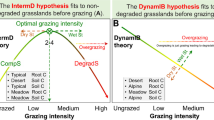
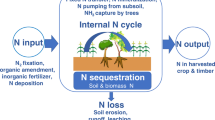
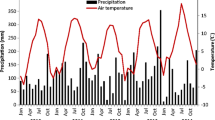
Abstract
The influence of nitrogen (N) on grassland production was demonstrated by the dramatic results presented in Chapter 3, and some mechanisms of its action were discussed in Chapter 2. Most information pertinent to N cycling in grassland ecosystems relates primarily to flows of N within biological pathways. Kline (1969), Whitehead (1970), Henzell and Ross (1973), Porter (1975), Charley (1977), and Frissel (1977) reviewed literature relating to N cycling in grasslands. Their publications illustrate that our greatest knowledge is of transfers within plant-dominated pathways. Reference is made by various authors to biological and chemical processes and to input and loss of N, but few quantitative data are presented. Henzell and Norris (1961) reviewed pathways of N input into tropical grasslands, but their values were not specific, being averages drawn from the literature. Bazilevich (1958), Rodin and Bazilevich (1967), and Bazilevich and Rodin (1971) reviewed world literature and presented data on transfers in plant parts within ecosystems. Reuss (1971) and Reuss and Innis (1977) discussed specific grassland sites and presented estimates of N additions based on results of Eriksson (1952). No estimates of total losses were given. Clark (1977) studied transfers of 15N in miniswards of blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis). His research focused on living and dead grass material and soil organic matter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M. 1961. Introduction to Soil Microbiology. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Barrow, N. J. 1960a. A comparison of the mineralization of nitrogen and of sulphur from decomposing organic materials. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 11:960–969.
Barrow, N. J. 1960b. Simulated decomposition of soil organic matter during the decomposition of added organic materials. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 11:331–338.
Barrow, N. J. 1961. Mineralization of nitrogen and sulphur from sheep faeces. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 12:644–650.
Bazilevich, N. I. 1958. The minor biological cycle of ash elements and nitrogen in the processes of meadow-steppe and steppe soil development. Soviet Soil Sci. 1958:1314–1330.
Bazilevich, N. I. and L. E. Rodin. 1971. Geographical regularities in productivity and the circulation of chemical elements in the earth’s main vegetation types. Soviet Geogr. Rev. Trans. 12:293–317.
Beauchamp, E. G., G. E. Kidd, and G. Thurtell. 1978. Ammonia volatilization from sewage sludge applied in the field. J. Environ. Qual. 7:141–146.
Bormann, F. H. and G. E. Likens. 1967. Nutrient cycling. Science 155:424–429.
Brown, J. M. and W. B. Bartholomew. 1963. Sorption of gaseous ammonia by clay minerals as influenced by sorbed aqueous vapor and exchangeable cations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 27:160–164.
Burton, T. M. and G. E. Likens. 1975. Energy flow and nutrient cycling in salamander populations in the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest, New Hampshire. Ecology 56:1068–1080.
Chao, T. T. and W. Kroontje. 1964. Relationships between ammonia volatilization, ammonia concentration, and water evaporation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 28(3):393–395.
Charley, J. L. 1977. Mineral cycling in rangeland ecosystems. In R. F. Sosebee (ed.), Rangeland Plant Physiology, Range Sci. Ser. No. 4, Society for Range Management, Denver, CO. pp. 215–256.
Chin, W., and W. Kroontje. 1963. Urea hydrolysis and subsequent loss of ammonia. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.. 27(3):316–318.
Clark, F. E. 1975. Viewing the invisible prairie. In M. K. Wali (ed.), Prairie: A Multiple View, pp. 181–197. Grand Forks: University of North Dakota Press.
Clark, F. E. 1977. Internal cycling of 15nitrogen in shortgrass prairie. Ecology 58:1322–1333.
Clark, F. E. and E. A. Paul. 1970. The microflora of grassland. Adv. Agron. 22:375–435.
Coleman, D. C, R. Andrews, J. E. Ellis, and J. S. Singh. 1977. Energy flow and partitioning in selected man-managed and natural ecosystems. Agro-Ecosystems 3:45–54.
Conrad, J. P. 1942. The occurrence and origin of urease like activities in soils. Soil Sci. 54:367–380.
Copley, P. W. and J. O Reuss. 1972. Evaluation of biological N2 fixation in a grassland ecosystem, US/IBP Grassland Biome Tech. Rep. No. 152. Fort Collins: Colorado State Univ.
Dahlman, R. C. and C. L. Kucera. 1968. Tagging native grassland vegetation with carbon-14. Ecology 49:1199–1203.
Dean, R. E. and R. W. Rice. 1974. Effects offences and corrals on grazing behavior. Proc. Western Sect. Am. Soc. Anim. Sci. 25:56–58.
Denmead, O. T., J. R. Simpson, and J. R. Freney. 1974. Ammonia flux into the atmosphere from a grazed pasture. Science 185:609–610.
Denmead, O. T., J. R. Freney, and J. R. Simpson. 1976. A closed ammonia cycle within a plant canopy. Soil Biol. Biochem. 8:161–164.
Doak, B. W. 1952. Some chemical changes in the nitrogenous constituents of urine when voided on pasture. J. Agric. Sci. 42:162–171.
Duvigneaud, P. and S. Denaeyer-DeSmet. 1975. Mineral cycling in terrestrial ecosystems. In D. E. Reichle, J. F. Franklin, and D. W. Goodall (eds.), Productivity of World Ecosystems, pp. 133–154. Washington, D.C.: National Academy of Science.
Edwards, C. A. 1974. Macroarthropods. In C. H. Dickinson and G. J. F. Pugh (eds.), Biology of Plant Litter Decomposition, pp. 533–554. New York: Academic Press, Inc.
Eriksson, E. 1952. Composition of atmospheric precipitation. 1. Nitrogen compounds. Tellus 4:215–232.
Ernst, J. W. and H. F. Massey. 1960. The effects of several factors on volatilization of ammonia formed from urea in the soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 24(2):87–90.
Faurie, G., A. Josserand, and R. Bardin. 1975. Influence des colloides argileux sur la retention d’ammonium et la nitrification. Rev. Ecol. Biol. Sol. 12:201–210.
Fenn, L. B. 1975. Ammonium volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils. III. Effects of mixing low and high loss ammonium compounds. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 39:366–369.
Fenn, L. B. and R. Escarzaga. 1976a. Ammonium volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils: V. Soil water content and method of nitrogen application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 40:537–541.
Fenn, L. B. and R. Escarzaga. 1976b. Ammonia volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds to calcareous soils as affected by initial soil water content and quantity of applied water. Agron. Abstr. 1976:127–128.
Fenn, L. B. and D. E. Kissel. 1973. Ammonia volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils: I. General theory. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 37:855–859.
Fenn, L. B. and D. E. Kissel. 1974. Ammonium volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils: II. Effect of temperature and rate of NH+ 4 = N application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 38:606–610.
Fenn, L. B. and D. E. Kissel. 1975. Ammonium volatilization from surface applications of ammonium compounds on calcareous soils: IV. Effect of calcium carbonate content. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 39:631–633.
Feth, J. H. 1966. Nitrogen compounds in natural water—a review. Water Resour. Res. 2:41–58.
Floate, M. J. S. 1970a. Decomposition of organic materials from hill soils and pastures. 2. Comparative studies on the mineralization of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus from plant materials and sheep faeces. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2:173–185.
Floate, M. J. S. 1970b. Decomposition of organic materials from hill soils and pastures. 3. The effect of temperature on the mineralization of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus from plant materials and sheep feces. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2:187–196.
Floate, M. J. S. 1970c. Decomposition of organic materials from hill soils and pastures. 4. The effects of moisture content on the mineralization of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus from plant materials and sheep faeces. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2:275–283.
Floate, M. J. S. and C. J. W. Torrance. 1970. Decomposition of the organic materials from hill soils and pastures. 1. Incubation method for studying the mineralization of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. J. Sci. Food Agric. 21:116–120.
Frank, H. 1954. On the nitrogen loss in aging plants (Trans. No. 3968 from “Über den Stickstoffverlust bei alternden Pflanzen”). Planta 44:319.
Frissel, M. J. (ed.). 1977. Cycling of mineral nutrients in agricultural ecosystems. Agro-Ecosystems 4:1–254.
Galloway, J. N. 1976. Critical factors in the collection of precipitation for chemical analysis. In D. H. Matheson and F. C. Elder (eds.) (Proc. First Specialty Symp. on Atmospheric Contribution to the Chemistry of Lake Waters Int. Assoc. Great Lakes Res.) pp. 65–81. Vol. 2, Supplement 1, Buffalo: State University College
Gasser, J. K. R. 1964. Urea as a fertilizer. Soils Fert. 27(3): 175–180.
Gillard, P. 1967. Coprophagous beetles in pasture ecosystems. J. Aust. Inst. Agric. Sci. 33:30–34.
Granat, L. 1976. Principles in network design for precipitation chemistry measurements. In D. H. Matheson and F. C. Elder (eds.) (Proc. First Specialty Symp. on Atmospheric Contribution to the Chemistry of Lake Waters Int. Assoc. Great Lakes Res.), pp. 42–55. Vol. 2, Supplement 1, Buffalo: State University College
Hanawalt, R. B. 1969. Environmental factors influencing the sorption of atmospheric ammonia by soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 33:231–234.
Hargrove, W. L., D. E. Kissel, and L. B. Fenn. 1977. Field measurements of ammonia volatilization from surface applications of ammonium salts to a calcareous soil. Agron. J. 69:473–476.
Harmsen, G. W. and G. J. Kolenbrander. 1965. Soil inorganic nitrogen. In W. V. Bartholomew and F. E. Clark (eds.) Soil Nitrogen, Agronomy 10, pp. 43–92. Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy.
Henzell, E. F. and D. O. Norris. 1961. Processes by which nitrogen is added to the soil/ plant system. Commonw. Bur. Pastures Field Crops Bull. 46:1–18.
Henzell, E. F. and P. J. Ross. 1973. The nitrogen cycles of pasture ecosystems. In G. W. Butler and R. W. Bailey (eds.), Chemistry and Biochemistry of Herbage, Vol. 2, pp. 227–246. New York: Academic Press, Inc.
Hilder, E. J. 1964. The distribution of plant nutrients by sheep at pasture. Proc. Aust. Soc. Anim. Prod. 5:241–248.
Hoeft, R. G., D. R. Keeney, and L. M. Walsh. 1972. Nitrogen and sulfur in precipitation and sulfur dioxide in the atmosphere in Wisconsin. J. Environ. Qual. 1:203–208.
Hutchinson, G. L., R. J. Millington, and D. B. Peters. 1972. Atmospheric ammonia: Absorption by plant leaves. Science 175:771–772.
Jackson, M. L., and S. C. Chang. 1947. Anhydrous ammonic retention by soils as influenced by depth of application soil texture, moisture content, pH value, and tilth. Agron. J. 39:623–633.
Jones, M. B., and R. G. Woodmansee. In press. Nitrogen cycling in annual grassland ecosystems. In L. T. Burcham and R. G. Woodmansee (eds.), Annual Grassland Ecosystems of California. Stroudsburg, Pa.: Dowden, Hutchinson and Ross, Inc.
Junge, C. E. 1958. The distribution of ammonia and nitrate in rain water over the United States. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 39:248.
Junge, C. E. 1963. Air Chemistry and Radioactivity. New York: Academic Press, Inc.
Junge, C. E. and P. E. Gustafson. 1956a. On the distribution of sea salt over the United States and its removal by precipitation. Tellus 9:164–173.
Junge, C. E. and P. E. Gustafson. 1956b. Precipitation sampling for chemical analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 37:244.
Khengre, S. T. and N. K. Savant. 1977. Distribution pattern of inorganic nitrogen following anhydrous ammonia injection into a vertisol. Soil Soc. Sci. Am. J. 41:1139–1141.
Kilmer, V. J. 1974. Nutrient losses from grasslands through leaching and runoff. In D. A. Mays (ed.) Forage Fertilization, pp. 341–362. Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America.
Kissel, D. E., H. L. Brewer, and G. F. Arkin. 1977. Design and test of afield sampler for ammonia volatilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41:1133–1138.
Kline, J. R. 1969. Soil chemistry as a factor in the function of grassland ecosystems. In R. L. Dix and R. G. Beidleman (eds.), The Grassland Ecosystem (Range Sci. Dep. Sci. Ser. No. 2.) pp. 71–88. Fort Collins: Colorado State Univ.
Lapins, P. and E. R. Watson. 1970. Loss of nitrogen from maturing plants. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb. 10:599–603.
Lauer, D. A., D. R. Bouldin, and S. D. Klausner. 1976. Ammonia volatilization from dairy manure spread on the soil surface. J. Environ. Qual. 5(2): 134–141.
Likens, G. E. 1976. Acid precipitation. Chem. Eng. News 1976:29–44.
Lofty, J. R. 1974. Oligochaetes. In C. H. Dickinson and G. J. F. Pugh (eds.), Biology of Plant Litter Decomposition. Vol. 2, pp. 467–488. New York: Academic Press, Inc.
Lotero, J., W. W. Woodhouse, Jr., and R. G. Petersen. 1966. Local effect on fertility of urine voided by grazing cattle. Agron. J. 58:262–265.
Malo, B. A., and E. R. Purvis. 1964. Soil absorption of atmospheric ammonia. Soil Sci. 97:242–247.
Martin, J. P., and H. D. Chapman. 1951. Volatilization of ammonia from surface-fertilized soils. Soil Sci. 71(l):25–34.
McConnell, J. C. 1973. Atmospheric ammonia. J. Geophy. Res. 78:7812–7820.
McGarity, J. W., and J. A. Rajaratnam. 1973. Apparatus for the measurement of losses of nitrogen as gas from the field and simulated field environments. Soil Biol. Biochem. 5:121–131.
Meyer, R. D., R. A. Olson, and H. F. Rhoades. 1961. Ammonia losses from fertilized Nebraska soils. Agron. J. 53(4):241–244.
Millar, C. S. 1974. Decomposition of coniferous leaf litter. In C. H. Dickinson and G. J. F. Pugh (eds.), Biology of Plant Litter Decomposition. Vol. 1, pp. 105–128. New York: Academic Press, Inc.
Mills, H. A., A. V. Barker, and D. N. Maynard. 1973. Ammonia volatilization from soils. Agron. J. 66(3):355–358.
Mortland, M. M. 1958. Reactions of ammonia in soils. Adv. Agron. 10:325–348.
Mortland, M. M. and A. R. Wolcott. 1965. Sorption of inorganic nitrogen compounds by soil materials. In W. V. Bartholomew and F. E. Clark (eds.), Soil Nitrogen, Agronomy 10, pp. 151–197. Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy.
Nommik, H. 1965. Ammonium fixation and other reactions involving a nonenzymatic immobilization of mineral nitrogen in soil. In W. V. Bartholomew and F. E. Clark (eds.), Soil Nitrogen, Agronomy 10, pp. 198–258. Madison, Wisc: American Society of Agronomy.
Odum, E. P. 1969. The strategy of ecosystems development. Science 164:262–270.
Olson, R. A., E. C. Scim, and J. Muir. 1973. Influence of agricultural practices on water quality in Nebraska: A survey of streams, groundwater, and precipitation. Water Resour. Bull. 9:301–311.
Overrein, L. N. and P. G. Moe. 1967. Factors affecting urea hydrolysis and ammonia volatilization in soil. Soil Sci. Am. Proc. 31(1):57–61.
Parr, J. F. and R. I. Papendick. 1966. Retention of anhydrous ammonia by soil: II. Effect of ammonia concentration and soil moisture. Soil Sci. 101:109–119,
Pearsall, W. H. and M. C. Billimoria. 1937. Loss of nitrogen from green plants. Biochem. J. 31:1734.
Porter, L. K. 1975. Nitrogen transfer in ecosystems. Soil Biochem. 4:1–30.
Porter, L. K., F. G. Viets, Jr., and G. L. Hutchinson. 1972. Air containing nitrogen-15 ammonia: Foliar absorption by corn seedlings. Science 174:759–761.
Power, J. F., J. A. Lessi, G. A. Reichman, and D. L. Grunes. 1973. Recovery, residual effects, and fate of nitrogen fertilizer sources in a semiarid region. Agron. J. 65:765–768.
Rashid, G. H. 1977. The volatilization losses of nitrogen from added urea in some soils of Bangladesh. Plant Soil 48:549–556.
Reuss, J. O. 1971. Decomposer and nitrogen cycling investigations in the Grassland Biome. In N. R. French (ed.) Preliminary Analysis of Structure and Function in Grasslands (Range Sci. Dep. Sci. Ser. No. 10), pp. 133–146. Fort Collins: Colorado State Univ.
Reuss, J. O. and G. S. Innis. 1977. A grassland nitrogen-flow simulation model. In G. S. Innes (ed.) Grassland Simulation Model. Ecological Studies, 26, pp. 186–203. New York: Springer-Verlag.
Richardson, A. E. V., H. C. Trumble, and R. E. Shapter. 1931. Factors affecting the mineral contents of pasture (Bull. No. 49). Council for Sci. Ind. Res.
Robinson, E. and R. C. Robbins. 1968. Sources, abundance, and fate of gaseous atmospheric pollutants (Report prepared for the American Petroleum Institute, SRI Proj. PR-6755). Menlo Park, Calif. Stanford Research Institute.
Rodin, L. E. and N. I. Bazilevich. 1967. Production and Mineral Cycling in Terrestrial Vegetation. (Transi.). London: Oliver and Boyd Ltd.
Rogler, G. A. and R. J. Lorenz. 1974. Fertilization of mid-continent range plants. In D. A. Mays (ed.), Forage Fertilization, pp. 231–254. Madison, Wisc: Agronomic Society of America, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America.
Schuman, G. E. and R. E. Burwell. 1974. Precipitation nitrogen contribution to surface runoff discharges. J. Environ. Qual. 3:366–369.
Simpson, J. R. 1968. Losses of urea nitrogen from the surface of pasture soils. Int. Congr. Soil Sci. Trans. 9(2):459–466.
Sims, P. L. and J. S. Singh. 1971. Herbage dynamics and net primary production in certain ungrazed and grazed grasslands in North America. In N.R. French (ed.), Preliminary Analysis of Structure and Function in Grasslands (Range Sci. Dep. Sci. Ser. No. 10) pp. 56–124. Fort Collins: Colorado State Univ.
Skujins, J. 1975. Nitrogen dynamics in stands dominated by some major cool desert shrubs, US/IBP Research Memorandum 75–33. Logan: Utah State Univ.
Söderlund, R. and B. H. Svensson. 1976. The global nitrogen cycle. In B. H. Svensson and R. Söderlund (eds.), Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur-Global Cycles SCOPE Rep. 7, Ecol. Res. Comm. Bull. No. 22, pp. 23–75. Stockholm: Statens naturvetenska-pliga forskningsråd.
Soulides, D. A. and F. E. Clark. 1958. Nitrification in grassland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 22:308–311.
Stewart, B. A. 1970. Volatilization and nitrification of nitrogen from urine under simulated cattle feedlot conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 4:479–582.
Stewart, B. A., F. G. Viets, Jr., G. L. Hutchinson, and W. A. Kemper. 1967. Nitrate and other water pollutants under fields and feed lots. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1:763.
Sturges, F. W., R. T. Holmes, and G. E. Likens. 1974. The role of birds in nutrient cycling in a northern hardwoods ecosystem. Ecology 55:149–155.
Tabatabai, M. A. and J. M. Laflen. 1976. Nitrogen and sulfur content and pH of precipitation in Iowa. J. Environ. Qual. 5:108–112.
Taylor, A. W., W. M. Edwards, and E. C. Simpson. 1971. Nutrients in streams draining woodland and farmland near Coshocton, Ohio. Water Resour. Res. 7:81–89.
Viets, F. G., Jr. 1975. The environmental impact of fertilizers. CRC Critical Rev. Environ. Control 5:423–453.
Vitousek, P. M., and W. A. Reiners. 1975. Ecosystem succession and nutrient retention: A hypothesis. Bio Science 25:376–381.
Voigt, G. H. 1965. Nitrogen recovery from decomposing tree leaf tissue and forest humus. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 29:756–759.
Volk, G. M. 1959. Volatile loss of ammonia following surface application of urea to turf or bare soils. Agron. J. 51(12):746–749.
Wahhab, A., M. S. Randhawa, and S. Q. Alam. 1957. Loss of ammonia from ammonium sulphate under different conditions when applied to soils. Soil Sci. 84(3):249–255.
Wakesman, S. A., T. C. Cordon, and N. Hulpoi. 1939. Influence of temperature upon the microbiological population and decomposition processes in composts of stable manure. Soil Sci. 47(2):83–113.
Watson, E. R. and P. Lapins. 1969. Losses of nitrogen from urine on soils from southwestern Australia. Aust. J. Exp. Agrie. Anim. Husb. 9:85–91.
Whitehead, D. C. 1970. The role of nitrogen in grassland productivity. Commonw. Agric. Bur. Bull. No. 48. Farnham Royal, Bucks, England.
Woodmansee, R. G. 1978. Additions and losses of nitrogen in grassland ecosystems. Bio Science 28:448–453.
Woodmansee, R. G., J. L. Dodd, R. A. Bowman, F. E. Clark, and C. E. Dickinson. 1978. Nitrogen budget for a shortgrass prairie ecosystem. Oecologia 34:363–376.
Zakharchenko, I. G. 1974. Supply of nitrogen with atmospheric precipitation and its losses during soil leaching in the Ukranian poless’ye and forest-steppe. Soviet Soil Sci. 1974:63–67.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1979 Spriger-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Woodmansee, R.G. (1979). Factors Influencing Input and Output of Nitrogen in Grasslands. In: French, N.R. (eds) Perspectives in Grassland Ecology. Ecological Studies, vol 32. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-6182-7_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-6182-7_8
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4612-6184-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4612-6182-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive