Abstract
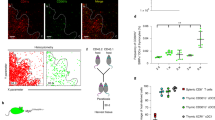
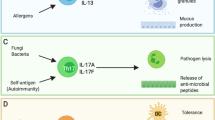
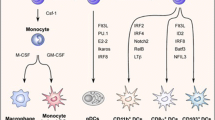
Are the dendritic cells (DC) found in the thymus similar in origin and function to those in other lymphoid tissues? Thymic DC are generally similar in morphological appearance to DC elsewhere, and share many cell surface markers. Thymic DC are shortlived cells which are, like DC elsewhere, of bone marrow origin1,2. However, it had not been clear whether they are continuously generated within the thymus itself, or arrive preformed via the bloodstream. Our work delineates a separate stream of DC generated within the thymus. Thymic DC form multicellular complexes with developing,T cells, giving rise to the rosette structures found in collagenase digests of thymic tissue3,4. The functional result of this DC-thymocyte interaction is believed to be the destruction of any self-reactive cells (negative selection)5. This outcome is different from that of the DC-T lymphocyte interactions in lymph nodes, where any T cells reactive with presented foreign antigens are stimulated to proliferate and differentiate6. Investigation of the basis of this difference has pointed to the state of maturation of the interacting T-lineage cells, rather than to any differences in the antigen-presenting DC7. Without questioning that the maturation state of the interactive T cells is an important factor, our work has raised the additional possibility that certain DC may be specialized for delivering negative signals to T cells.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Kampinga, P. Nieuwenhuis, B. Roser, R. Aspinall, Differences in turnover between thymic medullary dendritic cells and a subset of cortical macrophages, J. Immunol. 145:1659(1990)
A.N. Barclay and G. Mayrhofer, Bone marrow origin of la-positive cells in the medulla of rat thymus, J. Exp. Med. 153:1666 (1981)
B.A. Kyewski, R.V. Rouse, Kaplan, H.S.: Thymocyte rosettes: multicellular complexes of lymphocytes and bone marrow-derived stromal cells in the mouse thymus, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:5646 (1982)
K. Shortman and D. Vremec, Different subpopulations of developing thymocytes are associated with adherent (macrophage) or non-adherent (dendritic) thymic rosettes. Developmental Immunol. 1: 225–235 (1991)
P.J. Fairchild and J.M. Austyn, Thymic dendritic cells: phenotype and function.Intern. Rev. Immunol. 6:187 (1990)
R.M. Steinman, The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity, Annu. Rev.Immunol. 9:271 (1991)
P. Matzinger and S. Guerder, Does T-cell tolerance require a dedicated antigen-presenting cell? Nature 338:74 (1989)
D. Vremec, M. Zorbas, R. Scollay, D.J. Saunders, C.F. Ardavin, L. Wu, and K.Shortman, The surface phenotype of dendritic cells purified from mouse thymus and spleen: Investigation of the CD8 expression by a subpopulation of dendritic cells, J. Exp. Med. 176:47 (1992)
K. Winkel, F. Sotzik, D. Vremec, P.U. Cameron, and K. Shortman, CD4 and CD8 expression by human and mouse thymic dendritic cells. Immunol. Lett. 40:93 (1994)
G. Kraal, M. Breel, M. Janse, and G. Bruin, Langerhans‘ cells, veiled cells, and interdigitating cells in the mouse recognized by a monoclonal antibody’, J. Exp. Med. 163:981 (1986)
L. Wu, D. Vremec, C.-L. Li, C. Ardavin, K. Winkel, G. Suss, H. Georgiou, E.Maraskovsky, W. Cook, and K. Shortman, Mouse thymus dendritic cells: kinetics of development and changes in surface markers during maturation, in press (1994)
J. Wang and M.D. Cooper, Histidine residue in the zinc-binding motif of aminopeptidase A is critical for enzymatic activity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:1222(1993)
M.C. Nussenzweig, R.M. Steinman, M.D. Unkeless, M.D. Witmer, B. Gutchinov, and Z.A. Cohn, Studies of the cell surface of mouse dendritic cells and other leukocytes, J. Exp. Med. 154:168 (1981)
M. Crowley, K. Inaba, M. Witmer-Pack, and R.M. Steinman, The cell surface of mouse dendritic cells: FACS analysis of dendritic cells from different tissues including thymus. Cell. Immunol. 118:108 (1989)
L. Wu, R. Scollay, M. Egerton, M. Pearse, G.J. Spangrude, and K. Shortman, CD4 expressed on earliest T-lineage precursor cells in the adult murine thymus. Nature 349:71 (1991)
L. Wu, M. Antica, G.R. Johnson, R. Scollay, and K. Shortman, Developmental potential of the earliest precursor cells from the adult thymus, J. Exp. Med. 174: 1617(1991)
C. Ardavin, L. Wu, C.-L. Li, and K. Shortman, Thymic dendritic cells and T cells develop simultaneously within the thymus from a common precursor population, Nature 362:761 (1993)
S.R. Sambhara, and R.G. Miller, Programmed cell death of T cells signaled by the T cell receptor and the alpha3 domain of class I MHC. Science 252:1424 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shortman, K. et al. (1995). Thymic Dendritic Cells: Surface Phenotype, Developmental Origin and Function. In: Banchereau, J., Schmitt, D. (eds) Dendritic Cells in Fundamental and Clinical Immunology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 378. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1971-3_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1971-3_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5811-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1971-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive