Abstract
The use of resource-constrained devices, such as smartphones, PDAs, Tablet PCs, and Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) is spreading rapidly in the business community and our daily life. Accessing services from such devices is very common in ubiquitous environments, but mechanisms to describe, implement and distribute these services remain a major challenge. Web services have been characterized as an efficient and widely-adopted approach to overcome heterogeneity, while this technology is still heavyweight for resource-constrained devices. The emergence of REST architectural style as a lightweight and simple interaction model has encouraged researchers to study the feasibility of exploiting REST principles to design and integrate services hosted on devices with limited capabilities. In this chapter, we discuss the state-of-the-art in applying REST concepts to develop Web services for WSNs and smartphones as two representative resource-constrained platforms, and then we provide a comprehensive survey of existing solutions in this area. In this context, we report on the DigiHome platform, a home monitoring middleware solution, which enables efficient service integration in ubiquitous environments using REST architectural style. In particular, we target our reference platforms for home monitoring systems, namely WSNs and smartphones, and report our experiments in applying the concept of Component-Based Software Engineering (CBSE) in order to provide resource-efficient RESTful distribution of Web services for those platforms.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Introduction
Pervasive environments support context-aware applications that adapt their behavior by reasoning dynamically over the user and the surrounding information. This contextual information generally comes from diverse and heterogeneous entities, such as physical devices, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), and smartphones. In order to exploit the information provided by these entities, a middleware solution is required to collect, process, and distribute the contextual information efficiently. However, the heterogeneity of systems in terms of technology capabilities and communication protocols, the mobility of the different interacting entities, and the identification of adaptation situations make this integration difficult. Thus, this challenge requires a flexible solution in terms of communication support and context processing to leverage context-aware applications on the integration of heterogeneous context providers.
In particular, a solution dealing with context information and control environments must be able to connect with a wide range of device types. However, the resource scarceness in WSNs and mobile devices makes the development of such a solution very challenging. In this chapter, we propose the DigiHome platform, a simple but efficient service-oriented middleware solution to facilitate context-awareness in pervasive environments. Specifically, DigiHome provides support for the integration, processing and adaptation of the context-aware applications. Our solution enables the integration of heterogeneous computational entities by relying on the Service Component Architecture (SCA) model (Open SOA 2007), the REST (REpresentational State Transfer) principles (Fielding 2000), standard discovery and communication protocols, and resource representation formats. We combined SCA and REST in our solution in order to foster reuse and low coupling between the different services that compose the platform. We believe that the REST concepts of simplicity (in terms of interaction protocols) and flexibility (regarding the supported representation formats) make it a suitable architecture style for pervasive environments. The DigiHome platform presented in this chapter is an improved version of our work introduced in Romero et al. (2010a).
The remainder of this chapter is organized as follows. We start by reporting on the existing RESTful solutions for constrained devices (cf. RESTful Solutions for Constrained Platforms). Then, we describe a smart home scenario in which we identify the key challenges in pervasive environments that motivate this work (cf. RESTful Integration of Services: A Home Monitoring Scenario). We continue by the description of DigiHome, our middleware platform to support the integration of systems-of-systems in pervasive environments (cf. The DigiHome Service-Oriented Platform). Then, we discuss the benefits of our approach as well as future opportunities (cf. Future: Horizons and Challenges) before concluding (cf. Conclusion).
RESTful Solutions for Constrained Platforms
For years, the use of REST in mobile devices was restricted to client-side interaction from web browsers. As consequence of Moore’s law, the computing capabilities of mobile devices are quickly increasing. In particular, we observe that mobile devices move from simple service consumers to service providers. As an example, several activities have been recently initiated in order to enable the deployment of a web server within a mobile device (Wikman and Dosa 2006; Nokia 2008; Pham and Gehlen 2005; Srirama et al. 2006; The Apache Software Foundation 2009). Another example is the OSGi initiative, which includes a HTTPd bundle in most of its platforms (OSGi Alliance 2009, 2007). The strength of these mobile web servers is that the information they publish can be dynamically tuned depending on the context surrounding the mobile device.
From Supporting Lightweight Web Services. Recently, mobile phone platforms have drawn a lot of attention from manufacturers and users, mainly due to the opportunity to embark what has become lightweight computers in everyone’s pocket. As such, smartphones are now equipped with GPS, high speed cellular network access, wireless network interfaces, and various sensors (accelerometers, magnetometers, etc.). However, phone manufacturers keep offering platforms that differ radically in their operating system and API choices.
Android is an example of operating system for these mobile devices that includes middleware and key applications based on a tailored version of the Linux kernel. The Android platform allows developers to write application code in the Java language and to control the device via Google-based Java libraries. According to The Nielsen Company, unit sales for Android OS smartphones ranked first among all smartphone OS handsets sold in the U.S. during the first half of 2010. These numbers confirm the increasing success of smartphones in the population, and in the context of the DigiHome platform, we benefit from this acceptation to improve future applications by proposing a service-oriented platform exploiting smartphones and user usages.
Lightweight Web Services have been motivated by the concept of the Internet of Things – a technological revolution to connect daily objects and devices to large databases and networks, and therefore to the Internet. In this model, Web services standards are used to integrate WSNs and the Internet, e.g., in SOCRADES (de Souza et al. 2008), Web services are tailored at the gateway device where the Device Profile for Web Services (DPSW) is used to enable messaging, discovery, and eventing on devices with resource restrictions. However, in the context of WSN, since the current footprint of DPSW for sensor nodes is too large, this solution is only deployable on gateways. To overcome this issue, Priyantha et al. (2008) propose SOAP-based Web services, called Tiny web services, for WSNs. However, apart from its complexity, this work mainly focuses on low-level issues related to Web integration in TinyOS-based sensor networks.
To Providing RESTful Middleware Solutions. To the best of our knowledge, the number of middleware solutions dealing with the support of RESTful services in constrained devices is very limited. In fact, these approaches are proposed due to the high resource needs and complexity of SOAP-based Web Service protocols. The Restlet FrameworkFootnote 1 is the first RESTful web framework for Java developers that targets Android for deployment on compatible smartphones. Restlet’s vision is that the Web is becoming ubiquitous and that REST, as the architecture style of the Web, helps developers to leverage all HTTP features. In particular, Restlet on Android supports both client-side and server-side HTTP connectors. However, Restlet does not include support for the discovery of RESTful services, which is a fundamental requirement in pervasive environments.
In WSNs, TinyREST is one of the first attempts to integrate WSNs into the Internet (Luckenbach et al. 2005). It uses the HTTP-based REST architecture to retrieve/update the state of sensors/actuators. The TinyREST gateway maps a set of HTTP requests to TinyOS messages in order to link MICA motes (Hill and Culler 2002) to any Internet client. Beside the fact that in TinyREST only a gateway is able to connect to the Internet (not any individual sensor node), this approach fails to follow all standard HTTP methods. The work reported in Guinard et al. (2009) also presents a REST-based gateway to bridge the Web requests to powerful SunSPOT nodes.
RESTful Integration of Services: A Home Monitoring Scenario
In this section, we report on a smart home scenario to clarify the motivations of our work. A smart home generally refers to a house environment equipped with several types of computing entities, such as sensors, which collect physical information (temperature, movement detection, noise level, light, etc.), and actuators, which change the state of the environment. In this scenario, we consider a smart home equipped with occupancy, smoke detection, and temperature sensors. These tiny devices have the ability to collect context information and to communicate wirelessly with each other, in order to identify the context situation of the environment. In addition to that, we can also use actuators to physically control lights, TV, and air conditioning. Figure 9.1 illustrates the integration of these sensors and actuators in our scenario. As appreciated in this figure, the different entities use heterogeneous protocols to interact. In the scenario, the smartphones provide information about the user preferences for the home configuration. Conflicts between the user preferences are resolved by giving priority to the person who arrived first to the room. The mobile devices also have an application that enables the control of the actuators present in the different rooms. This application can be adapted when there are changes in the actuator’s configuration. Finally, there is a Set-Top Box (STB) which is able to gather information, and interact with the other co-located devices.
To show how the different elements of our scenario interact, we present three different situations:
Situation 1: Alice arrives to the living room. The occupancy sensor detects her presence and triggers the temperature sensors to decrease the sampling rate of data. It also notifies the STB that the room is occupied by somebody, which in turn tries to identify the occupant by looking for a profile in her mobile device. When Alice’s profile is found, the STB loads it and adjusts the temperature and lightening level of the room according to Alice’s preferences.
Situation 2: The sensors detect smoke and notify the STB, which in turn uses the occupancy sensor and realizes that the house is empty. The STB therefore sends an SMS to Alice, including a picture of the room captured using the surveillance camera. After checking the picture, Alice decides to remotely trigger the sprinklers using her mobile device. She also tells the system to alert the fire department about the problem. If Alice does not reply to the STB within 5 min, the system activates automatically the sprinklers and alerts the fire department.
Situation 3: Alice installs a new TV in the bedroom. The STB detects the presence of the new device, identifies it, and downloads the corresponding control software from an Internet repository. The platform tries to locate the available mobile devices, using a discovery protocol, and finds Alice’s mobile device. The STB proposes to update the mobile device with the components for controlling the new TV.
Key Challenges
The various situations we described above allow us to identify several key challenges in terms of:
-
1.
Integration of multi-scale entities: The mobile devices and sensors have different hardware and software capabilities, which make some devices more powerful than others. Therefore, the integration of these entities requires a flexible and simple solution that supports multiple interaction mechanisms and considers the restricted capabilities of some devices. In particular, regarding sensor nodes, the immaturity of high-level communication protocols, as well as the inherent resource scarceness, bring two critical challenges to our work: (1) how to connect sensor nodes to mobile devices and actuators through a standard high-level communication protocol and (2) the framework which runs over sensor nodes for supporting context-awareness and adaptation should not impose high resource demands.
-
2.
Entity mobility: In our scenario, computational entities appear and disappear constantly. In particular, mobile devices providing user profiles are not always accessible (they can be turned off or the owner can leave the house with them). In a similar way, the actuators can be replaced or new ones can be added. Thus, we need to discover new entities dynamically as well as to support device disconnections.
-
3.
Information processing and adaptation: In order to support adaptation, we first need to identify the situations in which the adaptation is required. We have a lot of information that is generated by the different devices in the environment. Therefore, we need to define which part of this information is useful to identify relevant situations and react accordingly. In our scenario, those situations include the load of Alice’s profile and the adjustment of the temperature, the sending of an alert via SMS in case of an emergency, and the adaptation of Alice’s mobile device to control the new TV in her bedroom.
The DigiHome Service-Oriented Platform
The integration, mobility and adaptation issues impose several requirements for the development of smart home environments. To deal with these issues, we propose a comprehensive and simple solution called DigiHome, which leverages on the integration of events and context information as well as the dynamic configuration of applications by using the REST architectural style. In particular, we propose a flexible architecture that modularizes the different concerns associated with event processing in ubiquitous environments by applying existing standards and approaches. In our solution, we support the integration of various event sources (e.g., sensors in our scenario), context providers (e.g., mobile devices), and other kind of services (e.g., actuators and reconfiguration services) implemented with a variety of technologies and interacting via different protocols. Indeed, DigiHome deals with protocol heterogeneity by enabling the runtime incorporation of different communication mechanisms when required thanks to the SCA isolation of non-functional concerns.
Background on SCA and FraSCAti
The Service Component Architecture (SCA) (Beisiegel et al. 2007) is a set of specifications for building distributed applications based on Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Component-Based Software Engineering (CBSE) principles. As illustrated in Fig. 9.2, the basic construction blocks of SCA are software components, which have services (or provided interfaces), references (or required interfaces) and expose properties. The references and services are connected by means of wires. SCA specifies a hierarchical component model, which means that components can be implemented either by primitive language entities or by subcomponents. In the latter case the components are called composites. SCA is designed to be independent from programming languages, Interface Definition Languages (IDL), communication protocols, and non-functional properties. In particular, to support interaction via different communication protocols, SCA provides the notion of binding. For SCA references, bindings describe the access mechanism used to invoke a service. In the case of services, the bindings describe the access mechanism that clients use to execute the service.
Listing 9.1 reflects part of the configuration depicted in Fig. 9.2 using the SCA assembly language:

The FraSCAti middleware platform focuses on the development and execution of SCA-based distributed applications (Seinturier et al. 2009). The platform itself is built as an SCA application – i.e., its different subsystems are implemented as SCA components. FraSCAti extends the SCA component model to add reflective capabilities in the application level as well as in the platform. In particular, Fig. 9.3 illustrates the FraSCAti Explorer toolset, which provides the capacity of introspecting and reconfiguring an SCA application and FraSCAti interactively. These reconfigurations can also be automated through the use of reconfiguration scripts based on the FScript syntax (David et al. 2009).
Furthermore, the FraSCAti platform applies interception techniques for extending SCA components with non-functional services, such as confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. In this way, FraSCAti provides a flexible and extensible component model that can be used in distributed environments to deal with heterogeneity. In our context, as later reported in this section, we benefit from the protocol independence of SCA to define REST-oriented bindings that provide a simple and flexible mechanism for tracking activities of mobile users as well as XQuery component implementations, which is not provided by the standard FraSCAti distribution. Furthermore, the FraSCAti capabilities in terms of runtime adaptation for applications and the platform itself, make it a suitable option for customizing the DigiHome platform whenever required.
DigiHome: An Example of RESTful Architecture
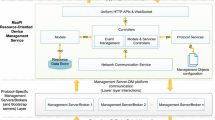
In DigiHome, we follow the REST principles (Fielding 2000) to reduce the coupling between entities by focusing on data exchange interactions, which can have multiple representations (e.g., XML and JSON). In a similar way, for supporting the integration of devices with restricted capabilities, DigiHome promotes the usage of a lightweight API and simple communication protocols as stated by REST. In particular, our solution benefits from WSNs in order to process simple events and make local decisions when possible, by means of the Remora component model (Taherkordi et al. 2010), which is a component model for WSNs based on SCA. Finally, the platform uses a Complex Event Processing (CEP) engine for event processing and the adaptation of applications and room configuration. Figure 9.4 depicts the general architecture of the platform, and in the rest of the section we provide a detailed description of the different elements of the platform.
DigiHome Kernel. The kernel of the platform modularizes the main responsibilities for home monitoring. This means that the kernel contains the functionalities required for event collecting, event processing, and deciding and executing the required adaptations of the applications deployed on DigiHome resources as well as the room configurations. In DigiHome, the Event Collector retrieves and stores the recent information produced by event and context sources, such as sensors and mobile devices. The CEP Engine is responsible for event processing and uses the Decision Executor to perform actions specified by the Adaptation Rules (defined in the CEP Engine). Following a plug-in mechanism, the different Actuator components grant access to the available actuator services in the environments. This means that the different actuators are optional, deployed according to the current service configuration and deployed on different devices.
To enable the communication between different clients and to support the mobility of services and mobile devices, we also incorporate ubiquitous bindings in SCA (Romero et al. 2010b). These bindings bring into SCA existing discovery protocols, such as UPnP (UPnP Forum 2008) and SLP (Guttman et al. 1999), providing the possibility to establish spontaneous communications. Furthermore, the ubiquitous bindings improve the context information advertisements with Quality of Context (QoC) (Krause and Hochstatter 2005) attributes for provider selection. Once the services are discovered, the ubiquitous bindings are flexible enough to allow the interaction via standard bindings, such as REST. The use of these ubiquitous bindings, as well as the modularization of the different concerns, makes it easy to distribute the different responsibilities in DigiHome.
DigiHome Resources. A DigiHome Resource is an SCA component providing and/or consuming events to/from other DigiHome Resources. In our scenario, the mobile device executes a DigiHome Resource that offers the user preferences as context information and hosts an adaptive application enabling the control of home appliances (that also consumes events indirectly in order to be adapted). The DigiHome Kernel can also be considered as a DigiHome Resource. Because our solution is based in standards, and in hiding the service implementation with SCA, we can easily integrate other services in the smart home that are not part of the infrastructure (in particular, the actuators). In a similar way, we are exposing the DigiHome Resources via ubiquitous bindings so that other applications (that are not part of DigiHome) can benefit from the services offered by the platform.
Listing 9.1 reports on the SCA assembly descriptor of the LightActuator component we developed for interacting with the X10-compliant light appliance using the REST architectural style (as described in Fig. 9.4):

This DigiHome Resource is developed in Java (line 3) and exposes the service it provides as a REST resource (lines 4–8). Technically, we extended the FraSCAti platform to support the REST architectural style (Fielding 2000). This extension includes the support for the Web Application Description Language (WADL) standard (W3C 2009) as a new interface type used to describe the resource actuator and for the HTTP communication protocol as a new binding type to access this resource. The REST bindings support multiple context representations (e.g., XML, JSON, and Java Object Serialization) and communication protocols (HTTP, XMPP, FTP, etc.). This flexibility allows us to deal with the heterogeneous context managers and context-aware applications as well as with the different capabilities of the devices that execute them. Details about the architecture of these bindings are further presented in Romero et al. (2009).
DigiHome CEP Engine. To manage the events in our scenario, we need a decision-making engine that can process them and create relations to identify special situations, using predefined rules. In order to identify the desired events, the CEP Engine requires to communicate with an Event Collector, which is in charge of dealing with the subscriptions to the event sources. When an adaptation situation is detected, a corresponding action is triggered, which can go from an instruction to an actuator, to the adaptation of the system by adding or removing functionality. These actions are received by the Decision Executor, which has the responsibility of communicating with the different actuators in the environment.
In DigiHome, for the event processing in the set-top box, we use Esper (EsperTech 2009), a Java open source stream event processing engine, to deal with the event management and decision making process. We chose Esper for our platform because it is the most supported open source project for CEP and is very stable, efficient, and fairly easy to use. The following code excerpt shows an example of an Esper rule used in our scenario:

In this rule, we can see the use of a time window, which is a moving interval of time. The rule collects all the events from the movement sensor from the last 60 s. By doing this, we can know if a user is still in the room or has already left, and adapt the room accordingly.
DigiHome Intermediaries. REST enables Web Intermediaries (WBI) to exploit the requests exchanged by the participants in the communication process. WBI are computational entities that are positioned between interacting entities on a network to tailor, customize, personalize, or enhance data as they flow along the stream (IBM 2009). Therefore, we can benefit from this opportunity to improve the performance of DigiHome. When the provided context information does not change much in time, the messages containing this information can be marked as cacheable within the communication protocol. This kind of annotation enables WBI caches to quickly analyze and intercept context requests always returning the same document. A similar optimization applies to security issues and the filtering of context requests. Indeed, by using proxy servers as WBI, we can control the requested context resources and decide whether the incoming (or outgoing) context requests need to be propagated to the web server publishing the context resource. Other kinds of WBI can also be integrated in the system to operate, for example, resource transcoding, enrichment or encryption.
DigiHome Wireless Sensor Network
In order to consume events from WSNs, we use the Remora Component Framework (Taherkordi et al. 2010). This framework is an extension of SCA that brings component-based development into WSNs. Remora proposes a RESTful mechanism to exchange events, which is encapsulated in an SCA component. We reuse this mechanism in order to define DigiHome resources for WSNs (so called Remora Resources), which are able to produce and consume simple objects in the DigiHome platform. With these resources, we improve the efficiency of the system because the WSN is able to process simple events instead of going through the DigiHome Kernel for making decisions. The core of our framework enables in-WSN decisions, whenever an event should be processed with other relevant events generated by other sensor nodes. As an example, when a temperature sensor detects a high temperature, to know if there is a fire, it needs to become aware of the smoke density in the room – i.e., communicating with the smoke detecting sensors. Furthermore, benefiting from the DigiHome modularization of concerns, as well as the transparent communication promoted by SCA, DigiHome objects can consume/notify events from/to Remora Resources with a small effort.
This framework presents an IP-based sensor network system where nodes can directly integrate to modern IT systems through RESTful Web services. This approach relies on the IP protocol stack implemented in Contiki operating system. Contiki has made a considerable effort on the provision of IPv4 and IPv6 protocols on the common types of sensor nodes with constrained resources. Software architecture of RESThing is shown in Fig. 9.5. It consists of HTTP Server, REST Engine, SAX based XML parser and Logger modules. RESThing offers an interface to create resources since they are the main abstractions of RESTful Web services.
The Remora runtime is integrated with the REST framework through the REST Wrapper API. Wrapper API is one of the main features of Remora, providing a well-described method for integrating a Remora application with underlying system software (Taherkordi et al. 2010). REST Broker contains a set of Remora components processing REST requests received from Remora runtime. Specifically, it is an intermediate module for handling the REST requests received from a Web client or sent from the sensor node to a node hosting RESTful Web services. The broker is also in charge of retaining the list of application-specific resources and the corresponding Remora Web services APIs.
HTTP server is a small footprinted server to handle the incoming and outgoing HTTP requests. It provides interface to perform certain HTTP related tasks such as accessing request details (headers, entity body and URL path), constructing an HTTP response, etc. Both REST Engine and SOAP Engine work on top of the HTTP server. The REST framework also includes a XML parser to parse requests in XML format. A simple XML parser developed by a third-party (simplexml parser) is ported to Contiki for this purpose. It is very small in code size and being a non-validating SAX based parser makes it memory efficient. A minimal SOAP processing engine is also provided to fulfill SOAP-based Web service invocations. To do that, it reuses the HTTP server and XML parser components. The engine parses the SOAP message using the XML parser, extracts the method information and executes it, finally the response SOAP message is built using the XML parser.
Future: Horizons and Challenges
Applications and technologies for the Internet of Things are still in the promotional phase of design and development. There are numerous hurdles against large-scale use of the Internet of Things originated from the lack of standards and unmature business models. We believe that the primary IoT concern in the future will be on the integration of large-scale enterprise systems with resource-constrained platforms. The future WSNs and RFID systems, for example, can trigger business processes, adversely; actions can be triggered on them by a business process being executed on the Internet. When such platforms are involved in the business process lifecycle, in addition to today’s communication and distribution issues, several new challenges arise that are enterprise-specific and difficult to be addressed on resource-limited platforms, such as workflow management systems. As a result, customizing the heavyweight enterprise software infrastructures for embedded and resource-poor systems is envisaged to be a potential research trend of IoT in the future. On the future horizons of IoT, internet services also serve a key role. The number of embedded and tiny devices integrated to future IoT will be dramatically increased so that distributed applications deployed over infrastructures that may encompass tens of thousands of tiny devices, where each device exhibits a high number of services. Strategies to locate services, as well as devices hosting the services could be a crucial challenge in the future IoT. It is required to shift the thoughts from things in the Internet to services, where applications deal with virtual things able to scale up to the plentiful services over the Internet. These virtual platforms offer a new higher level of abstraction that hides the low level real things and represent a different set of things which are characterized as the virtual and new members of IoT. The way to compose low level real services and expose them in the virtual things level could be a challenging area in the future IoT.
Conclusion
In this chapter, we have presented DigiHome, a platform addressing the mobility, heterogeneity, and adaptation of smart entities. In particular, DigiHome detects adaptation situations by integrating context information using an SCA-based architecture. This architecture promotes the modularization of concerns and fosters the application of the REST principles by exploiting the SCA extensibility. The simplicity and data orientation of REST, combined with the SCA independence of implementation technologies, make DigiHome an attractive solution to deal with heterogeneity in terms of interactions. The definition and application of ubiquitous bindings in the platform enable spontaneous communication by means of standard protocols (e.g., UPnP and SLP), and furnish context provider selection (based on QoC attributes). On the other hand, the modularized architecture of DigiHome allows the definition of variants for the platform, called DigiHome resources, that can be deployed on resource-constrained devices. The functionality of these resources is exposed as services, accessible via several protocols, which can be accessed by clients that do not have to be part of the platform. Furthermore, the clear separation of concerns in the DigiHome architecture encourages the exploitation of WSNs for simple processing and local decision making. The suitability of our platform for context integration was evaluated with different discovery and context representations.
Notes
- 1.
Restlet:http://www.restlet.org
References
simplexml parser http://simplexml.sourceforge.net, 2009.
M. Beisiegel et al. Service Component Architecture. http://www.osoa.org, 2007.
P.-C. David, T. Ledoux, M. Léger, and T. Coupaye. FPath and FScript: language support for navigation and reliable reconfiguration of Fractal architectures. Annales des Télécommunications, 64(1–2): 45–63, January 2009.
L. de Souza, P. Spiess, D. Guinard, M. Khler, S. Karnouskos, and D. Savio. SOCRADES: a web service based shop floor integration infrastructure. In The Internet of Things, volume 4952 of LNCS, pages 50–67. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 2008.
EsperTech. Esper. http://esper.codehaus.org, 2009.
R. Fielding. Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-based Software Architectures. PhD Thesis. University of California, Irvine, USA, 2000.
D. Guinard, V. Trifa, T. Pham, and O. Liechti. Towards physical mashups in the web of things. In INSS’09: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Networked Sensing Systems, pages 196–199, IEEE, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2009.
E. Guttman, C. Perkins, J. Veizades, and M. Day. Service Location Protocol, Version 2. RFC 2608 (Proposed Standard). http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2608, June 1999.
J. L. Hill and D. E. Culler. Mica: a wireless platform for deeply embedded networks. IEEE Micro, 22: 12–24, 2002.
IBM. Web Intermediaries (WIB). http://www.almaden.ibm.com/cs/wbi, 2009.
M. Krause and I. Hochstatter. Challenges in modelling and using quality of context (QoC). In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Mobility Aware Technologies and Applications, pages 324–333, Montreal, Canada, 2005.
T. Luckenbach, P. Gober, K. Kotsopoulos, A. Kim, and S. Arbanowski. TinyREST: a protocol for integrating sensor networks into the internet. In REALWSN’05: Proceedings of the Workshop on Real-World WSNs, Stockholm, Sweden, 2005.
Nokia. Mobile Web Server. http://wiki.opensource.nokia.com/projects/Mobile_Web_Server, 2008.
Open SOA. Service Component Architecture Specifications, 2007.
OSGi Alliance. OSGi – The Dynamic Module System for Java. http://www.osgi.org, 2009.
OSGi Alliance. About the Osgi Service Platform – Technical Whitepaper Revision 4.1. http://www.osgi.org/documents, 2007.
L. Pham and G. Gehlen. Realization and performance analysis of a SOAP server for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 11th European Wireless Conference, volume 2, pages 791–797, VDE Verlag, Nicosia, Cyprus, April 2005.
N. B. Priyantha, A. Kansal, M. Goraczko, and F. Zhao. Tiny Web Services: design and implementation of interoperable and evolvable sensor networks. In SenSys’08: Proceedings of the 6th ACM Conference on Embedded Network Sensor Systems, pages 253–266, ACM, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2008.
D. Romero, G. Hermosillo, A. Taherkordi, R. Nzekwa, R. Rouvoy, and F. Eliassen. RESTful integration of heterogeneous devices in pervasive environments. In Proceedings of the 10th IFIP International Conference on Distributed Applications and Interoperable Systems (DAIS’10), volume 6115 of LNCS, pages 1–14. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, June 2010.
D. Romero, R. Rouvoy, L. Seinturier, and P. Carton. Service discovery in ubiquitous feedback control loops. In Proceedings of the 10th IFIP International Conference on Distributed Applications and Interoperable Systems (DAIS’10), volume 6115 of LNCS, pages 113–126. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, June 2010.
D. Romero, R. Rouvoy, L. Seinturier, S. Chabridon, C. Denis, and P. Nicolas. Enabling context-aware web services: a middleware approach for ubiquitous environments. In Michael Sheng, Jian Yu, and Schahram Dustdar, editors, Enabling Context-Aware Web Services: Methods, Architectures, and Technologies. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London, 2009.
L. Seinturier, P. Merle, D. Fournier, N. Dolet, V. Schiavoni, and J. -B. Stefani. Reconfigurable sca applications with the frascati platform. In SCC’09: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Services Computing, pages 268–275, IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, USA, September 2009.
S. N. Srirama, M. Jarke, and W. Prinz. Mobile web service provisioning. In International Conference on Advanced International Conference on Telecommunications / Internet and Web Applications and Services, IEEE, page 120, 2006.
A. Taherkordi, F. Loiret, A. Abdolrazaghi, R. Rouvoy, Q. Le Trung, and F. Eliassen. Programming sensor networks using REMORA component model. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS’10), page 15, Santa Barbara, California, USA France, 06 2010.
The Apache Software Foundation. HTTP Server Project. http://httpd.apache.org, 2009.
UPnP Forum. UPnP Device Architecture 1.0. http://www.upnp.org/resources/documents.asp, 2008.
W3C. Web Application Description Language (WADL). http://wadl.dev.java.net, 2009.
J. Wikman and F. Dosa. Providing HTTP Access to Web Servers Running on Mobile Phones, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Taherkordi, A., Eliassen, F., Romero, D., Rouvoy, R. (2011). RESTful Service Development for Resource-Constrained Environments. In: Wilde, E., Pautasso, C. (eds) REST: From Research to Practice. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8303-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8303-9_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-8302-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-8303-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)