Abstract
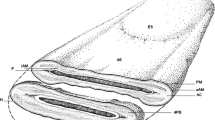
Mammalian eggs and embryos are enclosed and presumably protected by an extracellular shell termed the zona pellucida (Fig. 4-1). There has been intense interest in the zona pellucida in recent years because of increased recognition of the importance of the zona in fertilization and because of the developments of methods to isolate zonae pellucidae, to assay sperm binding to zonae, and to quantitatively access the acrosomal status of spermatozoa. Although there are numerous conflicting reports concerning the mechanism of sperm-zona binding and the role of the zona in the acrosome reaction, many workers now believe that one universal concept explains the function of the zona pellucida in these events. Briefly, this concept holds that sperm do not undergo the acrosome reaction until they bind to the zona pellucida and that one of the three macromolecules that compose the zona pellucida, ZP3, is responsible for sperm binding to the zona pellucida, as well as the initiation of the acrosome reaction. Because of the intense interest in the zona pellucida, its structure and function have been much discussed and recently reviewed in detail [1, 2]. What can I add to these good recent reviews without reiterating what can be found elsewhere?
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fournier-Delpech S, Courot M Sperm-Zona: Pellucida binding activity. Oxford Rev Reprod Biol 9:284–321, 1987.
Wassarman PM: Zona pellucida glycoproteins. Ann Rev Biochem 57: 415–42, 1988.
Phillips DM, Shalgi R: Surface properties of the zona pellucida. J Exp Zool 213: 1–8, 1980.
Nicolson GL, Yanagimachi R, Yanagimachi H: Ultras-tructural localization of lectin-binding sites on the zonae pellucidae and plasma membranes of mammalian eggs. J Cell Biol 66: 263–74, 1975.
Ahuja KK, Blowell GP: Probable asymmetry in the organization of components of the hamster zona pellucida. J Reprod Fertil 69: 49–55, 1983.
Vazquez, MH, Phillips DM, Wassarman P: Interaction of mouse sperm with purified sperm receptors covalently-linked to silica beads. J Cell Sci 92: 713–722, 1989.
Bleil JD, Wassarman PM: Galactose at the nonreducing terminus of O-linked oligosaccharides of mouse egg zona pellucida glycoprotein ZP3 is essential for the glycoprotein’s sperm receptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6778–6782, 1988.
Swenson CE, Dunbar BS: Specificity of sperm-zona interaction. J Expt Zool 219: 97–104, 1982.
Bedford JM: Sperm-egg interaction: The specificity of human spermatozoa. Anat Rec 188: 477–488, 1977.
Peterson RN, Russell LD, Hunt NP: Evidence for specific binding of uncapacitated boar spermatozoa to porcine zonae pellucidae in vitro. J Exp Zool 231: 137–147,1984.
Myles DG, Hyatt H, Primakoff P: Binding of both acrosome-intact and acrosome-reacted guinea pig sperm to the zona pellucida during in vitro fertilization. Dev Biol 121: 559–567, 1987.
Huang TTF, Fleming AD, Yanagimachi R: Only acro-some reacted spermatozoa can bind to and penetrate zona pellucida: A study using the guinea pig. J Exp Zool 217: 287–290, 1981.
Yanagimachi R, Phillips DM: The status of acrosomal caps of hamster spermatozoa immediately before fertilization in vivo. Gamete Res 9: 1–19, 1984.
Morales P, Cross NL, Overstreet J, Hanson FW: Acro-some intact and acrosome-reacted human sperm can initiate binding to the zona pellucida. Dev Biol 133: 385–392, 1989.
Cummins JM, Yanagimachi R: Sperm-egg ratio and the site of the acrosome reaction during in vivo fertilization in the hamster. Gamete Res 5: 239–256, 1982.
Cummins JM, Yanagimachi R: Development of the ability to penetrate the cumulus oophorus by hamster spermatozoa capacitated in vitro, in relation to the timing of the acrosome reaction. Gamete Res 15: 187–212, 1986.
Cherr GN, Lambert H, Meizel S, Katz DF: In vitro studies of the golden hamster sperm acrosome reaction: Completion on the zona pellucida and induction by homologous soluble zona pellucida. Dev Biol 114: 119–131, 1986.
Katz DF, Cherr GN, Lambert H: The evolution of hamster sperm motility during capacitation and interaction with the ovum vestments in vitro. Gamete Res 14: 333–346, 1986.
Saling PM, Storey BT: Mouse gamete interactions during fertilization rin vitro. Chlortetracycline as a fluorescent probe for the mouse sperm acrosome reaction. J Cell Biol 83: 544–554, 1979.
Lopez LC, Bayna EM, Litoff D, Shaper NL, Shaper JH, Shur BD: Receptor function of mouse sperm surface galactosyltransferase during fertilization. J Cell Biol 101: 1501–1510, 1985.
Shur BD, Hall NG: A role for mouse sperm surface galactosyltransferase in sperm binding to the egg zona pellucida. J Cell Biol 95: 574–579, 1982.
Lambert H, Van Le A: Possible involvement of a sialated component of the sperm plasma membrane in sperm-zona interaction in the mouse. Gamete Res 10: 153–163, 1984.
Huang TTF, Ohzu E, Yanagimachi R: Evidence suggesting that L-fucose is part of a recognition signal for sperm-zona pellucida attachment in mammals. Gamete Res 5: 355–361, 1982.
Huang TTF, Yanagimachi R: Fucoidin inhibits attachment of guinea pig spermatozoa to the zona pellucida through binding to the inner acrosomal membrane and equatorial domains. Expt Cell Res 153: 363–373, 1984.
Saling PM, Lakoski KA: Mouse sperm antigens that participate in fertilization. II. Inhibition of sperm penetration through the zona pellucida using monoclonal antibodies. Biol Reprod 33: 527–536, 1985.
Ahuja KK, Rudak EA, Richardson DW, Dor J, Djahan-Bahkch O, Templeton A A: The influence of anti-zona and anti-sperm antibodies on sperm-egg interactions. J Re-prod Fertil 62: 597–606, 1981.
O’Rand MG, Irons GP: Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit sperm auto-antigens. II. Inhibition of human sperm penetration of zona free hamster eggs. Biol Reprod 30: 731–736, 1984.
O’Rand MG, Irons GP, Porter JP: Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit sperm auto-antigens. I. Inhibition of in vitro fertilization and localization on the egg. Biol Reprod 30: 721–729, 1984.
Suarez SS, Wolf DP, Meizel S: Induction of the acrosome reaction in human spermatozoa by a fraction of human follicular fluid. Gamete Res 14: 107–121, 1986.
Austin CR, Bishop MWH: Role of the rodent acrosome and perforatorium in fertilization. Proc Soc (London) Ser B 149: 241–248, 1958.
Bedford JM: Ultrastructural changes in the sperm head during fertilization in the rabbit. Am J Anat 123: 329–358, 1968.
Bedford JM: An electron microscope study of sperm penetration into the rabbit egg after natural mating. Am J Anat 133: 213–254, 1972.
Bedford JM: Mechanisms involved in penetration of spermatozoa through the vestments of the mammalian egg. In: Coutinho EM, Fuchs F (eds), Physiology and Genetics of Reproduction Part B New York: Plenum Press, pp. 55–68, 1974.
Siiteri JE, Dandekar P, Meizel S: Human sperm acro-some-initiating activity associated with the human cumulus oophorus and mural granulosa cells. J Exp Zool 246: 71–80, 1988.
Yudin AI, Gottlieb W, Meizel S: Ultrastructural studies of the early events of the human sperm acrosome reaction as initiated by human follicular fluid. Gamete Res 20: 11–24, 1988.
Pereda J, Coppo M: An electron microscopic study of sperm penetration into human egg investments. Anat Embryol (Berlin) 173: 247–252, 1985.
Osman RA, Andria ML, Jones AD, Meizel S: Steroid induced exocytosis: The human acrosome reaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 160: 828–833, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Phillips, D.M. (1991). Structure and Function of the Zona Pellucida. In: Familiari, G., Makabe, S., Motta, P.M. (eds) Ultrastructure of the Ovary. Electron Microscopy in Biology and Medicine, vol 9. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3944-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3944-5_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6760-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3944-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive