Abstract
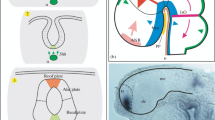
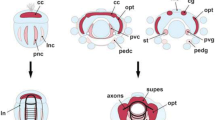
The structure of the teleost forebrain (and that of other actinopterygians) is unusual in that there are no lateral ventricles and the two hemispheres are solid lobes separated by a slitlike ventricle. The lobes are covered with an ependymal membrane which is attached to the dorsolateral margins of the hemispheres. One suggestion has been that this forebrain structure is the result of a process of eversion during development (Gage, 1893; Holmgren, 1922; Miller, 1940; Källén, 1947, 1951), whereas the forebrains of most other vertebrates develop by inversion followed by an evagination (Fig. 1B). The proposed eversion growth process would rearrange the functional organization of the dorsal telencephalon, and thus the hippocampal pallium would be in a lateral position, the general cortex dorsal, and the pyriform pallium dorsomedial (Fig. 1C), departing markedly from the arrangement found in inverted-evaginated brains, where the hippocampal pallium is dorsomedial and the pyriform pallium lateral (Fig. 1B).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ariëns-Kappers, C. U., 1906, The structure of the teleostean and selachian brian, J. Comp. Neurol. 16: 1.
Aronson, L. R., 1948, Problems in the behavior and physiology of a species of African mouth breeding fish, Trans. N.Y. Acad. Sci. Ser. 2 2: 33.
Aronson, L. R., 1963, The central nervous system of sharks and bony fishes with special reference to sensory and integrative mechanisms, in: Sharks and Survival ( P. W. Gilbert, ed.), pp. 165–241, Heath, Boston.
Aronson, L. R., and Kaplan, H., 1968, Function of the teleostean forebrain, in: The Central Nervous System and Fish Behavior ( D. Ingle, ed.), pp. 107–125, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Attardi, D. G., and Sperry, R. W., 1963, Preferential selection of central pathways by regenerating optic fibers, Exp. Neurol. 7: 46.
Bannister, L. H., 1973, Forebrain structure in Phoxinus phoxinus, a teleost of the cyprinid family, J. Hirnforsch. 14: 413.
Bernstein, J. J., 1962, Role of the telencephalon in color vision of fish, Exp. Neurol. 6: 173.
Bernstein, J. J., 1964, Relation of spinal cord regeneration to age in adult goldfish, Exp. Neurol. 9: 161.
Bernstein, J. J., 1967, The regenerative capacity of the telencephalon of the goldfish and rat, Exp. Neurol. 17: 44.
Berwein, M., 1941, Beobachtungen and Versuche über das geselige Leben von Elritzen, Z. Vgl. Physiol. 28: 402.
Braford, M. R., and Northcutt, R. G., 1974, Olfactory bulb projections in the bichir, Polypterus, J. Comp. Neurol. 156: 165.
Brunner, R. L., Rossis, R. R., Stutz, R. M., and Roth, T. G., 1970, Memory loss following posttrial electrical stimulation of the hippocampus, Psychon. Sci. 18: 159.
Chanconie, M., and Clairambault, P., 1975, Développement du télencéphale de Salmo irideus Gib., J. Hirnforsch. 16: 75.
Crosby, E. C., Dejonge, B. D., Schneider, R. C., 1966, Evidence for some of the trends in the phylogenetic development of the vertebrate telencephalon, in: Evolution of the Forebrain ( R. Hassler and H. Stephan, eds.), pp. 117–135, George Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart.
Davis, R. E., Kassel, J., and Schwagmeyer, P., 1976, Telencephalic lesions and behavior in the telost Macropodus opercularis: Reproduction, startle reaction, and operant behavior in the male, Behav. Biol. 18: 165.
Demski, L. S., and Knigge, K. M., 1971, The telencephalon and hypothalamus of the bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus): Evoked feeding, aggressive and reproductive behavior with representative frontal section, J. Comp. Neurol 143: 1.
Droogleever-Fortuyn, J., 1961, Topographical relations in the telencephalon of the sunfish, Eupom-otis gibbosus, J. Comp. Neurol. 116: 249.
Fiedler, K., 1967, Ethologische and neuroanatomische Auswirkungen von Vorderhirnexistirpationen bei Meerbrassen (Diplodus) and Lippfischen (Crenilaburs, Perciformes, Teleostei), J. Hirnforsch. 9: 481.
Finger, M., 1975, The distribution of the olfactory tract in the bullhead catfish, Ictalurus nebulosus, J. Comp. Neurol. 161: 25.
Friedlander, M. J., 1978, Structure and function of the visual diencephalon of the teleost fish, Micropterus salmoides, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Illinois.
Gage, S. P., 1893, The brain of Diemyctilus viridescens from larval to adult life and comparisons with the brain of Amia and Petromyzon, in: The Wilder Quarter Century Book, pp. 259–314, Ithaca, N.Y.
Gaze, R. M., and Keating, M. J., 1972, The visual system and “neuronal specificity,” Nature (London) 237: 375.
Goldstein, K., 1905, Untersuchungen über das Vorderhirn and Zwischenhirn einiger Knochenfische (nebst einigen Beitragen Mittelhirn und Kleinhirn derselben), Arch. Mikrosk. Anat. 66: 135.
Hale, E. B., 1956, Social facilitation and forebrain function in maze performance of green sunfish, Lempomis cyänellus, Physiol. Zool. 29: 93.
Healey, E. G., 1957, The nervous system, in: The Physiology of Fishes, Vol. 2 ( M. F. Brown, ed.), pp. 1–119, Academic Press, New York.
Herrick, C. J., 1922, Functional factors in the morphology of the forebrain of fishes, in: Libro en Honor de D. Santiago Ramón y Cajal, pp. 143–204, Jiménez y Molina, Madrid.
Herz, M. J., and Peeke, H. V. S., 1971, Impairment of extinction with caudate nucleus stimulation, Brain Res. 33: 519.
Holmgren, N., 1922, Points of view concerning forebrain morphology in lower vertebrates, J. Comp. Neurol. 34: 391.
Hosch, L., 1936, Untersuchungen über Grosshirnfunktionen der Elritze (Phoxinus laevis) und des Gruendlings (Gobio fluviatilis), Zool. Jahrb. Abt. All. Zool. Physiol. Tiere 57: 57.
Ito, H., 1973, Normal and experimental studies on synaptic patterns in the carp telencephalon with special reference to the secondary olfactory termination, J. Hirnforsch. 14: 237.
Ito, H., and Kishida, R., 1977, Tectal afferent neurons identified by the retrograde HRP method in the carp telencephalon, Brain Res. 130: 142.
Ito, H., and Kishida, R., 1978, Telencephalic afferent neurons identified by the retrograde HRP method in the carp diencephalon, Brain Res. 149: 211.
Jacobson, M., and Gaze, R. M., 1965, Selection of appropriate tectal connections by regenerating optic nerve fibers in adult goldfish, Exp. Neurol. 13: 418.
Johnston, J. B., 1911, The telencephalon of ganoids and teleosts, J. Comp. Neurol. 21: 489.
Källén, B., 1947, Some remarks on the subpallial parts of the teleost forebrain, K. fysiogr. Saellsk, Lund Foerh. 17: 203.
Källén, B., 1951, Embryological studies on the nuclei and their homologization in the vertebrate forebrain, Acta Univ. Lund. 62:No. 5.
Kaplan, H., and Aronson, L. R., 1967, Effect of forebrain ablation on the performance of a conditioned avoidance response in the teleost fish, Tilapia h. macrocephala, Anim. Behav. 15: 436.
Kassel, J., Davis, R. E., and Schwagmeyer, P., 1976, Telencephalic lesions and behavior in the teleost Macropodus opercularis: Further analysis of reproductive and operant behavior in the male, Behav. Biol. 18: 179.
Kesner, R. P., and Doty, R. W., 1968, Amnesia produced in cats by local seizure activity initiated from the amygdala, Exp. Neurol. 21: 58.
Kirsche, W., and Kirsche, K., 1961, Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Frage der Regeneration und Funktion des Tectum Opticum von Carassius carassius L., Z. Mikrosk. Anat. Forsch. 67: 140.
Kumakura, S., 1928, Versuche an Goldfischen, denen beide Hemisphären dés Grosshirns exstirpirt worden waren, Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 3: 19.
Marón, K., 1963, Endbrain regeneration in Lebistes reticulatus, Folia Biol. 11: 1.
Mcintyre, D. C., 1970, Differential amnesic effect of cortical vs. amygdaloid elicited convulsions in rats, Physiol. Behav. 5: 747.
Miller, R. N., 1940, The telencephalic zonal system of the teleost, Corydora paliatus, J. Comp. Neurol. 72: 149.
Morgan, G. C., 1974a, The early development of the telencephalon of the marine catfish, Galeichthys felis, J. Hirnforsch. 15: 427.
Morgan, G. C., 1974b, The late embryology and maturation of the telencephalon in the marine catfish, Galeichthys felis, J. Hirnforsch. 15: 449.
Morgan, G. C., 1975, The telencephalon of the sea catfish Galeichthys felis, J. Hirnforsch. 16: 131.
Nieuwenhuys, R., 1963, The comparative anatomy of the actinopterygian forebrain, J. Hirnforsch. 6: 172.
Nieuwenhuys, R., 1967, Comparative anatomy of olfactory centres and tracts, Prog. Brain Res. 23: 106.
Nieuwenhuys, R., Bauchot, R., and Arnoult, J., 1969, Le développement du télencéphale d’un poisson osseux primitif, Polypterus senegalus Cuvier, Acta Zool. 50: 101.
Noble, G. K., 1936, Function of the corpus striatum in the social behavior of fishes, Anat. Rec. 64: Suppl. 34.
Noble, G. K., 1937, Effects of lesions of the corpus striatum on the brooding behavior of cichlid fishes, Anat. Rec. 70: 58.
Overmier, J. B., and Gross, D., 1974, Effects of telencephalic ablation upon nest-building and avoidance behaviors in East African mouthbreeding fish, Tilapia mossambica, Behav. Biol. 12: 211.
Overmier, J. B., and Savage, G. E., 1974, Effects of telencephalic ablation on trace classical conditioning of heart rate in goldfish, Exp. Neurol. 42: 339.
Overmier, J. B., and Starkman, N., 1974, Transfer of control of avoidance behavior in normal and telencephalon ablated goldfish (Carassius auratus), Physiol. Behav. 12: 605.
Peeke, H. V. S., Peeke, S. C., and Williston, J. S., 1972, Long-term memory deficits for habituation of predatory behavior in the forebrain ablated goldfish (Carassius auratus), Exp. Neurol. 36: 288.
Peter, R. E., and Gill, V. E., 1975, A stereotaxic atlas and technique for forebrain nuclei of the goldfish, Carassius auratus, J. Comp. Neurol. 159: 69.
Peter, R. E., Macey, M. J., and Gill, V. E., 1975, A stereotaxic atlas and technique for forebrain nuclei of the killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus, J. Comp. Neurol. 159: 103.
Savage, G. E., 1969, Some preliminary observations on the role of telencephalon in food-reinforced behavior in the goldfish, Carassius auratus, Anim. Behav. 17: 363.
Scalia, F. and Ebbesson, S. O. E., 1971, The central projections of the olfactory bulb in a teleost (Gymnothorax funebris), Brain Behav. Evol. 4: 376.
Schnitzlein, H. N., 1962, The habenula and the dorsal thalamus of some teleosts, J. Comp. Neurol. 118: 225.
Schnitzlein, H. N., 1964, Correlation of habit and structure in the fish brain, Am. Zool. 4: 21.
Schnitzlein, H. N., 1977, The telencephala of division I of the teleost fishes, J. Hirnforsch. 18: 157.
Schnitzlein, H. N., Hamel, E. G., Carey, H. H., Brown, J. W., Hoffman, H. H., Faucette, J. R., and Showers, M. J. C., 1973, The interrelations of the striatum with subcortical areas through the lateral forebrain bundle, J. Hirnforsch. 13: 409.
Schwagmeyer, P., Davis, R. E., and Kassel, J., 1977, Telencephalic lesions and behavior in the teleost Macropodus opercularis (L.): Effects of telencephalon and olfactory bulb ablation on spawning and foamnest building, Behav. Biol. 20: 463.
Segaar, J., 1960. Ethophysiological experiments with male Gasterosteus aculeatus, in: Structure and Function of the Cerebral Cortex ( D. B. Tower and J. P. Shade, eds.), pp. 301–305, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Segaar, J., 1961, Telencephalon and behavior in Gasterosteus aculeatus, Behavior 28: 256.
Segaar, J., 1965, Behavioural aspects of degeneration and regeneration in fish brain: A comparison with higher vertebrates, Prog. Brain Res. 14: 143.
Shapiro, S., Schuckman, H., Sussman, D., and Tucker, A. M., 1974, Effects of telencephalic lesions on gill cover response of Siamese fighting fish, Physiol. Behav. 13: 749.
Sheldon, R. E., 1912, The olfactory tracts and centers in teleosts, J. Comp. Neurol. 22: 177.
Singh, H. R., 1969, Telencephalic nuclear areas in three Indian teleosts, Acta Anat. 73: 463.
Ten Cate, J., 1935, Physiologie des Zentralnervensystems der Fische, Ergeb. Biol. 11: 335.
Turowski, A., and Danner, H., 1977, Zur Morphologie des Telencephalons von Salmo irideus (Teleostei) Golgi-Imprägnationsstudie, J. Hirnforsch. 18: 37.
Vanegas, H., and Ebbesson, S. O. E., 1976, Telencephalic projections in two teleost species, J. Comp. Neurol. 165: 181.
Westerman, R. A., and von Baumgarten, R., 1964, Regeneration of olfactory paths in carp, Experienta 20: 519.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1980 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Schroeder, D.M. (1980). The Telencephalon of Teleosts. In: Ebbesson, S.O.E. (eds) Comparative Neurology of the Telencephalon. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2988-6_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2988-6_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-2990-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-2988-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive