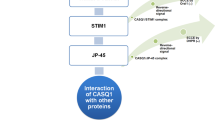
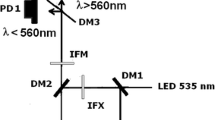
Abstract
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), the membrane-bound calcium store of skeletal muscle, controls the contraction-relaxation cycle by raising and lowering the myoplasmic free calcium concentration, and consists of two continuous yet distinct regions, the free or non-junctional SR and the junctional SR, i.e., the area of terminal cisternae (TC) directly facing the transverse tubules (Costello et al., 1986; Fleischer and Inui, 1989).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blount, P. and L.J.P. Merlie, 1991, BiP associates with newly synthesized subunits of the mouse nicotinic receptor, J. Cell Biol.,113: 1125.
Bole, D.G., L.M. Hendershot and J.F. Kenney, 1986, Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding proteins with nascent heavy chains in non secreting and secreting hybridomas. J. Cell Biol., 102: 1558.
Bole, D.G., R. Down, M. Doriaux and J.J. Jamieson, 1990, Immunocytochemical localization of BiP to the rough endoplasmic reticulum: evidence for protein sorting by selective retention. J. Histochem. Cytochem., 37: 1817.
Cala, S.E. and L.R. Jones, 1983, Rapid purification of calsequestrin from cardiac and skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles by Ca2+ -dependent elution from phenyl-Sepharose. J. Biol. Chem., 258: 11932.
Cala, S.E. and L.R. Jones, 1991, Phosphorylation of cardiac and skeletal muscle calsequestrin isoforms by casein kinase II. J. Biol. Chem., 266: 391.
Cala, S.E., B.T. Scott and L.R. Jones, 1990, Intraluminal sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-binding proteins. Sem. Cell Biol., 1: 265.
Chiesi, M. and E. Carafoli, 1982, The regulation of Ca2+ transport by rat skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Role of calmodulin and the 53,000 dalton glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem., 257: 984
Costello B., C. Chadwick, A. Saito, A. Chu, A. Maurer and S. Fleischer, 1986, Characterization of the junctional face membrane of terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Biol., 103: 741.
Damiani, E., and A. Margreth, 1990, Specific protein-protein interactions of calsequestrin with junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 172: 1253.
Damiani, E. and A. Margreth, 1991, Subcellular fractionation to junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum and biochemical characterization of the 170 kDa Ca2+- and LDL-binding protein in rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem. J., in press.
Damiani, E., P. Volpe and A. Margreth, 1990, Coexpression of two isoforms of calsequestrin in rabbit slow-twitch muscle. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil., 11: 522.
Earnshaw, W.C., 1987, Anionic regions in nuclear proteins. J. Cell Biol., 105:1479.
Ezerman, E.B. and H. Ishikawa, 1967, Differentiation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and T-system in developing chick skeletal muscle in vitro. J. Cell Biol., 35: 405.
Fambrough, D.M. and P.N. Devreotes, 1978, Newly synthesized acetylcholine receptors are located in the Golgi apparatus. J. Cell Biol., 76: 237.
Fleischer, S. and M. Inui, 1989, Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu. Rev. Piophys, Biophys, Chem., 18: 333.
Fliegel, L., K. Burns, M. Opas and M. Michalak, 1989a, The high-affinity calcium binding protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Tissue distribution and homology with calregulin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 982: 1.
Fliegel, L., E. Leberer, N.M. Green and D.H. MacLennan, 1989b, The fast-twitch muscle calsequestrin isoform predominates in rabbit slow-twitch soleus muscle. FEB3 Lett., 242: 297.
Fliegel, L., K. Burns, D.H. MacLennan, R.A.F. Reithmeier and M. Michalak, 1989c, Molecular cloning of the high affinity calcium binding protein (calreticulin) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem., 264: 21522.
Fliegel, L., E. Newton, K. Burns and M. Michalak, 1990, Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding a 55-KDa multifunctional thyroid hormone binding protein of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem., 265: 15496.
Fliegel, L., M. Ohnishi, M.R. Carpenter, V.H. Khanna, A.F. Reinhart, R.A.F Reithmeier and D.H. MacLennan, 1987, Amino acid sequence of rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle calsequestrin deduced from cDNA and peptide sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA), 84: 1167.
Franzini-Armstrong, C., L.J. Kenney and E. Varriano-Marston, 1987, The structure of calsequestrin in triads of vertebrate skeletal muscle: a deep-etch study. J. Cell Biol., 105: 49.
Gething, M.-J. and J. Sambrook, 1990, Transport and assembly processes in the endoplasmic reticulum. Sem. Cell Biol., 1: 65.
Hofmann, S.L., M.S. Brown, E. Lee, R.K. Pathak, R.G.W. Anderson and J.L. Goldstein, 1989a, Purification of a sarcoplasmic reticulum protein that binds calcium and plasma lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem., 264: 8260.
Hofmann, S.L., J.L. Goldstein, K. Orth, C.R. Moorman, C.A. Slaughter and M.S. Brown, 1989b, Molecular cloning of histidine-rich calcium binding protein of sarcoplasmic reticulum that contains highly conserved repeated elements. J. Biol. Chem., 264: 18083.
Ikemoto, N., M. Ronjat, L.G. Meszaros and M. Koshita, 1989, Postulated role of calsequestrin in the regulation of calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochemistry, 28: 6764.
Koch, G.L.E., 1987, Reticuloplasmins: a novel group of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci., 87: 491.
Leberer, E., J.M.H Charuk, N.M. Green and D.H. MacLennan, 1989a, Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a lumenal calcium binding glycoprotein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., (USA). 86: 6047.
Leberer, E., J.M.H. Charuk, D.M. Clarke, N.M. Green, E. Zubrzycka-Gaarn and D.H. MacLennan, 1989b, Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem., 264: 3484.
Leberer, E., B.G. Timms, K.P. Campbell and D.H. MacLennan, 1990, Purification, calcium binding properties, and ultrastructural localization of the 53,000 and 160,000 (sarcalumenin) dalton glycoproteins of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem., 265: 10118.
Leonards, K.S. and H. Kutchai, 1985, Coupling of Ca2+ transport to ATP hydrolysis by the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Potential role of the 53-Kilodalton glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 24: 4876.
Macer, D.R.J, and G.L.E. Koch, 1988, Identification of a set of calcium-binding proteins in reticuloplasm, the luminal content of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci., 91: 61.
MacLennan, D.H. and P.T.S. Wong, 1971, Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA). 68: 1231.
MacLennan, D.H., C.J. Brandl, B. Korczak and N.M. Green, 1985, Amino acid sequence of a Ca2++Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature (London). 316: 699.
MacLennan, D.H., K.P. Campbell and R.A.F Reithmeier, 1983, in: “Calcium and Cell Function:, Chung, W.Y. ed., Academic Press, New York, pp. 151–173.
Maylie, J., M. Irving, N. Leung Sizto, G. Boyarsky and W.K Chandler, 1987, Calcium signals recorded from cut frog twitch fibers containing tetramethylmurexide. J. Gen. Physiol., 89: 145.
Mitchell, R.D., H.K.B. Simmerman and L.R. Jones, 1988, Calcium binding effects on protein conformation and protein interactions of canine cardiac calsequestrin. J. Biol. Chem., 263: 1376.
Munro, S. and H.R.B. Pelham, 1987, A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell, 48: 899.
Nelson, T.E. and K. Nelson, 1990, Intra- and extraluminal sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane regulatory sites for Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release. FEBS Lett., 263: 292.
Ostwald, T.J. and D.H MacLennan, 1974, Isolation of a high affinity calcium-binding protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem., 249: 974.
Porter, K.R. and G.E. Palade, 1957, Studies on the sarcoplasmic reticulum. III. Its form and distribution in striated muscle cells. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol., 3: 269.
Saito, A., S. Seiler, A. Chu and S. Fleischer, 1984, Preparation and morphology of terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol., 99: 875.
Sambrook, J.F., 1990, The involvement of calcium in transport of secretory proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell, 61: 197.
Schiaffino, S. and A. Margreth, 1969, Coordinated development of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and T system during postnatal differentiation of rat skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol., 41: 855.
Scott, B.T., H.K.B. Simmerman, J.H. Collins, B. Nadal-Ginard and LR. Jones, 1988, Complete amino acid sequence of canine cardiac calsequestrin deduced by cDNA cloning. J. Biol. Chem., 263: 8958.
Smith, M.J. and Koch, G.L.E., 1989, Multiple zones in the sequence of calreticulin (CRP 55, calregulin, HACBP) a major calcium binding ER/SR protein. EMBO J., 8: 3581.
Takeshima, H., S. Nishimura, T. Matsumoto, H. Ishida, K. Kangawa, N. Minamino, H. Matsuo, M. Ueda, M. Hanaoka, T. Hirose and S. Numa, 1989, Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature (London). 339: 439.
Thomas, K., J. Navarro, R.J.J. Benson, K.P. Campbell, R.L. Rotundo and R.E. Fine, 1989, Newly synthesized calsequestrin, destined for the sarcoplasmic reticulum, is contained in early/intermediate Golgi-derived clathrin-coated vesicles. J. Biol. Chem., 264: 3140.
Tooze, J., M. Hollinshead, S.D. Fuller, S.A. Tooze and W.B. Huttner, 1989, Morphological and biochemical properties in AtT-20 cells and their growth cones. Eur. J. Cell Biol., 49: 259.
Valdivia, C., H. Valdivia, J. Vilven and R. Coronado, 1989, Proton gating of calcium release channels in vesicles derived from junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys. J., 55: 88a.
Villa, A., P. Podini, D.O. Clegg, T. Pozzan and J. Meldolesi, 1991, Intracellular Ca2+ stores in chicken Purkinje neurons: differential distribution of the low affinity-high capacity calcium binding protein, calsequestrin, of Ca2+ ATPase and of the ER lumenal protein, BiP. J. Cell Biol., 113: 779.
Volpe, P., 1989, The unraveling architecture of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Bioenerg. Biomem., 21: 215.
Volpe, P. and B.J. Simon, 1991, The bulk of calcium released to the myoplasm is free in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and does not unbind from calsequestrin. FEBS Lett., 278: 274.
Volpe, P., H.E. Gutweniger and C. Montecucco, 1987, Photolabeling of integral proteins of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Comparison of junctional and non-junctional membrane fractions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 253: 138.
Volpe, P., B.H. Alderson-Lang, L. Madeddu, E. Damiani, J.H. Collins and A. Margreth, 1990, Calsequestrin a component of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of chicken cerebellum. Neuron, 5: 713.
Waisman, D.M., B.P. Salimath and M.J. Anderson, 1985, Isolation and characterization of CAB-63, a novel calcium-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem., 260: 1652.
Yuan, S., W. Arnold and A.O. Jorgensen, 1991, Biogenesis of transverse tubules and triads: immunolocalization of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor, TS28, and the ryanodine receptor in rabbit skeletal muscle developing in situ. J. Cell Biol., 112: 289.
Zorzato, F. and P. Volpe, 1988, Calcium binding proteins of junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum. Detection by Ca2+ ligand overlay. Arch. Biochem Biophys., 261: 324.
Zorzato, F., J. Fujii, K. Otsu, M. Phillips, N.M. Green, F.A. Lai, G. Meissner and D.H. MacLennan, 1990, Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human and rabbit forms of the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem., 265: 2244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Volpe, P., Martini, A., Nori, A. (1992). The Sarcoplasmic Reticulum of Skeletal Muscle: A Look from Inside. In: Frank, G.B., Bianchi, C.P., ter Keurs, H.E.D.J. (eds) Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth Muscle. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 311. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3362-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-3362-7_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-6483-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-3362-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive