Abstract
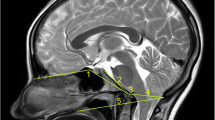
It is very important to recall that the cranio-vertebral junction is a key area because it contains the medulla oblongata, the location of life; numerous civilizations chose this structure as the site at which to kill by decapitation. From a clinical point of view, we may be schematic and say that one may distinguish six categories of pathologic patterns.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
References
Grisel P: Enucléation de l’atlas et torticolis nasopharyngien. Presse Med 38: 50–52, 1930.
Sullivan AW: Subluxation of the atlanto-axial joint. J Pediatrics 35: 451, 1949.
Le Double AF: Traité des variations des os du crâne de l’homme et de leur signification au point de vue de l’Anthropologie zooligique. Vigot Frères, Paris, 1903/1919.
Albrecht P: Anat Anz Leipzig, 1879 and Bult de la Soc d’Anthrop de Bruxelles, 1885.
Henle FGJ: Anatorn TIS 103 (given by Le Double).
Legge F: Varieta della osse del cranio e della faccia in alcuni crani Camerinesi, 1883, (nach Le Double).
Calori L: Sulle varie particolarità osteol. Mem d’Acad d Sci Bologna, 301, 1892.
Déjérine J: Dystrophie osseuse par aplasie de la substance spongieuse du corps basilaire de l’occipital. Rev Neurol 2: 181–300, 1926.
Adam-Falkiewiczova St, Nowicki W: Internationaler Neurologen Kongress, Bern 1931. Zentralb Neuchir 61: 472, 1934.
Bodechtel G, Guizetti UH: Pseudotumeur cerebri, bedingt durch eine röntgenologisch Faßbare Anomalie des Hinterhauptloches mit Verlagerung der beiden oberen Halswirbel. Z Gesamt Neurol Psychiatr 143: 470, 1933.
Morsier DeG, Junet R: L’aplasie de la lame basilaire de l’os occipital avec syndrome clinique de tumeur de la fosse postérieure. Rev Neurol 2: 1483–1492, 1936.
Virchow R: Untersuchungen über die Entwicklung des Schädel-grundes. Reimer, Berlin, 1857.
Schuller A: Zur Roentgendiagnose der basilaren Impression des Schädels. Wien Med Wochenschr 61: 2594, 1911.
Schmidt H, Fischer E: Die okzipitale Dysplasie. Thieme, Stuttgart, 1960.
Klaus E: Die basiläre Impression. S Hirtzel, Leipzig, 1969.
Lang J: Klinische Anatomie des Kopfes. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981.
Wackenheim A: Hypoplasia of the basi-occipital bone and persistence of the spheno-occipital synchondrosis in a patient with transitory supplementary fissure of the basi- occipital. Neuroradiology 27: 226–231, 1985.
Wackenheim A, Burguet JL, Sick H: Section of the odontoid process by a shortened transverse ligament (a possible etiology for the mobile odontoid). Neuroradiology 28: 281–282, 1986.
Wackenheim A: Cl/2 block vertebra, fusion of the anterior arch of the atlas with the axis, follow-up of the fusion in a child. Neuroradiology 16: 416–417, 1978.
Wackenheim A: Roentgen diagnosis of the Cranio-Vertebral Region. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1974.
Aboulezz AO, Sartor K, Geyer CA, Gado MH: Position of cerebellar tonsils in the normal population and in patients with Chiari malformation: a quantitative approach with MR Imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 1033–1036, 1985.
Bamberger-Bozo C: Malformation de Chiari II. Arnold-Chiari de la littérature. J Neuroradiology 9: 47–70, 1982.
De la Paz RL, Brady TJ, Buonanno FS: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance imaging of Arnold-Chiari type I malformation with hydromyelia. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 126–129, 1983.
Forbes WStC, Isherwood I: Computed tomography in a syringomyelia and the associated Arnold-Chiari type I malformation. Neuroradiology 15: 73–78, 1978.
Naidich TP, Pudlowski RM, Naidich JB: Computed tomography signs of Chiari II malformation: skull and dural partitions (part I). Radiology 134: 65–71, 1980.
Naidich TP, Pudlowski RM, Naidich JB: Midbrain and cerebellum (part II). Radiology 134: 391–398, 1980.
Naidich TP, Pudlowski RM, Naidich JB: Ventricles and cisterns (part III). Radiology 134: 657–663, 1980.
Naidich TP: Aspects tomodensitométriques des lésions crânio-cervicales de la mal-formation de Chiari II. Corrélations anatomo-tomodensitométriques. J Neuroradiol 8: 207–227, 1981.
Naidich TP, McLone DG, Fullin KH: The Chiari II malformation: part IV. The hind- brain deformity. Neuroradiology 25: 179–197, 1983.
Park TS, Hoffman HJ, Hendrick EB, Humphreys RP: Experience with surgical decompression of the Arnold-Chiari malformation in young infants with myelo-meningocele. Neurosurgery 13: 147–152, 1983.
Aboulker J: La syringomyélie et les liquides intra-rachidiens. Neurochirurgie 25 (Suppl 1):, 1979.
Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Jardin C: Computed tomography in 75 clinical cases of syrin-gomyelia. AJNR 2: 199–204, 1981.
Bonafe A, Manelfe C, Espagno J, Guiraud B, Rascol A: Evaluation of syringomyelia with metrizamide computed tomography myelography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 4: 797–802, 1980.
Cahan LD, Benison JR: Considerations in the diagnosis and treatment of syringomyelia and the Chiari malformation. J Neurosurg 57: 24–31, 1982.
Kokmen E, Marsh WR, Baker HL: Magnetic resonance imaging in syringomyelia. Neurosurgery 17: 267–270, 1985.
Yeates A, Brant-Zawadzki M, Norman D: Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of syringomyelia. AJNR 4: 234–237, 1983.
Kojima T, Waga S, Shimizu T: Dandy-Walker cyst associated with occipital meningocele. Surg Neurol 17: 52–56, 1982.
Lehman RM: Dandy-Walker syndrome in consecutive siblings: familial hindbrain malformation. Neurosurgery 8: 717–719, 1981.
Babcock DS, Han BK: Cranial sonographic findings in meningomyelocele. AJR 136:563–569, 1981; AJNR 1: 493–499, 1980.
Fenstermaker RA, Roessmann U, Rekate HL: Fourth ventriculoceles with extracranial extension. J Neurosurg 61: 348–350, 1984.
Marar BC, Orth MC, Balachandran N: Nontraumatic atlanto-axial dislocation in children. Clin Orthop 92: 220–226, 1973.
Parker Mickle J, McLennan JE: Malignant teratoma arising within a lipomeningocele. J Neurosurg 43: 761–763, 1975.
Zimmerman RD, Breckbill D, Dennis MW, Davil DO: Cranial CT finding in patients with meningomyelocele. AJR 132: 623–629, 1979.
Bonneville JF: En savoir plus sur le rachis cervical. Masson, Paris, 1980.
Debre R, Broca R, Cremieux M: Maladie de Still à début cervical. Bulletin de la Société de Pédiatrie de Paris. 234, 1932.
DiMeglio A, Ferran JL, Lutter L: Rachis cervical et arthrite chronique juvénile, in l’arthrite chronique juvénile. Masson, Paris, 1984, pp 74–85.
Bailey H, Sister Mary Gabriel, Hodgson AR, Shin JS: Tuberculosis of the spine in children. J Bone Joint Surg 54: 1633–1657, 1972.
Mozziconacci P, Abramovici M, Hassan M, Hayem F: Luxations atloido-axoidienne rhumatoide et syndrome de Grisel. Ann Pédiatr 20: 405–418, 1973.
Friedman WA, Mickle JP: Hydrocephalus in achondroplasia: a possible mechanism. Neurosurgery 7: 150–153, 1980.
Maroteaux P: Maladies osseuses de l’enfant. Flammarion, Paris, 1974.
Pueschel SM, Scola FH, Perry CD, Pezzullo JC: Atlantoaxial instability in children with Down’s syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 10: 129–132, 1981.
Watts RWE, Spellacy E, Kendall BE, Du Boulay G, Gibbs DA: Computed tomography studies on patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Neuroradiology 21:9– 23, 1981.
Barcat E, Rigault P, Padovant JP, Martin P: Fractures et luxations du rachis cervical chez l’enfant. Ann Chir Infant 17: 197–212, 1975.
Chagnon S, Blery M: Entorses et luxations du rachis cervical chez l’enfant. J Radiol 63: 465–470, 1982.
Chagnon S, Blery M: Les lésions traumatiques du rachis chez l’enfant. Cours de per- fectionnement post-universitaire. Paris, 1984.
Duncan AW, Stanley P, Isaacson J: Fracture— dislocation of the cervical spine in the newborn. AJR 135: 868, 1980.
Kaiser MC, Pettersson H, Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR, Chuang S: CT for trauma of the base of the skull and spine in children. Neuroradiology 22: 27–31, 1981.
McPhee IB: Spinal fractures and dislocations in children and adolescents. Spine 6: 533–537, 1981.
Pennecot GF, Leonard P, Peyrot des Gachons S, Hardy JR, Pouliquen JC: Traumatic ligamentar instability of the cervical spine in children. J Pediatr Orthop 4: 339–345, 1984.
Savader SJ, Martinez C, Reed Murtagh F: Odontoid fracture in a nine-month-old infant. Surg Neurol 24: 529–532, 1985.
Sherk HH, Nicholson JT, Chunk SMK: Fractures of the odontoid process in young children. J Bone Joint Surg 60: 921–924, 1978.
Wackenheim A: La dynamique de Fodontoide mobile. J Radiol Electrol 592: 107–108, 1978.
Dosch JC: Trauma. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1985.
Meyer JE, Oot RF, Lindfors KK: CT appearance of clival’chordomas. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1: 34–38, 1986.
Wold LE, Laws ER: Cranial chordomas in children and young adults. J Neurosurg 59: 1043–1047, 1983.
Lichtenstein L: Bone tumors. Mosby, St. Louis, 1972.
Holliday PO HI, Davis C, Angelo J: Multiple meningiomas of the cervical spinal cord associated with Klippel-Feil malformation and atlanto-occipital assimilation. Neurosurgery 14: 353–357, 1984.
Jeanmart L: Tumors. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1986.
Bibliography
Adam R, Greenberg JO: The mega cisterna magna. J Neurosurg 48: 190–192, 1978.
Arredondo F, Haughton VM, Hemmy DC, Zelaya B, Williams AL: The computed tomographic appearance of the spinal cord in diastematomyelia. Radiology 136: 685–688, 1980.
Anderson FM: Occult spinal dysraphism: a series of 73 cases. Pediatrics 55: 826–835, 1975.
Bewermeyer H, Dreesbach HA, Hunermann B, Heiss WD: MR imaging of familial basilar impression. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8: 953–956, 1984.
Byrd SE, Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR, Rogovitz DM: Computed tomography in the evaluation of encephaloceles in infants and children. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2: 81–87, 1978.
Caffey J: Pediatric X Ray Diagnosis. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago and London, 1978.
Chagnon S, Labrune M: Le rachis de l’enfant. Feuillets Radiol 21: 7–46, 1981.
Dorne HL, Just N, Lander PH: CT recognition of anomalies of the posterior arch of the atlas vertebra: differentiation from fracture. AJNR 7: 176–177, 1986.
Dublin AB, McGahan JP, Reid MH: Value of computed tomographic metrizamide myelography in the neuroradiological evaluation of the spine. Radiology 146: 79–86, 1983.
Fischgold H, Metzger J, Legré J, Djindjian R, Engel P: Neuroradiologie, canal rachidien, moelle et racines, in traité de radiodiagnostic. Tome 15, Masson, Paris, 1971.
Frank E, Berger T, Tew JM: Basilar impression and platybasia in osteogenesis imperfectatarda. Surg Neurol 17: 116–119, 1982.
Frank E, Berger T, Tew JM: Basilar impression and platybasia in osteogenesis imperfectatarda. Surg Neurol 17: 116–119, 1982.
Gehweiler JA, Daffner RH, Roberts L: Malformations of the atlas vertebra simulating the Jefferson Fracture. AJR 140: 1083–1086, 1983.
Gras M, Bourbotte G, Boluix B, Castan P, Pous JG, Dimeglio A, Frerebeau P: Scolioses malformatives avec ou sans dysraphie spinale occulte. A propos de 82 observations de l’enfant. J. Radiol 63: 383–395, 1982.
Hamilton, Boyd, Mossmans: Human Embryology, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1978.
Hammock MK, Milhorat TH: Cranial Computed Tomography Infancy and Childhood. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1981.
Han JS, Huss RG, Benson JE, Kaufman B, Yoon YS, Morrison SC, Alfidi RJ, Rekate HL, Ratcheson RA: ME Imaging of the skull base. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8: 944–952, 1984.
Han JS, Kaufman K, El Yousef SJ: NMR imaging of the spine. AJNR 4: 1151–1159, 1983;
Han JS, Kaufman K, El Yousef SJ: NMR imaging of the spine. AJR 141: 1137–1145, 1983.
Han JS, Benson JE, Yoon YS: Magnetic resonance imaging in the spinal column and cranio-vertebral junction. Radiol Clin North Am 22: 805–827, 1984.
Han JS, Bonstelle CT, Kaufman B: Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of the brainstem. Radiology 150: 705–712, 1984.
Harwood-Nash CC, Fitz CR: Neuroradiology in Infants and Children. Mosby, St. Louis, 1976.
Harwood-Nash DCF, Fitz CR, Margareta Resjo I, Chuang S: Congenital spinal and cord lesions in children and computed tomographic metrizamide myelography. Neuroradiology 16: 69–70, 1978.
Harwood-Nash DC: Tomodensitométrie des anomalies cérébrales chez le nouveau-né. J Neuroradiol 8: 125–142, 1981.
Harwood-Nash DC: Techniques neuroadiologiques pédiatriques. J Neuroradiol 8: 73–91, 1981.
Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR: Neuroradiology in infants and children. Mosby, St. Louis, 1976.
Haughton VM, Williams AL: Computed Tomography of the Spine. Mosby, St. Louis, 1982.
Hawkes RC, Holland GN, Moore WS: Craniovertebral junction pathology: assessment by NMR. AJNR 4: 232–233, 1983.
Henrys P, Lyne ED, Lifton C, Salciccioli G: Clinical review of cervical spine injuries in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res 129: 172–176, 1977.
Holt JF: Neurofibromatosis in children. AJR 130: 615–639, 1978.
Hunter GA: Non-traumatic displacement of the atlanto-axial joint. J Bone Joint Surg 50B: 44–51, 1968.
Just NWM, Goldenburg M: Computed tomography of the enlarged cisterna magna. Radiology 131: 385–391, 1979.
Kaiser MC, Pettersson H, Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR, Armstrong E: Direct coronal CT of the spine in infants and children. AJNR 2: 465–466, 1981.
Kaufman RA, Dunbar JS, Botsford JA, McLaurin RL: Traumatic longitudinal atlanto- occipital distraction injuries in children. AJNR 3: 415–419, 1982.
Labrune M, Chagnon S: Le rachis de l’enfant. Feuillets Radiol 21: 47–54, 1981.
Levine RS, Geremia GK, McNeill TW: CT demonstration of cervical diastematomyelia. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9: 592–594, 1985.
McGinnis BD, Brady TJ, New PFJ: Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of tumors in the posterior fossa. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 575–584, 1983.
McRae DL: Bony abnormalities in the region of the foramen magnum: correlation of anatomic and neurologic findings. Acta Radiol (Stockh) 40: 335, 1953.
Martin K, Krastel A, Hamer J, Banniza UK: Symptomatology and diagnosis of diastematomyelia of children. Neuroradiology 16: 89–90, 1978.
Martin N, Gaston A, Brugieres P, Guilbeau JC, Marsault C, Nahum H: Bilan radiologique actuel des dysraphismes. Feuillets Radiol 25: 331–344, 1985.
Matsumara M, Nojiri K, Yumoto Y: Persistent primitive hypoglossal artery associated with Arnold-Chiari type I malformation. Surg Neurol 24: 241–244, 1985.
Miller JH, Reid BS, Kemberling CR: Utilization of ultrasound in the evaluation of spinal dysraphism in children. Radiology 143: 737–740, 1982.
Modic MT, Weinstein MA, Pavlicek W: Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine. Technical and clinical observations. AJR 141: 1129–1136, 1983.
Nagib MG, Maxwell RE, Chou SN: Identification and management of High-risk patients with Klippel-Feil syndrome. J Neurosurg 61: 523–550, 1984.
Naidich TP, Epstein F, Lin JP, Kricheff H, Hochwald GM: Evaluation of pediatric hydrocephalus by computed tomography. Radiology 119: 337–345, 1976.
Newton TH, Potts DG: Computed Tomography of the Spine and Spinal Cord. Clavadel Press, San Anselmo, 1983.
Osborne D, Triolo P, Dubois P: Assessment of cranio-cervical junction and atlanto-axial relation using metrizamide-enhanced CT in flexion and extension. AJNR 4: 843–845, 1983.
Park TS, Cail WS, Maggio WM, Mitchell DC: Progressive spasticity and scoliosis in children with myelomeningocele. J Neurosurg 62: 367–375, 1985.
Pennecot GF, Gouraud D, Hardy JR, Pouliquen JC: Roentgenologic study of the stability of the cervical spine in children. J Pediatr Orthop 4: 346–352, 1984.
Petterson H, Harwood-Nash DC: CT and Myelography of the Spine and Cord. Springer- Verlag, Berlin, 1982.
Probst FP, Brun A: Recurrent meningoencephalitis and ascending myelitis caused by dermal sinus tract of extraordinary length. Neuroradiology 19: 161–165, 1980.
Probst FP, Brun A: Recurrent meningoencephalitis and ascending myelitis caused by dermal sinus tract of extraordinary length. Neuroradiology 19: 161–165, 1980.
Resjo IM, Harwood-Nash DCF, Fitz CR, Chuang S: Normal cord in infants and children examined with computed tomographic metrizamide myelography. Radiology 130: 691–696, 1979.
Resjo IM, Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR, Chuang S: Computed tomographic metrizamide myelography in spinal dysraphism in infants and children. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2: 549–558, 1978.
Rougerie J: Les Compressions Médullaires non Traumatiques de l’Enfant. Masson, Paris, 1973.
Sauser G: Intrakraniale Manifestation des letzten Occipital-Wirbels. Z Anat Entwickl Gesch 104: 159–168, 1935.
Sauvegrain J: Radiologie des affections ostéoarticulaires de l’enfant. Journées de radiologie pédiatrique. Hôpital Trousseau, Paris, 1979.
Sauvegrain J, Mareschal JL: Malformations de la charnière crànio-cervicale chez l’enfant. A propos de 35 observations. Ann Radiol 15: 263–277, 1972.
Schuller A: The diagnosis of “basilar impression.” Radiology 34: 214, 1940.
Scotti G, Musgrave MA, Harwood-Nash DC, Fitz CR, Chuang SH: Diastematomyelia in children: metrizamide and CT metrizamide myelography. AJR 135: 1225–1232, 1980.
Smith MT, Huntington HW: Inverse cerebellum and occipital encephalocele. A dorsal fusion defect uniting the Arnold-Chiari and Dandy-Walker spectrum. Neurology 27: 246–251, 1977.
Stark GD: Spina bifida. Blackwell, Oxford, 1977.
Suss RA, Zimmerman RD, Leeds NE: Pseudospread of the atlas: false sign of Jefferson fracture in young children. AJR 140: 1079–1082, 1983.
Swischuk LE: Anterior displacement of C2 in children: physiologic or pathologic? A helpful differentiating line. Radiology 122: 759–763, 1977.
Taveras JM, Wood EH: Diagnostic neuroradiology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1976.
Trial R, Bacques O, Plainfossé MC, Blery M, Chevrot A: Traité de Radiodiagnostic n° 12, os et Articulations. Pathologie Régionale. Masson, Paris, 1983.
Wackenheim A: Occipitalization of the ventral part and vertebralization of the dorsal part of the atlas with insufficiency of the transverse ligament. Neuroradiology 24: 45–47, 1982.
Woodring JH, Selke AC, Duff DE: Traumatic atlantooccipital dislocation with survival. AJR 137: 21–24, 1981.
Yanai Y, Tsuji R, Ohmori S, Kubota S, Nagashima C: Foramen magnum syndrome caused by a dolichoodontoid process. Surg Nerol 24: 95–100, 1985.
Young IR, Burl M, Clarke GJ: Magnetic resonance properties of hydrogen: imaging the posterior fossa. AJR 137: 895–901, 1981.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1989 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wackenheim, A., Dutreix, J.L., Zöllner, G. (1989). The Normal and Abnormal Aspects of the Cranio-Vertebral Junction. In: Raimondi, A.J., Choux, M., Di Rocco, C. (eds) The Pediatric Spine II. Principles of Pediatric Neurosurgery. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8829-6_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-8829-6_2
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-8831-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-8829-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive