Abstract
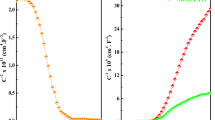
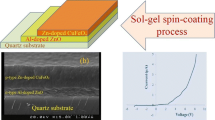
In the current study, Zn-incorporated CuO (CuO:Zn) and pure CuO thin film heterojunction devices have been fabricated on n-Si (\(\langle 100\rangle\)) substrate, applying vapor–liquid–solid (VLS), for their potential application as photovoltaic devices. The uniformity of the thin films on Si-substrate and their crystalline orientation are verified using FESEM images and XRD studies, respectively. EDS and XPS measurements analyze the chemical stoichiometry and valance states of the as-grown oxides. The influence of incorporating Zn atoms on the structural stabilities of Zn-incorporated CuO was further studied using the DFT (density functional theory) simulation. From spectroscopic ellipsometry measurement, the direct energy bandgaps of CuO:Zn and CuO thin films are assessed to be 2.26 eV and 2.05 eV, respectively. Further, the electronic properties of such heterojunctions are investigated from the junction current–voltage and capacitance–voltage characteristics. The comparative photovoltaic study of CuO:Zn and CuO films suggests that the introduction of Zn into the CuO matrix enhances the power conservation efficiency (PCE %) and external quantum efficiency (EQE%) by almost 2 times. Also, a high spectral responsivity (~ 0.30 A/W @ 0 V) as well as detectivity (1.96 × 1012 cm Hz1/2/W @ 0 V) have been achieved for the CuO:Zn/n-Si photodetector. Therefore, the incorporation of ZnO into the CuO lattices by employing the cost-effective VLS mechanism suggests a significant improvement of optoelectronic and photovoltaic properties of such films for the fabrication of future devices.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All required data, used in manuscript, can be found.
References
https://www.iea.org/commentaries/the-global-energy-crisis-pushed-fossil-fuel-consumption-subsidies-to-an-all-time-high-in-2022. Accessed 05 June 2023
A.K. Rana, J.T. Park, J. Kim, C.-P. Wong, See-through metal oxide frameworks for transparent photovoltaics and broadband photodetectors. Nano Energy 64, 103952 (2019)
A. Bhattacharya, J. Sultana, S. Sikdar, R. Saha, S. Chattopadhyay, Investigating the impact of thermal annealing on the photovoltaic performance of chemical bath deposited SnO2/p-Si heterojunction solar cells. Microsyst. Technol. 26, 1351–1358 (2020)
S. Chakraborty, R. Saha, A. Karmakar, S. Chattopadhyay, Fabrication and characterization of zinc oxide nanowire based two-electrode capacitive biosensors on flexible substrates for estimating glucose content in a sample. Electroanalysis 33, 1185–1193 (2021)
Y. Yoon, P.L. Truong, D. Lee, S.H. Ko, Metal–oxide nanomaterials synthesis and applications in flexible and wearable sensors. ACS Nanosci. Au 2, 64–92 (2021)
X. Yu, T.J. Marks, A. Facchetti, Metal oxides for optoelectronic applications. Nat. Mater. 15, 383–396 (2016)
M. Engin, F. Atay, S. Kose, V. Bilgin, I. Akyuz, Growth and characterization of Zn-incorporated copper oxide films. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 787–796 (2009)
A. Tripathi, T. Dixit, J. Agrawal, V. Singh, Bandgap engineering in CuO nanostructures: dual-band, broadband, and UV-C photodetectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116, 111102 (2020)
A. Kaphle, E. Echeverria, D.N. Mcllroy, P. Hari, Enhancement in the performance of nanostructured CuO–ZnO solar cells by band alignment. RSC Adv. 10, 7839–7854 (2020)
Y.S. Lee, J. Heo, M.T. Winkler et al., Nitrogen-doped cuprous oxide as a p-type hole-transporting layer in thin-film solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 15416–15422 (2013)
A. Bhattacharya, J. Sultana, S. Sikdar, R. Saha, S. Chattopadhyay, in International Conference on Opto-Electronics and Applied Optics (Optronix), 2019 (IEEE, 2019)
A. Das, B. Nag Chowdhury, R. Saha et al., Formation of high-pressure phase of titanium dioxide (TiO2-II) Thin films by vapor–liquid–solid growth process on GaAs substrate. Phys. Status Solidi A 216, 1800640 (2019)
A. Menazea, A.M. Mostafa, Ag doped CuO thin film prepared via pulsed laser deposition for 4-nitrophenol degradation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 104104 (2020)
J. Sultana, A. Bhattacharya, A. Karmakar, G.K. Dalapati, S. Chattopadhyay, Graphene-nanoparticle incorporated responsivity tuning of p-CuO/n-Si-based heterojunction photodetectors. Bull. Mater. Sci. 42, 194 (2019)
Q. Zhang, K. Zhang, D. Xu et al., CuO nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, growth mechanisms, fundamental properties, and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 60, 208–337 (2014)
R. Saha, G.K. Dalapati, S. Chakrabarti, A. Karmakar, S. Chattopadhyay, Yttrium (Y) doped ZnO nanowire/p-Si heterojunction devices for efficient self-powered UV-sensing applications. Vacuum 202, 111214 (2022)
D.K. Sharma, S. Shukla, K.K. Sharma, V. Kumar, A review on ZnO: fundamental properties and applications. Mater. Today Proc. 49, 3028–3035 (2022)
O. Mnethu, S.S. Nkosi, I. Kortidis et al., Ultra-sensitive and selective p-xylene gas sensor at low operating temperature utilizing Zn doped CuO nanoplatelets: insignificant vestiges of oxygen vacancies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 576, 364–375 (2020)
M. Aadil, W. Hassan, H. Somaily et al., Synergistic effect of doping and nanotechnology to fabricate highly efficient photocatalyst for environmental remediation. J. Alloys Compd. 920, 165876 (2022)
P. Kumar, M.C. Mathpal, J. Prakash, B.C. Viljoen, W. Roos, H. Swart, Band gap tailoring of cauliflower-shaped CuO nanostructures by Zn doping for antibacterial applications. J. Alloys Compd. 832, 154968 (2020)
R. Wu, H. Zhang, J. Pan et al., Spatio-design of multidimensional prickly Zn-doped CuO nanoparticle for efficient bacterial killing. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 3, 1600472 (2016)
S.S.K. Jacob, I. Kulandaisamy, I.L.P. Raj, A.A. Abdeltawab, S.Z. Mohammady, M. Ubaidullah, Improved optoelectronic properties of spray pyrolysis coated Zn doped Cu2O thin films for photodetector applications. Opt. Mater. 116, 111086 (2021)
S. Das, V.C. Srivastava, An overview of the synthesis of CuO–ZnO nanocomposite for environmental and other applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 7, 267–282 (2018)
P. Isherwood, Copper zinc oxide: Investigation into a p-type mixed metal oxide system. Vacuum 139, 173–177 (2017)
https://www.synopsys.com/silicon/quantumatk.html. Accessed 5 June 2023
C.P. Goyal, D. Goyal, S.K. Rajan et al., Effect of Zn doping in CuO octahedral crystals towards structural, optical, and gas sensing properties. Crystals 10, 188 (2020)
J. Iqbal, T. Jan, S. Ul-Hassan et al., Facile synthesis of Zn doped CuO hierarchical nanostructures: structural, optical and antibacterial properties. AIP Adv. 5, 127112 (2015)
W. Chen, H. Zhang, Z. Ma, B. Yang, Z. Li, High electrochemical performance and lithiation–delithiation phase evolution in CuO thin films for Li-ion storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 14202–14209 (2015)
A. Khalid, P. Ahmad, A.I. Alharthi et al., Structural, optical, and antibacterial efficacy of pure and zinc-doped copper oxide against pathogenic bacteria. Nanomaterials 11, 451 (2021)
H. Fujiwara, Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Principles and Applications (Wiley, Hoboken, 2007)
H.G. Tompkins, J.N. Hilfiker, Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Practical Application to Thin Film Characterization (Momentum Press, Santa Monica, 2015)
G. Papadimitropoulos, N. Vourdas, V.E. Vamvakas, D. Davazoglou, Optical and structural properties of copper oxide thin films grown by oxidation of metal layers. Thin Solid Films 515, 2428–2432 (2006)
J. Sultana, S. Paul, A. Karmakar, G.K. Dalapati, S. Chattopadhyay, Optimizing the thermal annealing temperature: technological route for tuning the photo-detecting property of p-CuO thin films grown by chemical bath deposition method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 12878–12887 (2018)
J. Sultana, S. Paul, R. Saha, S. Sikdar, A. Karmakar, S. Chattopadhyay, Optical and electronic properties of chemical bath deposited p-CuO and n-ZnO nanowires on silicon substrates: p-CuO/n-ZnO nanowires solar cells with high open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current. Thin Solid Films 699, 137861 (2020)
M. Ferhat, A. Zaoui, R. Ahuja, Magnetism and band gap narrowing in Cu-doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 142502 (2009)
B. Ehrler, K.P. Musselman, M.L. Böhm et al., Preventing interfacial recombination in colloidal quantum dot solar cells by doping the metal oxide. ACS Nano 7, 4210–4220 (2013)
W. Yin, J. Yang, K. Zhao et al., High responsivity and external quantum efficiency photodetectors based on solution-processed Ni-doped CuO films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 11797–11805 (2020)
S.M. Sze, Y. Li, K.K. Ng, Physics of Semiconductor Devices (Wiley, Hoboken, 2021)
A. Chen, K. Zhu, Effects of TCO work function on the performance of TCO/n-Si hetero-junction solar cells. Sol. Energy 107, 195–201 (2014)
S. Chandrasekaran, A novel single step synthesis, high efficiency and cost effective photovoltaic applications of oxidized copper nano particles. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 109, 220–226 (2013)
F. Gao, X.-J. Liu, J.-S. Zhang, M.-Z. Song, N. Li, Photovoltaic properties of the p-CuO/n-Si heterojunction prepared through reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 084507 (2012)
S. Masudy-Panah, G.K. Dalapati, K. Radhakrishnan et al., p-CuO/n-Si heterojunction solar cells with high open circuit voltage and photocurrent through interfacial engineering. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 23, 637–645 (2015)
S. Masudy-Panah, G.K. Dalapati, K. Radhakrishnan, A. Kumar, H.R. Tan, Reduction of Cu-rich interfacial layer and improvement of bulk CuO property through two-step sputtering for p-CuO/n-Si heterojunction solar cell. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 074501 (2014)
Funding
Anannya Bhattacharya likes to thank the DST-India (INSPIRE fellowship) to fund her work. The authors are also thankful to the WBDITE, DST Purse program, and Centre of Excellence (COE-TEQIP) for funding the equipments and financial support to carry out the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB: Device fabrication and characterization, Formal analysis, manuscript writing and revision; SK: DFT Simulation, Writing, editing; NB: DFT Simulation, writing, editing; GKD: Material characterization; SR: Material characterization; SC: Data analysis, writing, editing and overall supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, A., Kanungo, S., Bahadursha, N. et al. Investigating the opto-electronic and photovoltaic properties of Zn-incorporated CuO thin film grown by vapor–liquid–solid (VLS) method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 171 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11905-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11905-6