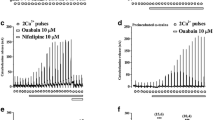
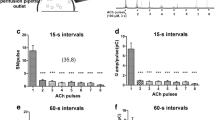
Abstract
The requirement of extracellular calcium for secretion of catecholamines from the adrenal medulla was first demonstrated by Douglas and Rubin in 1961 [10]. They proposed that acetylcholine stimulated secretion by promoting the influx of calcium into chromaffin cells, thus initiating intracellular events resulting in the release of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Evidence consistent with this hypothesis was obtained by Douglas and Poisner [9] who showed that perfused cat adrenal glands treated with acetylcholine retained more of a loading dose of 45Ca2+ than did untreated glands. Because of the limited experimental flexibility of the perfused gland system it was not possible to carry out a detailed analysis of calcium uptake, but continued studies of stimulus-secretion coupling provided evidence that entry of calcium into the cell was an early step in secretion [8]. With the advent of methods for maintaining primary cultures of adrenal medulla chromaffin cells, it became possible to determine directly the effects of stimulation on the entry of calcium as well as other ions into the cells. Several laboratories have undertaken such studies [20,23,28], and the essential features are described here.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amy, C. M.; Kirshner, N. Phosphorylation of adrenal medulla cell proteins in conjunction with stimulation of catecholamine secretionJ. Neurochem. 36: 847–854, 1981.
Arqueros, L.; Daniels, A. J. Manganese as agonist and antagonist of calcium ions: Dual effect upon catecholamine release from adrenal medullaLife Sci 28: 1535–1540, 1981.
Biales, B.; Dichter, M.; Tischler, A. Electrical excitability of cultured adrenal chromaffin cellsJ. Physiol. (London) 262: 743–753, 1976.
Chalfie, M.; Hoodley, D.; Pastan, S.; Perlman, R. L. Calcium uptake into rat pheochromocytoma cellsJ. Neurochem. 27: 1405–1409, 1976.
Conn, P. M.; Kilpatrick, D.; Kirshner, N. Ionophoretic Ca2+ mobilization in rat gonadotropes and bovine adrenomedullary cellsCell Calcium 1: 29–133, 1980.
Corcoran, J. J.; Kirshner, N. Inhibition of calcium uptake, sodium uptake and catecholamine secretion by methoxyverapamil (D600) in primary cultures of adrenal medulla cellsJ. Neurochem. 40: 1106–1109, 1983.
Corcoran, J. J.; Kirshner, N. Effects of manganese and other divalent cations on calcium uptake and catecholamine secretion by primary cultures of bovine adrenal medullaCell Calcium 4: 127–137, 1983.
Douglas, W. W. Involvement of calcium in exocytosis and the exocytosis vesiculation sequenceBiochem. Soc. Symp.
Douglas, W. W.; Poisner, A. M. On the mode of action of acetylcholine in evoking adrenal medullary secretion: Increased uptake of calcium during the secretory responseJ. Physiol. (London) 162: 385–392, 1962.
Douglas, W. W.; Rubin, R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholineJ. Physiol. (London) 159: 40–57, 1961.
Douglas, W. W.; Rubin, R. P. The effects of alkaline earths and other divalent cations on adrenal medullary secretionJ. Physiol. (London) 175: 231–241, 1964.
Douglas, W. W.; Rubin, R. P. Stimulant action of barium on the adrenal medullaNature (London) 203: 305–307, 1964.
Douglas, W. W.; Kanno, T.; Sampson, S. R. Influence of the ionic environment on the membrane potential of adrenal chromaffin cells and on the depolarizing effect of acetylcholineJ. Physiol. (London) 191: 107–121, 1967.
Dunn, L. A.; Holz, R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated adrenal medullary chromaffin cellsJ. Biol. Chem. 258: 4989–4993, 1983.
Fenwick, E. M.; Marty, A.; Neher, E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholineJ. Physiol. (London) 331: 577–597, 1982.
Fenwick, E. M.; Marty, A.; Neher, E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cellsJ. Physiol. (London) 331: 599–635, 1982.
Ferris, R. M.; Viveros, O. H.; Kirshner, N. Effects of various agents on the Mg2+ -ATP stimulated incorporation and release of catecholamines by isolated bovine adrenomedullary storage vesicles and on secretion from the adrenal medullaBiochem. Pharmacol. 19: 505–514, 1970.
Galper, J. B.; Catterall, W. A. Inhibition of sodium channels by D600Mol. Pharmacol. 15: 174–178, 1979.
Haycock, J. W.; Meligeni, J. A.; Bennett, W. F.; Waymire, J. C. Phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine hydroxylase mediate the acetylcholine-induced increase in catecholamine biosynthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 12641–12648, 1982.
Holz, R. W.; Sentor, R. A.; Frye, R. A. Relationship between Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion in primary dissociated cultures of adrenal medullaJ. Neurochem. 39: 635–646, 1982.
Kenigsberg, R. L.; Cote, A.; Trifaro, J. M. Trifluoperazine, a calmodulin inhibitor, blocks secretion in cultured chromaffin cells at a step distal from calcium entryNeuroscience 7: 2277–2286, 1982.
Kidikoro, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Ozawa, S. Acetylcholine-induced membrane depolarization and potential fluctuations in the rat adrenal chromaffin cellJ. Physiol. (London) 324: 221–237, 1982.
Kilpatrick, D. L.; Slepetis, R. J.; Corcoran, J. J.; Kirshner, N. Calcium uptake and catecholamine secretion by cultured bovine adrenal medulla cellsJ. Neurochem. 38: 427–435, 1982.
Kirshner, N.; Smith, W. J. Metabolic requirements for secretion from the adrenal medullaLife Sci 8: 799–803, 1969.
Knight, D. E.; Baker, P. F. Calcium-dependence of catecholamine release from bovine adrenal medullary cells after exposure to intense electric fieldsJ. Membr. Biol. 68: 107–140, 1982.
Kohlhardt, M.; Bauer, B.; Krause, H.; Fleckenstein, A. Differentiation of the transmembrane Na and Ca channels in mammalian cardiac fibers by the use of specific inhibitorsPfluegers Arch 335: 309–322, 1972.
Nawrath, H.; Ten Eick, R. E.; McDonald, T. F.; Trautwein, W. On the mechanism underlying the action of D600 on slow inward current and tension in mammalian myocardiumCirc. Res. 40: 408–414, 1977.
Oka, M.; Isosaki, M.; Watanabe, J. Calcium flux and catecholamine release in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells: Effects of nicotinic and muscarinic stimulation. In: Advances in the Biosciences, Volume 36, Synthesis, Storage and Secretion of Adrenal Catecholamines, F. Izumi, K. Kumakura, and M. Oka, eds., Elmsford, N.Y.; Pergamon Press, 1982, pp. 29–36.
Pinto, J. E. B.; Trifaro, J. M. The different effects of D600 (methoxyverapamil) on the release of adrenal catecholamines induced by acetylcholine, high potassium or sodium deprivationBr. J. Pharmacol. 57: 127–132, 1976.
Ritchie, A. K. Catecholamine secretion in a rat pheochromocytoma cell line: Two pathways for calcium entryJ. Physiol. (London) 286: 541–561, 1979.
Rubin, R. P. The role of energy metabolism in calcium-evoked secretion from the adrenal medullaJ. Physiol. (London) 206: 181–192, 1970.
Slepetis, R.; Kirshner, N. Inhibition of 45Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion by phenothiazines and pimozide in adrenal medulla cell culturesCell Calcium 3: 183–190, 1982.
Stallcup, W. B. Sodium and calcium fluxes in a clonal nerve cell lineJ. Physiol. (London) 286: 525–540, 1979.
Wada, A.; Yanagihara, N.; Izumi, F.; Sakuroi, S.; Kobayashi, H. Trifluoperazine inhibits 45Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion and synthesis in adrenal medullary cellsJ. Neurochem. 40: 481–486, 1983.
Wilson, S. P.; Kirshner, N. Calcium-evoked secretion from digitonin-permeabilized adrenal medullary chromaffin cellsJ. Biol. Chem. 258: 4994–5000, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1985 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Krishner, N., Corcoran, J.J., Wilson, S.P. (1985). Role of Calcium in Stimulus-Secretion Coupling in Bovine Adrenal Medullary Cells. In: Rubin, R.P., Weiss, G.B., Putney, J.W. (eds) Calcium in Biological Systems. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2377-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2377-8_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4612-9453-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4613-2377-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive