhagwat, G., 1973, Anaerobic metabolism in Lake Washington sedi-ments, Limnology and Oceanography 18: 611–627.
Parsons, T., and Takahasi, M., 1973, Biological Oceanographic Processes, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 186 pp.
Riley, G. A., 1970, Particulate organic matter in sea water, Advances in Marine Biology 8: 1–118.
Smayda, T. J., 1970, The suspension and sinking of phytoplankton in the sea, Oceanog-raphy and Marine Biology Annual Review 8: 353–141.
Sokolova, M. N., 1972, Trophic structure of deep-sea maciobenthos, Marine Biology 16: 1– 12.
Steele, J. H., (ed.), 1970, Marine Food Chains, Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh, 552 pp.
Thiel, H., 1971, Die Bedeutung der Meiofauna in Küstenfernen benthischen Lebensgenein-verschiedener geographischer Regionen, Verhandlungen der Deutschen Zoologischen Gesellschaft 65: 37–42.
Vinogradov, M. E., 1955, Vertical migration of Zooplankton and their importance for the nutrient of abyssal pelagic fauna, Trudy Institua Okeanologii-Akademiya Nauk SSSR 13: 71–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1976 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
McCave, I.N. (1976). Metabolism at the Benthic Boundary. In: McCave, I.N. (eds) The Benthic Boundary Layer. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-8747-7_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-8747-7_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4615-8749-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-8747-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive