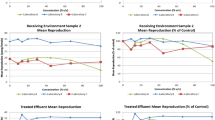
Abstract
The use of experimental systems, sensitive to environmental levels of pollutants provide an important alternative to biomonitoring studies, in particular, those involving whole, in vivo systems from which the fraction of organisms showing a particular change in relation with some causal factor, can be identified. Whether in some of the organisms this response is showed earlier than in the rest of the population exposed, it could be an alert that should to be attended to avoid more organisms being affected.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar W.A., and Gabal M.S. (1991) Cytogenetic study in workers occupationally exposed to mercury fulminate, Mutagenesis, 6: 3,189–192.
Armienta M.A., Rodrίguez R., and Villaseñor (1993) Estudio de reconocimiento de la contaminación por arsénico en la zona de Zimapán, Hidalgo. Report to the Municipality of Zimapán: Geophysics Institute, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, 85 pp.
Armienta M.A., Rodrίguez R., and Cruz 0. (1997) Arsenic content in hair of people exposed to natural arsenic polluted groundwater at Zimapán, México, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 59, pp. 583–589.
Arriaga N., and y Daniel R. (1996) Bases geológicas del origen y movilidad del arsénico en el Valle de Zimapán, Hidalgo, Tesis Ing. Geol., Escuela Superior de Ingenierίa y Arquitectura, IPN, México.
C.N.A. (1992) Estudio de prospección geohidrológica y exploración geofίsica en la zona de Tecozautla-Vizarron, Estados de Hidalgo y Queretaro. IGAMSA, Informe Técnico.
Cernβ M., Pastorkovβ A., SmÝd J., Bavorovfβ H., OcadlÝkovlβ D., Rossner P, and Zavadil J. (1996) Genotoxicity of industrial effluents, river waters, and their fractions using the Ames test and in vitro cytogenetic assay, J. Toxicol. Lett., 88: 1–3,191–197.
Chroust K., KuglÝk P., Relichovβ J., Holoubek I., Cβsasy J., Veselsk β R., Ryskovlβ M., and BenedÝk J. (1997) Drosophila melanogaster, Vicia faba and Arabidopsis thaliana short-term bioassays in genotoxicity evaluation of air and soil samples from sites surrounding two industrial factories in the Czech Republic, Folia. Biol. (Praha) 43: 2, 71–78.
Demerec M. Ed. (1965) Biology of Drosophila, Hafner Publishing Co., 632 p.
Frei H., and Würgler F.E. (1988) Statistical methods to decide whether mutagenicity test data from Drosophila assay indicate a positive, negative, or inconclusive result, Mutation Res., 203: 297–308.
Frei H., and Würgler F E. (1995) Optimal experimental design and sample size for the statistical evaluation of data from somatic mutation and recombination tests (SMART) in Drosophila, Mutation Res., 334: 247–258. [33]
Garcίa E., and Falcon Z (1993) Atlas, Porrua, México, 50–51 p.
Gimmler-Luz M., Erdtmann B., and Balbueno R. (1992) Analysis of clastogenic effect of Porto Alegre drinking water supplies on mouse bone marrow cells, Mutat. Res., 279: 4,227–231.
Gomez-Arroyo S., Armienta M.A., Cortes-Eslava J., and Villalobos-Pietrini R. (1997) Sister chromatid exchanges in Vicia faba induced by arsenic-contaminated drinking water from Zimapán, Hidalgo, México. Mutat. Res., 394: 1–3, 1–7.
Gomez-Arroyo S., Hernandez-Garcίa A., and Villalobos-Pietrini R. (1988) Induction of sister-chromatid exchanges in Vicia faba by arsenic-contaminated drinking water, Mutat. Res., 208: 3–4, 219–224.
Gonzalez-César E., and Ramos-Morales P. (1997) Sodium azide induces mitotic recombination in Drosophila melanogaster larvae, Mutation Res., 389: 157–165.
Graf U., Würgler E, Katz A., Frei H., Juon H., Hall C., and Kale P. (1984) Somatic mutation and recombination test in Drosophila melanogaster,Environmental Mutagenesis 6: 153–188.
Graf U., and Singer D. (1989) Somatic mutation and recombination test in Drosophila melanogaster (Wing spot test): effects of extracts of airborne particulate matter from fire-exposed and non fire-exposed building ventilation filters. In: Suter K.E., Gruntz U., and Schlatter Ch. (Eds.) (1989) Analytical and toxicological investigations of respiratory filters and building ventilation filters exposed to combustion gases of the chemical warehouse fire in Schweirzehalle, Chemosphere, 19(7): 1019–1109.
Graf U., Heo O.S., and Olvera O. (1992) The genotoxicity of chromium (VI) oxide in the wing spot test of Drosophila melanogaster is over 90% due to mitotic recombination, Mutation Res., 266: 197–203.
Hebert P.D., and Luiker M.M. (1996) Genetic effects of contaminant exposure¨Ctowards an assessment of impacts on animal populations. Sci. Total Environ., 191: 1–2, 23–58.
I.N.E.G.I. (1990) Zimapán de Reyes, Estado de Hidalgo, Cuaderno Estadistico Municipal. H. Ayuntamiento de Zimapán de Reyes, 86 pp.
I.N.E.G.I. (1994) Zimapán de Reyes, Estado de Hidalgo, Cuaderno Estadistico Municipal. H. Ayuntamiento de Zimapán de Reyes, 92 pp.
I.N.E.G.I. (1995) Tecozautla, Estado de Hidalgo, Cuaderno Estadistico Municipal. H. Ayuntamiento de Tecozautla, 96 pp.
Iwado H., Naito M., and Hayatsu H. (1991) Mutagenicity and antimutagenicity of air-borne particulates, Mutat. Res., 246(1): 93–102.
Jaylet A., Deparis P., and Gaschignard D. (1986) Induction of micronuclei in peripheral erythrocytes of axolotl larvae following in vivo exposure to mutagenic agents, Mutagenesis, 1: 3,211–215.
Jaylet A., Gauthier L., and Fernandez M. (1987) Detection of mutagenicity in drinking water using a micronucleus test in newt larvae (Pleurodeles waltl), Mutagenesis 2: 3, 211–214.
Kilbey B.J., MacDonald DJ, Auerbach C., Sobels FH., and Vogel E.W. (1981) The use of D. melanogaster in tests for environmental mutagens, Mutation Res., 85: 141–146.
Koren H. (1991) Handbook of Environmental Health and Safety. Principles and Practices, Lewis Publishers, 2 a. ed. Vol. I, pp. 109, 147–148, 243–244, 252.
Lewtas J., Claxton L., Mumford J., and Lofroth G. (1993) Bioassay of complex mixtures of indoor air pollutants. IARC Sci. Publ., 109: 85–95.
Lindsley D.L., and Zimm G.G. (1992) The genome of Drosophila melanogaster,Academic Press, New York, 1133 p.
Meybeck M., Chapman D., and Helmer R. Eds. (1990) GEMS: Global Environment Monitoring System. Global Freshwater Quality. A first Assessment, WHO, UNEP, 306 pp.
Nothiger E. (1970) Sucrose density separation: A method for collecting large numerous of Drosophila larvae. DIS 45: 177.
Pandey P., McGowen R.M., Vogel E.W., and Butterworth F.M. (1995) Genotoxicity of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) and polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) mixtures in the white/white+ eye-mosaic assay, In: Biomonitors and biomarkers as indicators of environmental change. Eds: F.M. Butterworth, L.D. Corkum, and J. Guzmán-Rincón, Plenum, New York, 1995,183–191.
Ramos Leal J.A. (1996) Parámetros estructurales que controlan la hidrodinamica de las aguas subterráneas en el área de Zimapán, Hgo., Tesis Maestrίa en Ciencias de la Tierra, UNAM, México.
Rao P.V. (1998) Statistical Research Methods in the Life Sciences, Duxbury, New York, 889 p.
S.A.R.H. (1977) Estudio geohidrológico, zona Ixiniquilpan—Zimapán, Estado de Hidalgo. Geohidrológica Mexicana, S.A. Reporte Técnico.
Steel G.D., Torrie J.H., and Dickey D.A. (1997) Principles and Procedures of Statistics. A Biometrical Approach, McGraw-Hill, New York, 666 p.
Steinkeliner H., Mun-Sik K., Helma C., Ecker S., Ma TH., Horak O., Kundi M., and Knasmuller S. (1998) Genotoxic effects of heavy metals: comparative investigation with plant bioassays. Environ. Mol. Mutagen, 31: 2,183–191.
Suter W. (1989a) Ames test: mutagenicity determination of material extracted from respiratory masks worn at the site of the fire. In: Suter K.E., Gruntz U., and Schlatter Ch. (Eds.) (1989) Analytical and toxicological investigations of respiratory filters and building ventilation filters exposed to combustion gases of the chemical warehouse fire in Schweirzehalle, Chemosphere, 19(7): 1019–1109.
Suter W. (1989b) Ames test: mutagenic activity of airborne particulate matter from fire-exposed and non fire-exposed building ventilation filters. In: Suter K.E., Gruntz U., and Schlatter Ch. (Eds.) (1989) Analytical and toxicological investigations of respiratory filters and building ventilation filters exposed to combustion gases of the chemical warehouse fire in Schweirzehalle, Chemosphere, 19(7): 1019–1109.
Tabor M.W., and Loper J.C. (1985) Analytical isolation, separation and identification of mutagens from nonvolatile organics of drinking water, Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem., 19: 4 281–318.
Van Hummelen P, Zoll C., Paulussen J., Kirsch-Volders M., and Jaylet A. (1989) The micronucleus test in Xenopus: a new and simple ’in vivo’ technique for detection of mutagens in fresh water, Mutagenesis 4: 1, 12–16.
Vogel E. (1988) Summary report on the performance of the Drosophila assays. En: Ashby J., de Serres F, Shelby M., Margolin B., Ishidate M., and Becking G. (1988) Evaluation of short-term tests for carcinogens. WHO, Cambridge University Press, 2.227–2.285.
Vogel E., and Szakmary A. (1990) Basic principles and evaluation of results of assays measuring genotoxic damage in somatic cells of Drosophila, Mutation and the Environment, Part b: 149–158.
Vogel E.W., and Nivard M.J.M. (1993) Performance of 181 chemicals in a Drosophila assay predominantly monitoring interchromosomal mitotic recombination, Mutagenesis 8(1): 57–81.
Wilcox P., Williamson S., Lodge D.C., and Bootman J. (1988) Concentrated drinking water extracts, which cause bacterial mutation and chromosome damage in CHO cells, do not induce sex-linked recessive lethal mutations in Drosophila, Mutagenesis, 3: 5, 381–387.
Woodruff C.R., Mason J.M., Valencia R., and Zimmering S. (1985) Chemical mutagenesis testing in Drosophila V. Results of 53 coded compounds tested for the National Toxicology Program, Environmental Mutagenesis 7: 677–702.
Würgler RE., and Vogel E.W. (1986) In vivo mutagenicity testing using somatic cells of Drosophila melanogaster, In: Chemical Mutagens, Vol. 10, F.J. de Serres (ed.), Plenum, New York, pp. 1–59.
Zimmering S., Mason J.M., Valencia R., and Woodruff R.C. (1985) Chemical mutagenesis testing in Drosophila. II. Results of 20 coded compounds tested for the National Toxicology Program. Environ. Mutagen., 7: 1,87–100.
Zwanenburg T.S.B. (1989) Chromosomal aberrations induced by extracts of airborne particulate matter from fire-exposed and non fire-exposed building ventilation filters. In: Suter K.E., Gruntz U., and Schlatter Ch. (Eds.) (1989) Analytical and toxicological investigations of respiratory filters and building ventilation filters exposed to combustion gases of the chemical warehouse fire in Schweirzehalle, Chemosphere, 19(7): 1019–1109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ramos-Morales, P. et al. (2001). Drosophila is a Reliable Biomonitor of Water Pollution. In: Butterworth, F.M., Gunatilaka, A., Gonsebatt, M.E. (eds) Biomonitors and Biomarkers as Indicators of Environmental Change 2. Environmental Science Research, vol 56. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1305-6_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1305-6_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-5488-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-1305-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive