Abstract
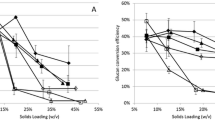
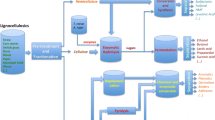
In ethanol production from lignocellulose by enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation, it is desirable to minimize addition of fresh-water and waste-water streams, which leads to an accumulation of substances in the process. This study shows that the amount of fresh water used and the amount of waste water thereby produced in the production of fuel ethanol from softwood, can be reduced to a large extent by recycling of either the stillage stream or part of the liquid stream from the fermenter. A reduction in fresh-water demand of more than 50%, from 3 kg/kg dry raw material to 1.5 kg/kg dry raw material was obtained without any negative effects on either hydrolysis or fermentation. A further decrease in the amount of fresh water, to one-fourth of what was used without recycling of process streams, resulted in a considerable decrease in the ethanol productivity and a slight decrease in the ethanol yield.
Author to whom all correspondence and reprint requests should be addressed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vallander, L and Eriksson, K. E. (1990), Adv. Biochem. Eng/Biotech. 42, 63–95.
Katzen, R., and Fowler, D. E. (1994), Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 45/46, 697–707.
Lynd, L. R., Cushman, J. H., Nichols, R. J, and Wyman, C. E. (1991), Science 251, 1318–1323.
Grethlein, H. E. and Converse, A. (1991), Biores. Technol. 36, 77–82.
Schell, D. J., Torget, R., Power, A., Walter, P. J., Grohmann, K., and Hinman, N. D. (1991), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 28/29, 87–97.
Ramos, L. P., Breuil, C., and Saddler, J. N. (1992), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 34/35, 37–48.
Mackie, K. L., Brownell, H. H., West, K. L., and Saddler, J. N. (1985), J. Wood Chem. Technol. 5(3), 405–425.
Eklund, R., Galbe, M., and Zacchi, G (1995), Bioresour. Eng. 52, 225–229.
Mamers, H., and Menz, D. N. J. (1984), Appita 37(8), 644–649.
Clark, T. A. and Mackie, K. L. (1987), J. Wood. Chem. Technol. 7(3), 373–403.
Schwald, W., Smaridge, T., Chan, M., Breuil, C., and Saddler, J. N. (1989), Enzyme Syst. Lignocellul. Degrad., [Proc. Workshop Prod., Charact. Appl. Cellul.-, Hemicellul.-LigninDegrading Enzyme Syst.], 231–242. Coughlan, M. P., ed., Elsevier, London, UK.
Sinitsyn, A. P., Clesceri, L. S., and Bungay, H. R. (1982), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 7(6), 455–458.
Mes-Hartree, M., and Saddler, J. N. (1983), Biotechnol. Lett. 5(8), 531–536.
Dekker, R. F. H. (1988), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 593–598.
Clark, T. A. and Mackie, K. L. (1984), J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol. 34B, 101–110.
Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., Galbe, M., and Zacchi, G. (1995), Enzym. Microbiol. Technol. 19, 470–476.
Galbe, M. and Zacchi, G. (1993), Biotechnology in Agriculture 9, Saddler, J. N., CAB International, Wallingford, UK, pp. 291–321.
Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., Galbe, M., Larsson, M., Stenberg, K., Szengyel, Z., Tengborg, C., and Zacchi, G. (1996) Biores. Technol. 58, 171–179.
Larsson, M., Galbe, M., and Zacchi G. (1997), Biores. Technol., 60, 143–151.
Hägglund, E. (1951), in Chemistry of Wood, Academic, New York.
Mandels, M., Andreotti, R., and Roche, C. (1976) Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 6, 21–33.
Berghem, L. E. R. (1974), Eur. J. Biochem. 46, 295–305.
Sanchez, B., and Bautista, J. (1988), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 10, 315–318.
Boyer, L. J., Vega, J. L., Klasson, K. T., Clausen, E. C., and Gaddy, J. L. (1992), Biomass Bioenergy 3(1), 41–48.
Maiorella, L. J., Blanch, H. W., and Wilke, C. R. (1983), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 25, 103–121.
Linden, T., Peetre, J., and Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (1992), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58(5), 1661–1669.
Buchert, J., Puls, J., and Poutanen, K. (1989), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 20/21, 309–318.
Nevado, J., Navarro, A., and Heredio, G. F. (1994), Yeast 10, 59–65.
Ramos, L. P., Breuil, C., and Saddler, J. N. (1993), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 15, 19–25.
Busche, R. M. (1983), Biotech. Bioeng. Symp. 13, 597–615.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Stenberg, K., Tengborg, C., Galbe, M., Zacchi, G., Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (1998). Recycling of Process Streams in Ethanol Production from Softwoods Based on Enzymatic Hydrolysis. In: Finkelstein, M., Davison, B.H. (eds) Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1814-2_64
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1814-2_64
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-4612-7295-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4612-1814-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive