Abstract
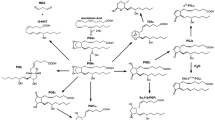
In mammalian cells, prostaglandin (PG)-biosynthetic pathways utilizing endogenous arachidonic acid (AA) are subdivided into three distinct phases, which show different kinetics and may recruit different sets of biosynthetic enzymes. The constitutive immediate response, which occurs within several minutes after stimuli causing a rapid and transient increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+, is regulated by post-translational activation of constitutively expressed enzymes. The delayed response, which proceeds gradually for several hours after proinflammatory stimuli, requires de novo synthesis of particular biosynthetic enzymes. The induced immediate response, which is elicted by Ca2+-mobilizing stimuli after priming by proinflammatory stimuli, reflects the combination of the above two responses, and involves both constitutive and inducible enzymes. Here we introduce the differential coupling of the initial [phospholipase A2 (PLA2)], intermediate [cyclooxygenase (COX)], and terminal [terminal PG synthase (tPGS)] biosynthetic enzymes in each phase using rat peritoneal macrophages, mouse osteoblasts and other cell types as model systems.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Naraba, M. Murakami, H. Matsumoto, S. Shimbara, A. Ueno, I. Kudo, and S. Oh-ishi. Segregated coupling of phospholipases A2, cyclooxygenases, and terminal prostanoid synthases in different phases of prostanoid biosynthesis in rat peritoneal macrophages. J. Immunol.160: 2974 (1998)
H. Matsumoto, H. Naraba, M. Murakami, I. Kudo, I., K. Yamaki, A. Ueno, and S. Oh-ishi. Concordant induction of prostaglandin E2 synthase with cyclooxygenase-2 leads to preferred production of prostaglandin E2 to thromboxane and prostaglandin D2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rat peritoneal macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.230: 110 (1997)
M. MacPhee, K.P. Chepenik, R. Liddell, K.K. Nelson, L.D. Siracusa, and A.M. Buchberg. The secretory phospholipase A2 gene is a candidate for the Momllocus, a major modifier of Apcmin-induced intestinal neoplasia.Ccll 81: 957 (1995)
M. Murakami, H. Kuwata, H., Y. Amakasu, S. Shimbara, Y. Nakatani, G. Atsumi, and I. Kudo. Prostaglandin E2 amplifies cytosolic phospholipase A2 and cyclooxygenase-2-dependent delayed prostaglandin E2 generation in mouse osteoblastic cells: enhancement by secretory phospholipase A2.J. Biol. Chem.272: 19891 (1997)
Q-R. Chen, C. Miyaura, S. Higashi, M. Murakami, I. Kudo, S. Saito, T. Hiraide, Y. Shibasaki, and T. Suda. Activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2, by platelet-derived growth factor is essential for cyclooxygenase-2-dependent prostaglandin E2 synthesis in mouse osteoblasts cultured with interleukin-1. J. Biol. Chem.272: 5952 (1997)
M. Murakami, K. Tada, K. Nakajima, and I. Kudo. Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent delayed prostaglandin D2 generation is initiated by nerve growth factor in rat peritoneal mast cells: its augmentation by extracellular type II secretory phospholipase A2. J. Immunol.159: 439 (1997)
H. Kuwata, Y. Nakatani, M. Murakami, and I. Kudo. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is required for cytokine-induced expression of type IIA secretory phospholipase A2 that mediates optimal cyclooxygenase-2-dependent delayed prostaglandin E2 generation in rat 3Y1 fibroblasts. J. Biol Chem. 273: 1733 (1998)
M. Murakami, R. Matsumoto, K. F. Austen, and J. P. Arm. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-1 and-2 couple to different transmembrane stimuli to generate prostaglandin D2 in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. J. Biol Chem. 269: 22269 (1994)
M. Murakami, C. O. Bingham, R. Matsumoto, K. F. Austen, and J. P. Arm. IgE-dependent activation of cytokine-primed mouse cultured mast cells induces a delayed phase of prostaglandin D2 generation via prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-2. J. Immunol. 155: 4445 (1995)
S. T. Reddy, M. V. Winstead, J. A. Tischfield, and H. R. Herschman. Analysis of the secretory phospholipase A2 that mediates prostaglandin production in mast cells. J. Biol Chem. 272: 13591 (1997)
F. Bartoli, H.-K. Lin, F. Ghomashchi, M. H. Gelb, M. K., Jain, and R. Apitz-Castro. Tight binding inhibitors of 85-kDa phospholipase A2, but not 14-kDa phospholipase A2, inhibit release of free arachidonate in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J. Biol Chem. 269: 15625 (1994)
M. Murakami, I. Kudo, and K. Inoue. Molecular nature of phospholipase A2 involved in prostaglandin I2 synthesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells: possible participation of cytosolic and extracellular type II phospholipases A2. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 839 (1993)
C.O. Bingham, M. Murakami, H. Fujishima, J. E. Hunt, K. F. Austen, and J. P. Arm. A heparin-sensitive phospholipase A2 and prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-2 are functionally linked in the delayed phase of prostaglandin D2 generation in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 25936 (1996)
M. Murakami, R. Matsumoto, Y. Urade, K.F. Austen, and J.P. Arm. c-Kitligand mediates increased expression of cytosolic phospholipase A2, prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase-1, and hematopoietic prostaglandin D2 synthase and increased IgE-dependent prostaglandin D2 generation in immature mouse mast cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 3239 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kudo, I., Murakami, M. (1999). Diverse Functional Coupling of Prostanoid Biosynthetic Enzymes in Various Cell Types. In: Honn, K.V., Marnett, L.J., Nigam, S., Dennis, E.A. (eds) Eicosanoids and Other Bioactive Lipids in Cancer, Inflammation, and Radiation Injury, 4. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 469. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4793-8_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-4793-8_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7171-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-4793-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive