Abstract
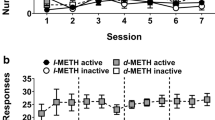
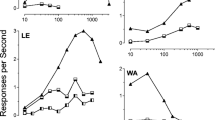
The reinforcing activity of 31 psychoactive drugs was evaluated. Drugs were offered by intravenous self-administration to groups of naive rats. Reinforcement is indicated by an injection rate greater than that for rats offered only saline. Two similar protocols were used. In the first protocol, rats were offered drug at a selected dose for 5 days, then the dose was reduced by one log unit (to 0.1 times the initial dose) for an additional 4 days. In the second protocol, saline only was offered the first 3 days to eliminate rats with high or low operant rates, and the dose was reduced 0.5 log unit (to 0.32 times the initial dose) instead of one log unit. An empirical score, based on the injection rates during the last 3 days of each period, describes the reinforcing activity. Replicate tests using both protocols gave similar scores. Literature data for reinforcing activity in monkeys was available for 27 of the drugs tested. Results for rats and monkeys agreed for 24 of the 27 drugs. Nalorphine and ethylketazocine were reinforcers only in rats, and ethanol was a reinforcer only in monkeys.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collins, R. J., Weeks, J. R., Cooper, M. M., Good, P. I., & Russell, R. R. (1984). Prediction of abuse liability of drugs using intravenous self-administration by rats. Psychopharmacology, 82, 6–13.
Griffiths, R. R., & Balster, R. L. (1979). Opioids: Similarity between evaluation of subjective effects and animal self-administration results. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 25, 611–617.
Griffiths, R. R., Bigelow, G. E., & Henningfield, J. E. (1980). Similarities in animal and human drug-taking behavior. In N. K. Mello (Ed.), Advances in substance abuse (Vol. 1, pp. 1–90). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
Griffiths, R. R., Brady, J. V., & Bradford, L. D. (1979). Predicting the abuse liability of drugs with animal drug self-administration procedures: Psychomotor stimulants and hallucinogens. In T. Thompson & P. B. Dews (Eds.), Advances in behavioral pharmacology (Vol. 2, pp. 163–208). New York: Academic Press.
Johanson, C. W., & Balster, R. L. (1978). A summary of the results of a drug self-administration study using substitution procedures in rhesus monkeys. Bulletin of Narcotics, 20, 43–54.
Morrison, D. F. (1967). Multivariate statistical methods. San Francisco: McGraw-Hill.
van Ree, J. M. (1979). Reinforcing stimulus properties of drugs. Neuropharmacology, 18, 963–969.
Schuster, C. W., & Thompson, T. (1969). Self-administration of and behavioral dependence on drugs. Annual Review of Pharmacology, 9, 483–502.
Thompson, T., & Unna, D. R. (Eds.). (1977). Predicting dependence liability of stimulant and depressant drugs. Baltimore: University Park Press.
Weeks, J. R. (1972). Long-term intravenous infusion. In R. D. Myers (Ed.), Methods in psychobiology (Vol. 2, pp. 155–168). London: Academic Press.
Weeks, J. R. (1977). The pneumatic syringe: A simple apparatus for self-administration of drugs by rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior, 7, 559–562.
Weeks, J. R. (1979). A method for administration of prolonged intravenous infusion of prostacyclin (PGI2) to unanesthetized rats. Prostaglandins, 17, 495–499.
Weeks, J. R. (1981). An improved pneumatic syringe for self-administration of drugs by rats. Pharmacology Biochemistry & Behavior, 14, 573–574.
Weeks, J. R., & Collins, R. J. (1976). Changes in morphine self-administration induced by prostaglandin E1 and naloxone. Prostaglandins, 12, 11–19.
Weeks, J. R., & Collins, R. J. (1979). Dose and physical dependence as factors in the self-administration of morphine by rats. Psychopharmacology, 65, 171–177.
Woods, J. H., Smith, C. B., Medzihradsky, F., & Swain, H. H. (1979). Preclinical testing of new analgesic drugs. In R. E. Beers & E. G. Bassett (Eds.), Mechanisms of pain and analgesic compounds, (pp. 429–445). New York: Raven Press.
Yanagita, T. (1977). Brief review on the use of self-administration techniques for predicting drug dependence potential. In T. Thompson & K. R. Unna (Eds.), Predicting dependence liability of stimulant and depressant drugs, (pp. 231–242). Baltimore: University Park Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1987 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Weeks, J.R., Collins, R.J. (1987). Screening for Drug Reinforcement Using Intravenous Self-Administration in the Rat. In: Bozarth, M.A. (eds) Methods of Assessing the Reinforcing Properties of Abused Drugs. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4812-5_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4812-5_2
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4612-9163-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4612-4812-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive