Abstract
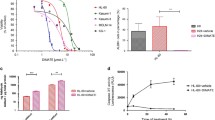
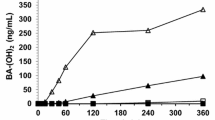
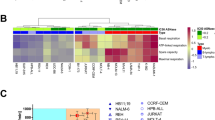
Cyclophosphamide (CP) and mafosfamide (MF) are converted in various tissues to 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide, and subsequently to aldophosphamide (AP). In target cells, AP is further broken down to the toxic compounds phosphoramide mustard and acrolein. AP can be oxidized to a nontoxic metabolite (carboxyphosphamide) catalyzed by one or more types of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) isoenzymes. Thus, intracellular ALDH activity appears to be an important determinant in modulating sensitivity to CP in patients undergoing chemotherapy. The class 1 cytosolic enzyme (ALDH1) has been shown to be particularly important in the metabolism of CP and MF derivatives in bone marrow cells (Kohn and Sladek, 1985; Kastan et al., 1990; Dockham et al., 1992). The overall contribution of blood ALDH in this respect is, however, not known. In the present study, we have determined ALDH activity in human blood subfractions from healthy subjects and malignant lymphoma patients undergoing combination chemotherapy plus or minus CP.
This work will be a part of the MD thesis of M. Metzenthin to be submitted to the Faculty of Medicine, University of Hamburg.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, D.P., von Eitzen, U., Meier-Tackmann, D. and Goedde, H.W.: Metabolism of cyclophosphamide by aldehyde dehydrogenases. In: Enzymology and Molecular Biology of Carbonyl Metabolism 5. Eds. H. Weiner, R.S. Holmes and D.W. Crabb. Plenum Press, New York (1995) pp 115–122.
Dockham, P.A., Lee, M.O. and Sladek, N.E.: Identification of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenases that catalyze the oxidation of aldophosphamide and retinaldehyde. Biochem. Pharmacol. 43 (1992) 2453–2469.
Faraj, B.A., Lenton, J.D., Kutner, M., Camp, V.M., Stammers, T.W., Lee, S.R., Lolies, P.A. and Chandora, D.: Prevalence of low monoamine oxidase function in alcoholism. Alcoholism Clin. Exp. Res. 11 (1987) 464–467.
Kastan, M.B., Schlaffer, E., Russo, J.E., Colvin, O.M., Civin, C.I. and Hilton, J.: Direct demonstration of elevated aldehyde dehydrogenase in human hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood 75 (1990) 1947–1950.
Kohn F.R. and Sladek, N.E.: Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity as the basis for the relative insensitivity of murine pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells to oxazaphosphorines. Biochem. Pharmacol. 34 (1985) 3465–3471.
von Eitzen, U., Meier-Tackmann, D., Agarwal, D.P. and Goedde, H.W.: Detoxification of cyclophosphamide by human aldehyde dehydrogenase isozymes. Cancer Lett. 76 (1994) 45–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Metzenthin, M., Meier-Tackmann, D., Agarwal, D.P., Zschaber, R., Weh, HJ. (1996). Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-Mediated Metabolism of Acetaldehyde and Mafosfamide in Blood of Healthy Subjects and Patients with Malignant Lymphoma. In: Weiner, H., Lindahl, R., Crabb, D.W., Flynn, T.G. (eds) Enzymology and Molecular Biology of Carbonyl Metabolism 6. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 414. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5871-2_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5871-2_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7692-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-5871-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive