Abstract
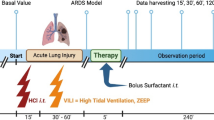
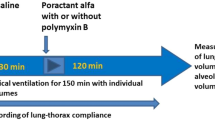
Massive aspiration of gastric contents is one of the most feared complications of general anesthesia and is known to be an important cause of the adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (for review, see Gibbs and Modell, 1990 and Fowler et al., 1983). Due to direct damage of the alveolar-capillary membrane, especially to the type I and II pneumocytes, protein-rich edema fluid enters the alveolar space (Awe et al., 1966; Greenfield et al., 1969; Grimbert et al., 1981; Kobayashi et al., 1990; Manny et al., 1986). It has been established that these plasma derived proteins are potent surfactant inhibitors (Ennema et al., 1988; Fuchimukai et al., 1987; Holm et al., 1988; Ikegami et al., 1984; Seeger et al., 1985). Besides this, it has been proposed that hydrochloric acid (HC1) directly damages the surfactant system (Greenfield et al., 1969; Winn et al., 1983). As the surfactant system seems to be involved in the pathophysiology of respiratory failure caused by HC1 aspiration, a study was designed to investigate the effect of different treatment strategies with an exogenous surfactant preparation on lung function of rats suffering from respiratory failure after intratracheal HC1 instillation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awe, W.C., Fletcher, W.S. and Jacob S.W., 1966, The pathophysiology of aspiration pneumonitis, Surgery, 60: 232.
Ennema, J.J., Kobayashi, T., Robertson, B. and Curstedt, T., 1988, Inactivation of exogenous surfactant in experimental respiratory failure induced by hyperoxia, Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand., 32: 665.
Fowler, A.A., Hamman, R.F., Good, J.T., Benson, K.N., Baird, M., Eberle, D.J., Petty, T.L. and Hyers, T.M., 1983, Adult respiratory distress syndrome: risk with common predispositions, Ann. Intern. Med., 98: 593.
Fuchimukai, T., Fùjiwara, T., Takahashi, A. and Enhorning, G., 1987, Artificial pulmonary surfactant inhibited by proteins, J. Appl. Physiol., 62: 429.
Gibbs, C.P. and Modell, J.H., 1990, Management of aspiration pneumonitis, in: “Anesthesia” (third edition), R.D. Miller, ed., Churchill Livingstone, New York, Edinburgh, London, Melbourne, 1293.
Greenfield, L.J., Singleton, R.P., McCaffree, D.R. and Coalson, J.J., 1969, Pulmonary effects of experimental graded aspiration of hydrochloric acid, Ann. Surg., 170: 74.
Grimbert, F.A., Parker, J.C. and Taylor, A.E., 1981, Increased pulmonary vascular permeability following acid aspiration, J. Appl. Physiol., 51: 335.
Holm, B.A., Notter, R.H. and Finkelstein, J.N., 1985, Surface property changes from interactions of albumin with natural lung surfactant and extracted lung lipids, Chem. Phys. Lipids., 38: 287.
Holm, B.A. and Notter, R.H., 1987, Effects of hemoglobin and cell membrane lipids on pulmonary surfactant activity, J. Appl. Physiol., 63: 1434.
Holm, B.A., Enhorning, G. and Notter, R.H., 1988, A biophysical mechanism by which plasma proteins inhibit lung surfactant activity, Chem. Phys. Lipids., 49: 49.
Ikegami, M., Jobe, A., Jacobs, H. and Lam, R., 1984, A protein from airways of premature lambs that inhibits surfactant function, J. Appl. Physiol., 57: 1134.
Kobayashi, T., Ganzuka, M., Tanigushi, J., Nitta, K. and Murakami, S., 1990, Lung lavage and surfactant replacement for hydrochloric acid aspiration in rabbits, Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand., 34: 216.
Lachmann, B., Hallman, M. and Bergmann, K.C., 1987, Respiratory failure following anti-lung serum: study on mechanisms associated with surfactant system damage, Exp. Lung Res., 12: 163.
Manny, J., Manny, N., Lelcuk, S., Alexander, F., Feingold H., Kobzik, L., Valeri, R., Shepro, D. and Hechtman, H.B., 1986, Pulmonary and systemic consequences of localized acid aspiration, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 162: 259.
Metcalfe, I.L., Enhorning, G. and Possmayer, F., 1980, Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins: their role in the expression of surface activity, J. Appl. Physiol., 49: 34.
Seeger, W., Stöhr, G., Wolf, H.R.D. and Neuhof, H., 1985, Alteration of surfactant function due to protein leakage: special interaction with fibrin monomer, J. Appl. Physiol., 58: 326.
Strohmaier, W., Redl, H. and Schlag, G., 1990, Studies of the potential role of a semisynthetic surfactant preparation in an experimental aspiration trauma in rats, Exp. Lung Res., 16: 101.
Winn, R., Stothert, J., Nadir, B. and Hildebrandt, J., 1983, Lung Mechanics following aspiration of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid, J. Appl. Physiol., 55: 1051.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Eijking, E.P., Gommers, D., Kullander, J., de Buijzer, E., Beukenholdt, R.W., Lachmann, B. (1992). Different Surfactant Treatment Strategies for Respiratory Failure Induced by Hydrochloric Acid Aspiration in Rats. In: Erdmann, W., Bruley, D.F. (eds) Oxygen Transport to Tissue XIV. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 317. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3428-0_38
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6516-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3428-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive